Consumo de alimentos ultraprocesados en niños y adolescentes con patología digestiva y riesgo de enfermedades no transmisibles
Resumen
ESCUCHE EL RESUMEN HANCIENDO CLIC EN EL IDIOMA DE SU PREFERENCIA:
EspañolEnglish
Portugues
Japones
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Cainelli EC, Gondinho BVC, Palacio DDC, Oliveira DB, Reis RA, Cortellazzi KL, et al. Ultra-processed foods consumption among children and associated socioeconomic and demographic factors. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2021;19(6):eAO5554. doi:10.31744/einstein_journal/2021A O5554.
Lane MM, Gamage E, Du S, Ashtree DN, McGuinness AJ, Gauci S, et al. Ultra-processed food exposure and adverse health outcomes: umbrella review of epidemiological meta-analyses. BMJ. 2024;384:e077310. doi:10.1136/bmj-2023-077310.
Monteiro CA, Cannon G, Levy RB, et al. Ultra-processed foods: what they are and how to identify them. Public Health Nutr. 2019;22(5):936-41. doi:10.1017/S136898001800376 2.
Díaz MC, Glaves A. Relación entre consumo de alimentos procesados, ultraprocesados y riesgo de cáncer: una revisión sistemática. Rev Chil Nutr. 2020;47(5):808-21. doi:10.4067/S0717-75182020000500808.
Filgueiras AR, Almeida VBP, Nogueira PCK, Domene SMÁ, Silva CE, Sesso R, et al. Exploring the consumption of ultra-processed foods and its association with food addiction in overweight children. Appetite. 2019;135:137-45. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2018.11.005.
Aguayo-Patrón SV, Calderón de la Barca AM. Old fashioned vs. ultra-processed-based current diets: possible implication in the increased susceptibility to type 1 diabetes and celiac disease in childhood. Foods. 2017;6(11):100. doi:10.3390/foods6110100.
Tristan Asensi M, Napoletano A, Sofi F, Dinu M. Low-grade inflammation and ultra-processed foods consumption: a review. Nutrients. 2023;15(6):1546. doi:10.3390/nu15061 546.
Tosi M, Montanari C, Bona F, Tricella C, Agostinelli M, Dolor J, et al. Potencial inflamatorio de la dieta en enfermedades pediátricas: una revisión narrativa. Nutrients. 2023;15(24):5095. doi:10.3390/nu15245095.
Whelan K, Bancil AS, Lindsay JO, Chassaing B. Ultra-processed foods and food additives in gut health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;21(6):406-27. doi:10.1038/s41575-024-00893-5.
Rico A, Martínez MA, Alvarez I, Mendonça RD, de la Fuente C, Gómez C, et al. Association between consumption of ultra-processed foods and all-cause mortality: SUN prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2019;365:l1949. doi:10.1136/bmj.l1949.
Song J, Chen S, Qian K, Ye W. Association of ultra-processed foods consumption with increased liver steatosis in U.S. adults. Front Nutr. 2025;12:1536989. doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1536989.
Henney AE, Gillespie CS, Alam U, Hydes TJ, Cuthbertson DJ. Ultra-processed food intake is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2023;15(10):2266. doi:10.3390/nu15102266.
Al Hourani H, Shhadeh HA, Al-Jawaldeh A. Association between consumption of ultra-processed foods and obesity among Jordanian children and adolescents. Sci Rep. 2025;15:9326. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-93506-3.
Organización Mundial de la Salud. Monitoreo de avances en materia de las enfermedades no transmisibles 2020 [Internet]. Ginebra: OMS; 2020. Disponible en: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/332338
Pan American Health Organization. Leading causes of death and burden of disease in the Region of the Americas, 2021 [Internet]. Washington (DC): PAHO; 2021. Disponible en: https://www.paho.org/en/enlace/burden-noncommunica ble-diseases
Fonseca MM, Coimbra RVG, Oliveira JSE, Soares ADN, Gomes JMG. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and associated factors in children from Barbacena (MG), Brazil. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2023;42:e2022127. doi:10.1590/1984-0462/2024/42/2022127.
Dicken SJ, Qamar S, Batterham RL. Who consumes ultra-processed food? A systematic review of sociodemographic determinants of ultra-processed food consumption from nationally representative samples. Nutr Res Rev. 2024;37(2):416-56. doi:10.1017/S0954422423000 240.
Encuesta Nacional de Condiciones de Vida (ENCOVI). Décima edición [Internet]. Caracas: Proyecto ENCOVI; 2024. Disponible en: https://www.proyectoencovi.com/en covi-2024
Soto M, Martín C. Analysis of food advertising and its relationship with childhood obesity. Nutr Clin Diet Hosp. 2021;41(4):55-67. doi:10.12873/414soto.
Carrasco M, Ramírez E, Álvarez M, Chávez A, Roldán JA, Cortés T. Diferencias por nivel socioeconómico y escolar en la adquisición de alimentos de la población mexicana. Nutr Hosp. 2023;40(3):591-6. doi:10.20960/nh.04396.
Leffa PS, Hoffman DJ, Rauber F, Sangalli CN, Valmórbida JL, Vitolo MR. Longitudinal associations between ultra-processed foods and blood lipids in childhood. Br J Nutr. 2020;124(3):341-8. doi:10.1017/S000711452000 1233.
Lacerda AT, Carmo AS, Sousa TM, Santos LC. NOVA food groups' consumption associated with nutrient intake profile of school children aged 8-12 years. Public Health Nutr. 2023;26(1):56-62. doi:10.1017/S1368980022000441.
Organización Mundial de la Salud. Directriz: ingesta de azúcares para adultos y niños [Internet]. Ginebra: OMS; 2015. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/publications/i/ item/9789241549028
World Health Organization. Carbohydrate intake for adults and children: WHO guideline [Internet]. Geneva: WHO; 2023. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/publications /i/item/9789240080287
Meza-Miranda ER, Nuñez-Martínez BE. Nutrientes críticos de alimentos procesados y ultraprocesados destinados a niños y su adecuación al perfil de la Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Rev Esp Nutr Hum Diet. 2022;25(2):128-42. doi:10.14306/renhyd.25.2.1085.
Martí A, Calvo C, Martínez A. Consumo de alimentos ultraprocesados y obesidad: una revisión sistemática. Nutr Hosp. 2021;38(1):177-85. doi:10.20960/nh.03151.
Mescoloto SB, Pongiluppi G, Domene SMÁ. Ultra-processed food consumption and children and adolescents’ health. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2024;100 Suppl 1:S18-30. doi:10.1016/j.jped.2023.09.006.
Martínez Steele E, Popkin BM, Swinburn B, Monteiro CA. The share of ultra-processed foods and the overall nutritional quality of diets in the US: evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional study. Popul Health Metr. 2017;15(1):6. doi:10.1186/s12963-017-0119-3.
Schönenberger KA, Huwiler VV, Reber E, Mühlebach S, Stanga Z, Pestoni G, et al. Dietary fibre intake and its association with ultra-processed food consumption in the general population of Switzerland: analysis of a population-based, cross-sectional national nutrition survey. BMJ Nutr Prev Health. 2024;7:e000727. doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2023-000727.
Calcaterra V, Cena H, Rossi V, Santero S, Bianchi A, Zuccotti G. Ultra-processed food, reward system and childhood obesity. Children (Basel). 2023;10(5):804. doi:10.3390/children10050804.
Geladari EV, Kounatidis D, Christodoulatos GS, Psallida S, Pavlou A, Geladari CV, et al. Ultra-processed foods and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): what is the evidence so far? Nutrients. 2025;17(13):2098. doi:10.3390/nu17132098.
García S, Monserrat-Mesquida M, Ugarriza L, Casares M, Gómez C, Mateos D, et al. Ultra-processed food consumption and metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): a longitudinal and sustainable analysis. Nutrients. 2025;17(3):472. doi:10.3390/nu17030472.
Lee Gy, Lim JH, Joung H, Yoon D. Association between ultraprocessed food consumption and metabolic disorders in children and adolescents with obesity. Nutrients. 2024;16(20):3524. doi:10.3390/nu16203524.
Santos PQ, Cotrim HP, Rocha R, Daltro CH, Andrade SCS, Costa APC, et al. Enfermedad hepática esteatósica asociada a disfunción metabólica y características de la ingesta alimentaria en niñas, niños y adolescentes: un estudio transversal. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2025;90(3):349-56. doi:10.1016/j.rgmx.2024.12.007.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v79i4.787
IMÁGENES GEN
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
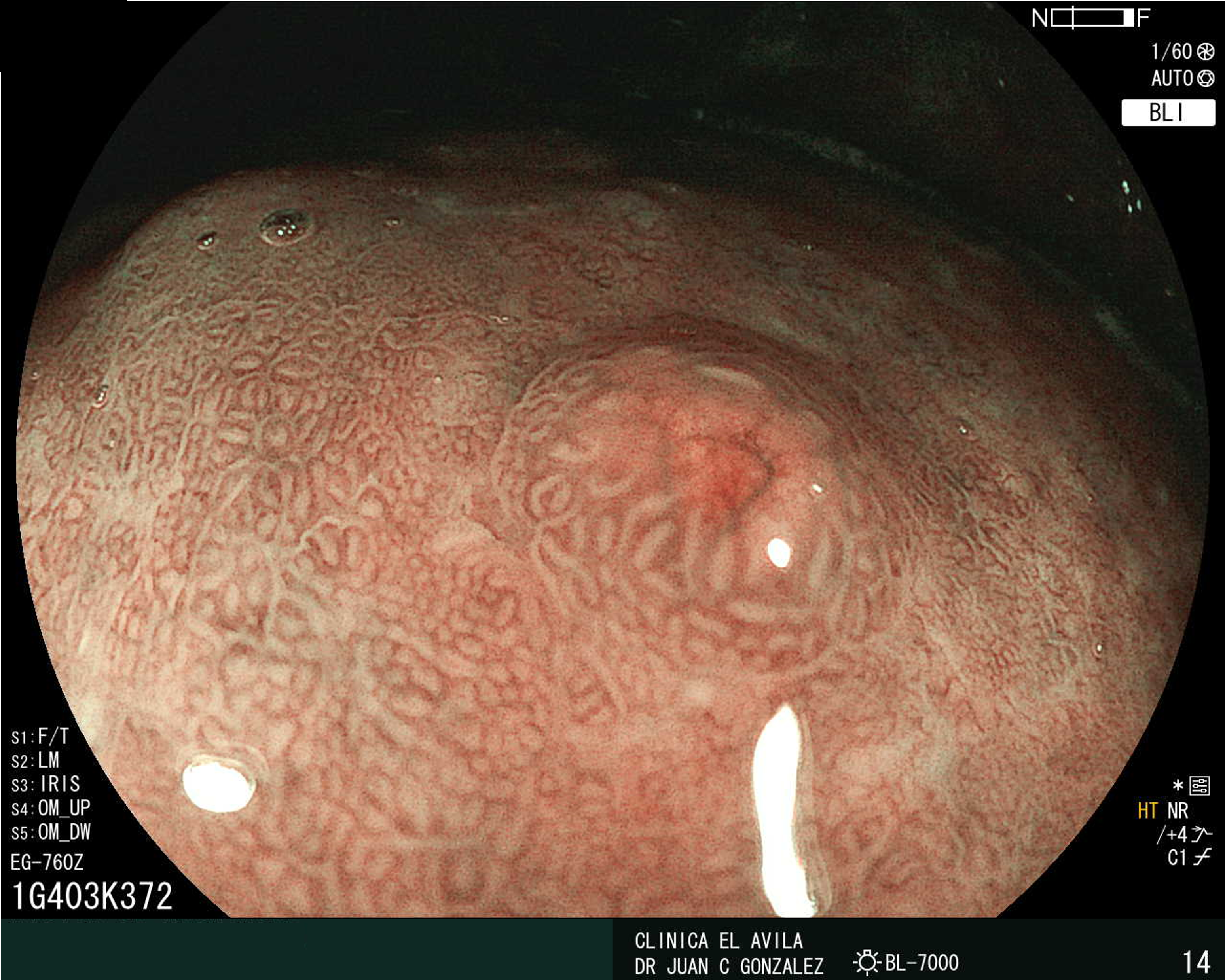 | 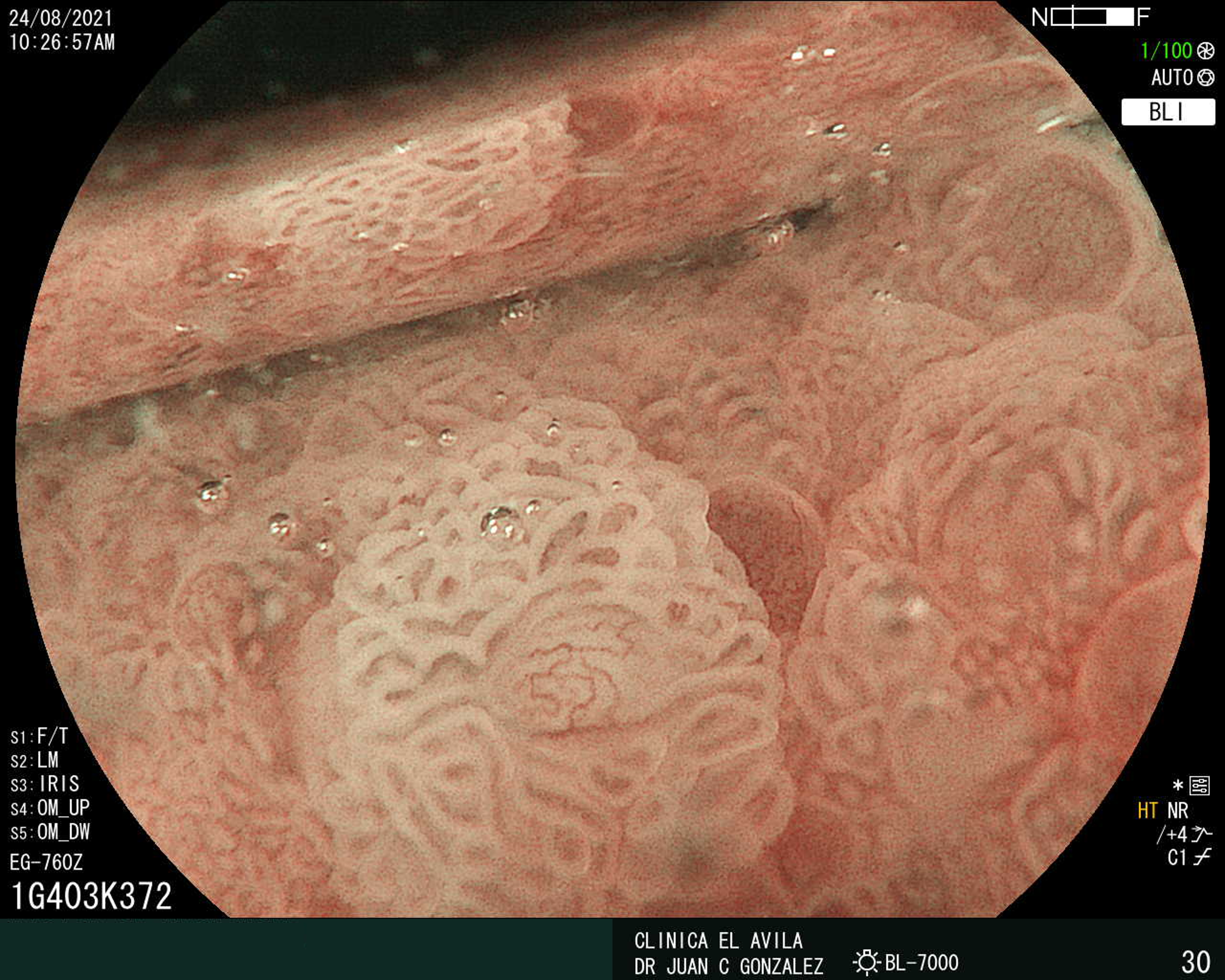 |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X