Ciencia de la Nutrición y Salud. Microbioma. Fibras. Enfermedades Metabólicas. Alimentos Antiinflamatorios y Anticáncer
Resumen
La mayoría de las enfermedades no infecciosas, están asociadas a una mala alimentación, son crónicas, inflamatorias y degenerativas. El Síndrome y disfunción metabólicos, se identifican como ejes centrales de las enfermedades no trasmisibles (ENT), resultado de alteraciones de ocho procesos celulares esenciales: glicosilación, resistencia a la insulina, estrés oxidativo, inflamación, disfunción mitocondrial, integridad de membranas, factores del ambiente y autofagia. La raíz de la enfermedad y la salud reside en el intestino. Una dieta equilibrada, rica en nutrientes esenciales, fibras, fitoquímicos y grasas omega-3, son elementos esenciales para fomentar una salud intestinal óptima, que depende en buena parte del microbioma humano formado por bacterias, hongos, parásitos virus y arqueas, los cuales residen en la piel, intestino y otros sitios del cuerpo.
ESCUCHE EL RESUMEN HANCIENDO CLIC EN EL IDIOMA DE SU PREFERENCIA:
EspañolEnglish
Portugues
Japones
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
World Health Organization. Non-communicable diseases 2010. Geneva: WHO; 2011.
Roser M. Link between health spending and life expectancy: the U.S. is an outlier. Our World in Data. 2017. Disponible en: https://ourworldindata.org
Woolf SH, Schoomaker H. Life expectancy and mortality rates in the United States, 1959-2017. JAMA. 2019;322(20):1996-2016.
Brownstein R. The eye-popping cost of Medicare for all. The Atlantic. 2019 Oct 16.
Romero NE. Rev Cub Urol. 2025;8(1): enero-abril.
Lustig RH. Metabolical: The lure and the lies of processed food, nutrition and modern medicine. New York: HarperCollins; 2021.
Mogre V, Scherpbier AJJA, Dornan T, Stevens F, Aryee PA, Cherry MG, et al. Why nutrition education is inadequate in the medical curriculum: a qualitative study of students’ perspectives on barriers and strategies. BMC Med Educ. 2018; 18:26.
Bremer AA, Mietus-Snyder M, Lustig RH. Toward a unifying hypothesis of metabolic syndrome. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):557-70.
Bunn HF, Higgins PJ. Reaction of monosaccharides with proteins: possible evolutionary significance. Science. 1981;213(4504):222-4.
Dandekar A, Mendez R, Zhang K. Cross talk between ER stress, oxidative stress, and inflammation in health and disease. Methods Mol Biol. 2015; 1292:205-14.
López-Lluch G, Santos-Ocaña C, Sánchez-Alcázar JA, Fernández-Ayala DJ, Asencio-Salcedo C, Rodríguez-Aguilera JC, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolism and ageing: shared mechanisms and outcomes? Biogerontology. 2018;19(5):461-80.
Haas JT, Biddinger SB. Dissecting the role of insulin resistance in the metabolic syndrome. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009;20(3):206-10.
Park LK, Friso S, Choi SW. Nutritional influences on epigenetics and age-related disease. Proc Nutr Soc. 2012;71(1):75-83.
Nicklin P, Bergman P, Zhang B, Triantafellow E, Wang H, Nyfeler B, et al. Bidirectional transport of amino acids regulates mTOR and autophagy. Cell. 2009;136(3):521-34.
Bulsiewicz W. Fiber fueled. New York: Penguin Random House; 2020. p. 123-40.
Enders G. Gut: The inside story of our body’s most underrated organ. Melbourne: Scribe; 2015.
Kosumi K, Mima K, Baba Y, Ogino S. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota and colorectal cancer: the key target of molecular pathological epidemiology. J Lab Precis Med. 2018 Sep;3:73. doi: 10.21037/jlpm.2018.09.05.
Quigley MM. Prebiotics and probiotics in digestive health. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(2):333-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.09.028
Song M, Wu K, Meyerhardt JA, Ogino S, Wang M, Fuchs CS, et al. Fiber intake and survival after colorectal cancer diagnosis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(1):71-9. doi: 10.1001/ja maoncol.2017.3684.
Bulsiewicz W. Fiber fueled: The plant-based gut health program for losing weight, restoring your health and optimizing your microbiome [Internet]. New York: William Morrow; 2020. Disponible en: https://theplantfedgut.com.
Kimura I, Ozawa K, Inoue D, Imamura T, Kimura K, Maeda T, et al. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1829. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2852.
Béliveau R, Gingras DG. Foods that fight cancer. New York: McClelland & Stewart; 2006.
Luzardo LI, Zschaeck DW. Comida antiinflamatoria y anticáncer. 3ª ed. Caracas: Editorial SIAP; 2023.
Luzardo LI, Zschaeck DW. Alimentos con fibras y salud intestinal. Caracas: Editorial SIAP; 2022.
Aggarwal BB. Healing spices. New York: Sterling; 2007.
Servan-Schreiber D. Anticancer: a new way of life. New York: Penguin Group; 2008.
Luzardo LI. Mi historia ayuda a sanar tu cáncer. Caracas: Editorial SIAP; 2024.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v79i4.783
IMÁGENES GEN
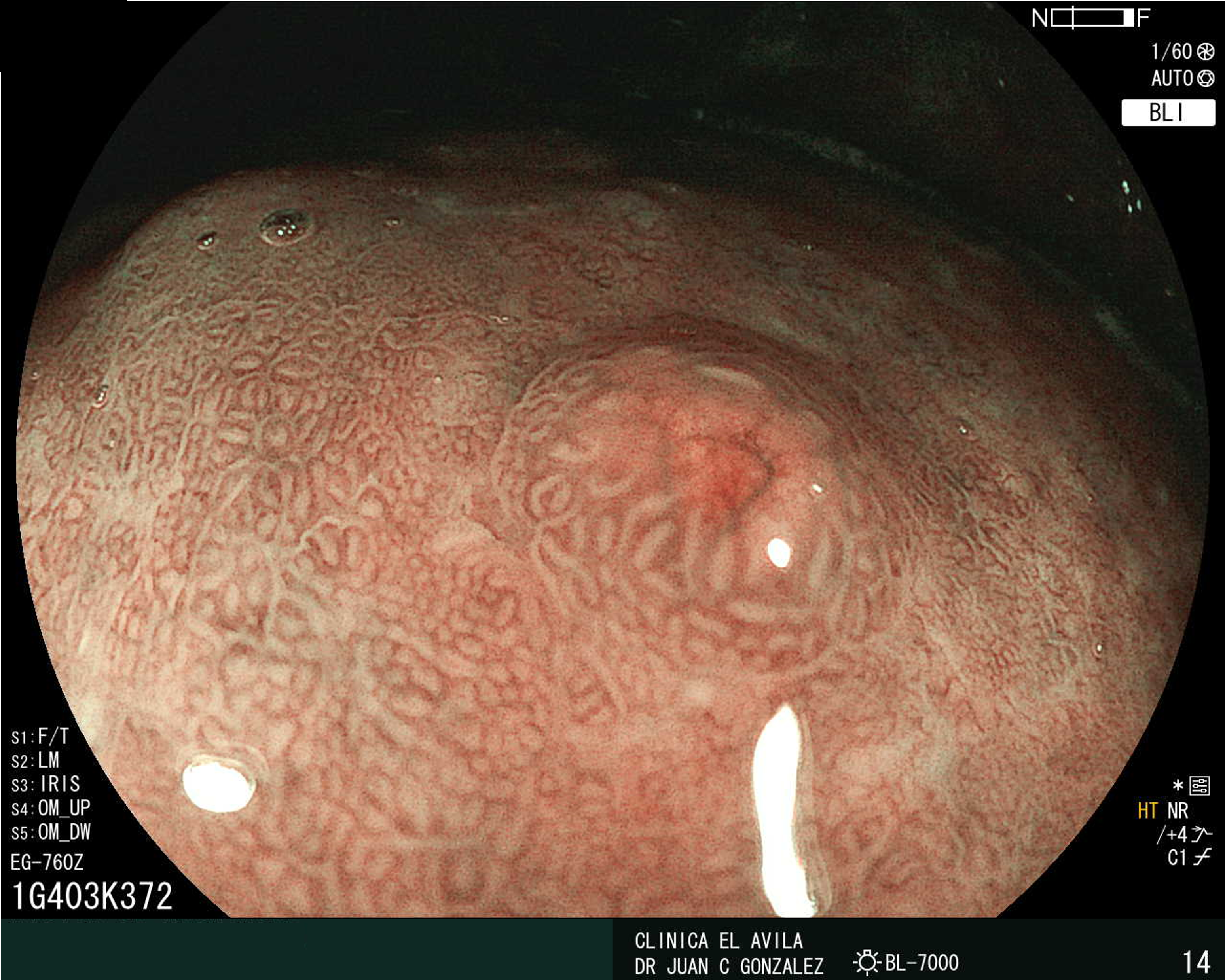
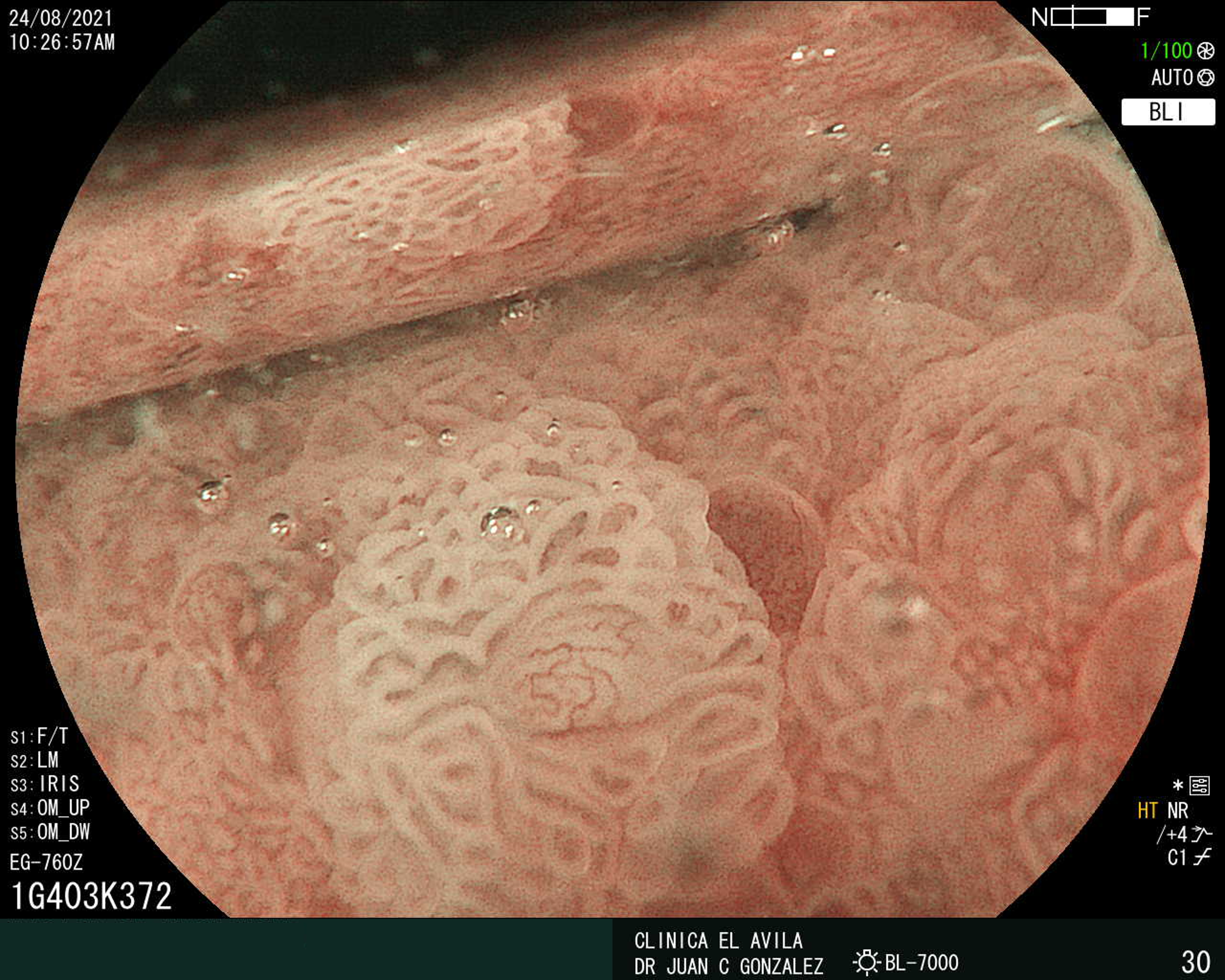
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X