Influencia de la microbiota intestinal en la enfermedad hepática crónica. Su rol en el hepatocarcinoma
Resumen
El incremento de la traslocación de bacterias intestinales es característico en pacientes con enfermedad hepática crónica y favorece la inflamación y la fibrosis del hígado.1-3 Se ha implicado a la microbiota intestinal en la patogénesis y progresión de enfermedades hepáticas como Enfermedad Grasa Hepática No alcohólica, Esteatohepatitis no alcohólica, Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria, Enfermedad hepática por Falla intestinal y el Hepatocarcinoma. Numerosas investigaciones al respecto, vienen señalando que la microbiota intestinal y los receptores tipo Toll (TLRs) promueven el Hepatocarcinoma (HCC).1,4 La Hepatocarcinogenesis involucra a los TLR4 y a la microbiota intestinal, pero estos, no son requeridos para la iniciación del HCC sino para su promoción, mediante el incremento de la proliferación, expresión de la epiregulina hepatomitogena y la prevención de la apoptosis.4,5 La esterilización del intestino en etapas tardías de la hepatocarcinogenesis , previenen el HCC , por lo que de allí se desprenden que tanto la microbiota como estos receptores tipo Toll, representan blancos terapéuticos para la prevención del HCC en pacientes con enfermedad hepática crónica avanzada.4-6
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
WGO Handbook on Gut Microbes. May 2014.
Marion Darnaud ,Jamila Faivre , Nicolas Moniaux. Targeting gut flora to prevent progression to hepatocellular carcinoma.J. of Hepatol 2013;58: 385-387.
Nolan JP. The role of intestinal endotoxin in liver injury: a long and evolving history. Hepatology 2010;52: 1829-1835.
Eamonn M.M. Quigley, Catherine Stanton , Eileen F. Murphy. The gut microbiota and the liver. Pathophysiological and clinical implications. J. of Hepatol 2013; 58: 1020-1027.
Dapito DH et al. Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by intestinal microbiota and TLR4.Cancer cell 2012; 31; 504-516.
Guarner C, Soriano G. Bacterial traslocation and its consequences in patients with cirrhosis. Eur j Gastroenterol and Hepatol.2005;17 : 27-31.
Villanueva A, Savic R, Llovet JM. Linphotoxins: New targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2009; 16: 272- 273.
Clemente JC et al. The Impact of the gut microbiota in human health: an integrative view. Cell 2012; 148: 1248-1270.
Gupta A et al. Role of the small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and delayed gastrointestinal transit time in cirrhosis patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J of Hepatol.2010; 53 ;849-855.
Purohit V et al. Alcohol, intestinal bacterial growth, intestinal permeability to endotoxin and medical consequences: summary of a symposium. Alcohol 2008; 42: 349-361.
Almeida J et al. Gut flora and bacterial translocation in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12: 1493-1502.
Cohen MJ et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients with ascites, without gastro-intestinal bleeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009:2: CD004791.
Lata J, Jurankova J, Kopacova M, Vitev P. Probiotics in Hepatology. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17; 2890-2896.
Frazier TH, DiBaise JK, McClaine CJ. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability obesity-induced inflammation and liver injury. J. Parenter Enteral Nutr 2011; 35: 14S-20S.
Ying Ying Yang and Han Chieh Lin. Bacterial infections in patients with Cirrhosis .Chin Med Assoc. October 2005; 68:447-451.
Stephen Riordan and Roger Williams. The intestinal flora and bacterial infections in cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 2006; 45.
García Tsao Guadalupe. Bactertial Infectios in Cirrhosis: treatment and prophylaxis. Journal of Hepatology 2005;42.
Vlachogiannakos Jiannis et al. Long-term administration of rifaximin improves the prognosis of patients with descompesated alcoholic cirrhosis .J. of Gastroenterol and Hepatol 2013;28: 450-455.
Gomez F. et al. Impaired function of macrophage Fc gamma receptors and bacterial infection in alcoholic cirrhosis. The New Eng J of Med. 1994;331:1122-1128.
Bajaj Jasmohan et al. Bacterial infections in end-stage liver disease: current challenges and future directions.Gut 2012;61: 1219-1225.
Rimola A. et al. Oral, nonabsorbable antibiotics prevent infections in cirrhotics with gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Hepatology 1985;5: 463-467.
Soriano G. et al. Norfloxacin prevents bacterial infections in cirrhotics with gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology 1992;103: 1267-1272.
Gines P. et al. Norfloxacin prevents spontaneous bacterial peritonitis recurrence in cirrhosis :results of a double blind placebo controlled trial. Hepatology 1990;12: 716-724.
Bass N, Mullen K, Sigal S, et al. Rifaximin is effective in maintaining remission in hepatic encephalopathy: results of a large, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Program and abstracts of the 44th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of the Liver; April 22-26, 2009; Copenhagen, Denmark. Abstract 93.
Maclayton DO, Eaton-Maxwell A. Rifaximin for treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Ann Pharmacother. 2008;Dec 17[Epub ahead of print].
Sanyal A, Bass N, Teperman L, et al. Chronic administration of rifaximin for the maintenance of remission of hepatic encephalopathy: a subgroup analysis of a phase 3 trial. Program and abstracts of the 44th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of the Liver; April 22-26, 2009; Copenhagen, Denmark. Abstract 222.
Mullen K, Sigal S, Sheikh M, et al. Safety of rifaximin in patients with hepatic encephalopathy: results of a randomized, phase 3, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Program and abstracts of the 44th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of the Liver; April 22-26, 2009; Copenhagen, Denmark. Abstract 207.
Bucci L, Palmieri GC. Double-blind, double-dummy comparison between treatment with rifaximin and lactulose in patients with medium to severe degree hepatic encephalopathy. Curr Med Res Opin. 1993;13:109-118.
Festi D, Mazzella G, Orsini M, et al. Rifaximin in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy: results of a multicenter study of efficacy and safety. Curr Ther Res. 1993;54:598-609.
Puxeddu A, Quartini M, Massimetti A, Ferrieri A. Rifaximin in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Curr Med Res Opin. 1995;13:274-281.
Paik YH, Lee KS, Han KH, et al. Comparison of rifaximin and lactulose for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective randomized study. Yonsei Med J. 2005;46:399-407.
Mas A, Rodes J, Sunyer L, et al. Comparison of rifaximin and lactitol in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: results of a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled clinical trial. J Hepatol. 2003;38:51-58.
Loguercio C, Federico A, De Girolamo V, Ferrieri A, Del Vecchio Blanco C. Cyclic treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy with rifaximin: results of a double-blind clinical study. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2003;49:53-62.
Pedretti G, Calzetti C, Missale G, Fiaccadori F. Rifaximin versus neomycin on hyperammoniemia in chronic portal systemic encephalopathy of cirrhotics: a double-blind, randomized trial. Ital J Gastroenterol. 1991;23:175-178.
Di Piazza S, Filippazzo MG, Valenza LM, et al. Rifaximin versus neomycin in the treatment of portosystemic encephalopathy. Ital J Gastroenterol. 1991;23:403-407.
Prasad S, Dhiman RK, Duseja A, Chawla YK, Sharma A, Agarwal R. Lactulose improves cognitive functions and health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis who have minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2007;45:549-559.
Bajaj JS, Saeian K, Christensen KM, et al. Probiotic yogurt for the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:1707-1715.
Garcia-Tsao G, Sanyal AJ, Grace ND, Carey WD. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2007;46:922-938.
Ghassemi S, Garcia-Tsao G. Prevention and treatment of infections in patients with cirrhosis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;21:77-93.
Fernández J, Navasa M, Planas R, et al. Primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis delays hepatorenal syndrome and improves survival in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:818-824.
Terg R, Fassio E, Guevara M, et al. Ciprofloxacin in primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Hepatol. 2008;48:774-779.
Saab S, Hernandez JC, Chi AC, Tong MJ. Oral antibiotic prophylaxis reduces spontaneous bacterial peritonitis occurrence and improves short-term survival in cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:993-1001.
Loomba R, Wesley R, Bain A, Csako G, Pucino F. Role of fluoroquinolones in the primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:487-493.
Barochia A et al. Eritoram tetrasidium (E5564) treatment for sepsis: review preclinical and clinical studies. Expert Opin Drugs Metab Toxicol 7: 479-494.
Sha T et al. Therapeutics effects of TAK 242, a novel selective Toll-like receptor 4 signal transduction inhibitor, in mouse endotoxin shock model. Eur J Pharmacol 2007; 571: 231-239.
Luedde T, Schwabe RF. NF-Kappa B in the liver-linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;8: 108-118.
Kim GP et al. An international, multicenter Phase II trial of Bortezomib in patients with hepatocellular cancer. Invest New Drugs 2012; 30: 387-394.
Hoshida Y. et al. Gene expression signature predicts outcome of liver cirrosis. Hepatology 2009; 50 (supplement 4): 312A.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v70i2.98
IMÁGENES GEN
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
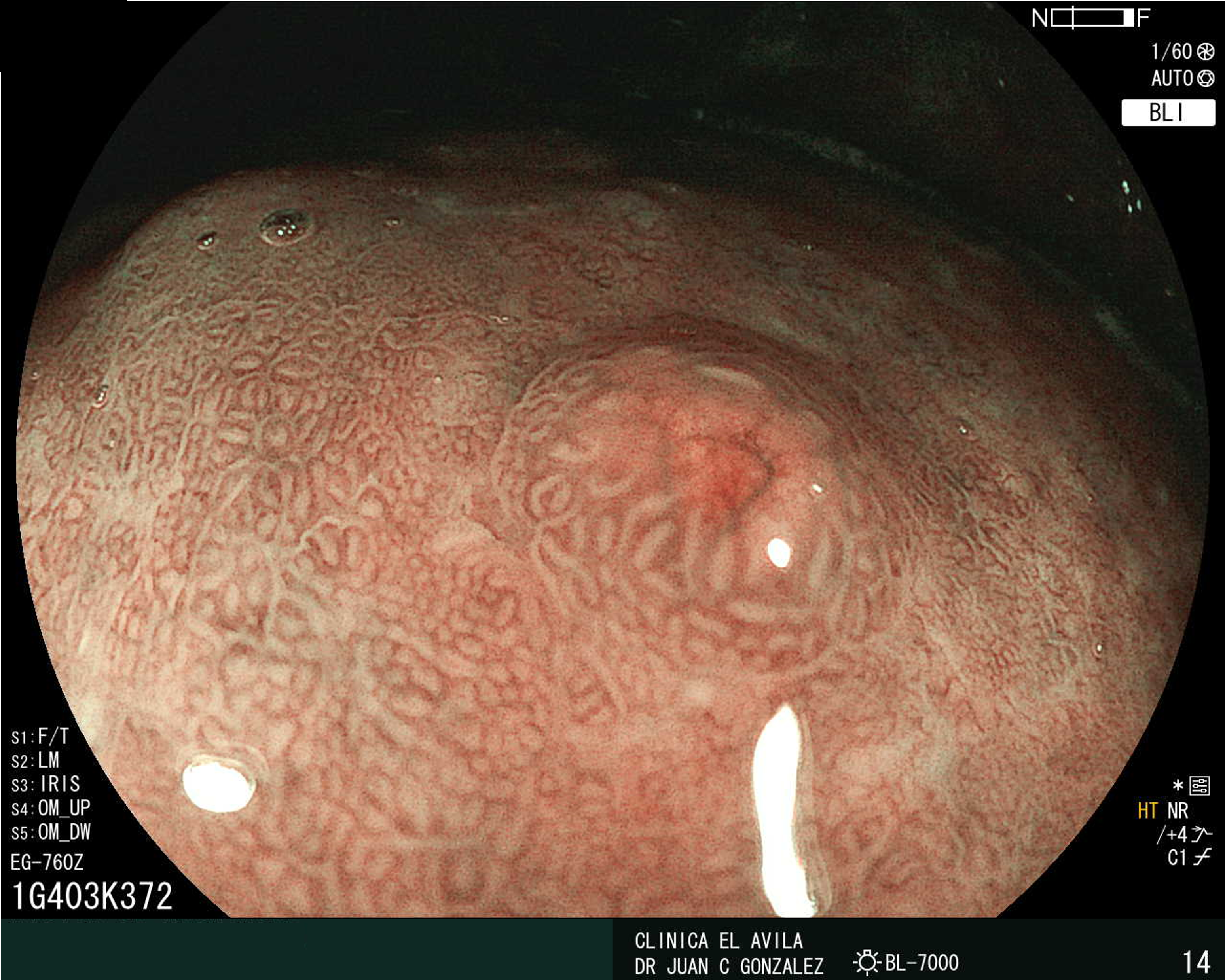 | 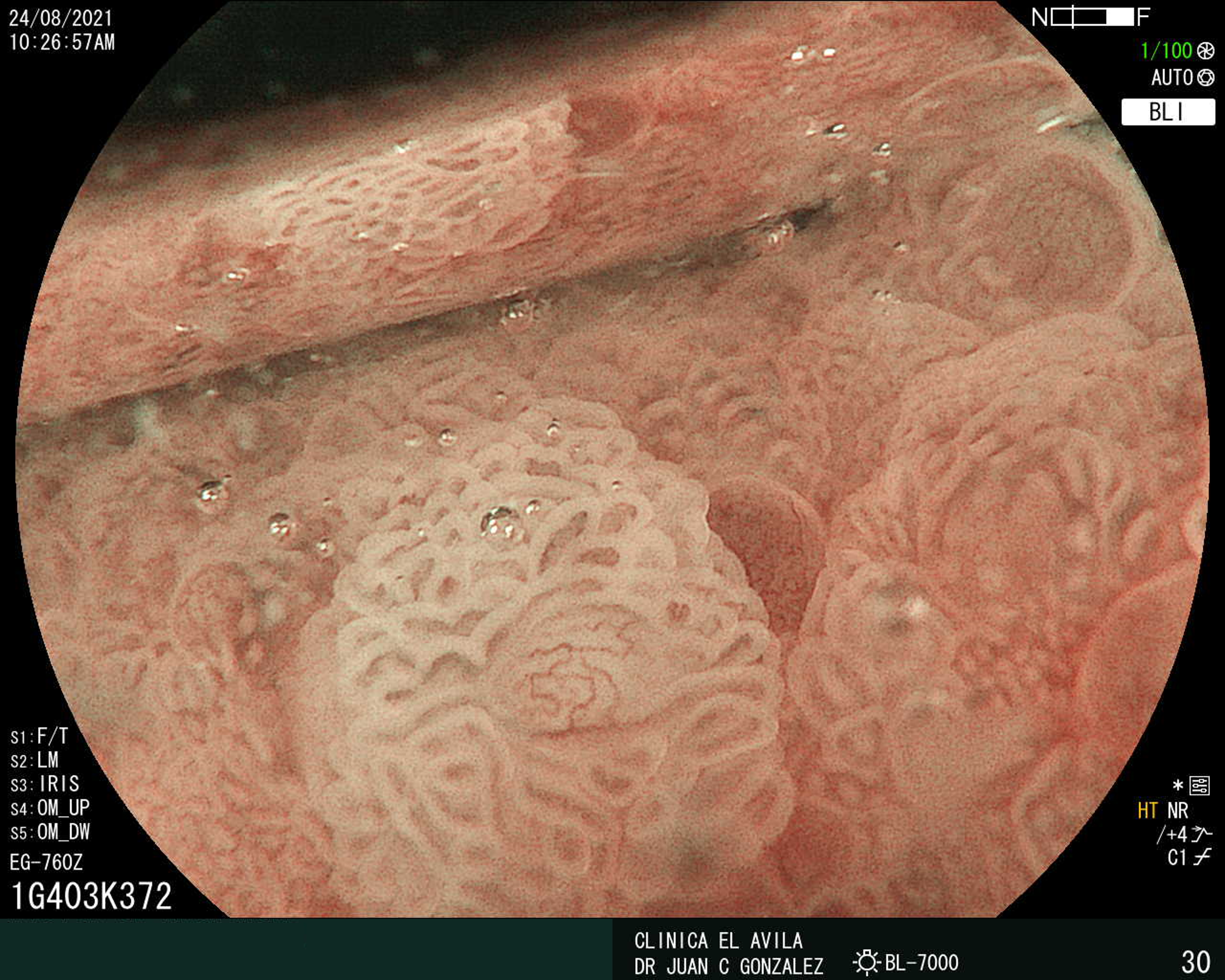 |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X









 ESCUCHAR RESUMEN DEL ARTICULO
ESCUCHAR RESUMEN DEL ARTICULO