Análisis inmunohistoquímico de P53, CERB-B2, EGFR y PCNA en cáncer gástrico
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: Diffuse and socalled intestinaltype carcinoma. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 1965; 64:31-49. [ Links ]
Qota K, Sobin LH. Histological typing of gastric and esophageal tumors. International histological classification of tumours. No, 18, Geneva WHO, 1977 [ Links ]
Nakamura K, Sugano H, Takagi K. Carcinoma of stomach: Its histogénesis and histological appearance. Gann 1968; 59: 251-258. [ Links ]
Correa P. A human model of gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 1988; 48:3354-3560. [ Links ]
Tahara E. Genetic alterations in human gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer 1995; 75(Suppl):1410-1417. [ Links ]
Lane DP. P-53, Guardian del Genome. Nature 1992;358:15-16. [ Links ]
Levine A, et al. The P-53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature 1991;351:453. [ Links ]
Brito Mj, Filipe MI. Expresión of p53 in early (Ti) gastric carcinoma and precancerous adjacent mucosa. Gut 1994;35:1697-1700. [ Links ]
Craanen ME, Blok P, Dekker W, Offerhaus GJ, Tytgat UN. Chronology of p53 protein accumulation in gastric carcinogenesis. Gut 1995;36(6): 848-52. [ Links ]
Kubicka S, Claas C, et al. P53 mutation pattern and expression of c-erb B2 and c-met in gastric cancer: relation to hystological subtypes, Helicobacter pylori infection, and prognosis. Dig Dis Sci 01Jan-2002;47(1): 114-21. [ Links ]
Ranzani GN, Luinetti O, et al. P53 gene mutations and protein nuclear accumulation are early events in intestinal type gastric cancer but late events in diffuse type. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prev 1995Apr-May;4(3):223-31. [ Links ]
Rugge M, Shiao YH, et al. The p53 gene in patients under the age 40 with gastric cancer: mutation rates are low but are associated with a cardial location. Mol Pathol 01Aug-2000; 53(4): 207-10. [ Links ]
Sanz-Ortega J, Steinberg SM, et al. Comparative study of tumor angiogenesis and immunohistochemitry for p53, c-erb B2 and EGFR as prognostic factors in gastric cancer. Histol Histopathology 01Apri-2000; 15(2): 455-62. [ Links ]
Kazuo Sugiyaina, Yutaka Yonemura, ltsuo Miyazaki. Immunohistochemical Study of Epidermal Growth Factor and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Gastric Carcinoma. Cancer 1989; 63:1557-1561. [ Links ]
Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell 1991; 64:249-270. [ Links ]
Cross M, Dexter T M. Growth factors in development, transformation and tumorogenesis. Cell 1991; 64:271-280. [ Links ]
Ross JS, et al. The Her-2/neu oncogene in tumors of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Cancer Invest 2001; 19(5): 554-68. [ Links ]
Allgayer II, Babic R, et al. c-erb B2 is of independent prognostic relevance in gastric cancer and is associated with the expression of tumor-associated protease systems. J Clin Oncol. Jun2000; 18(11):220 1-9. [ Links ]
Aoyagi K, Kohfuji K, et al. Evaluation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and cerb B2 in superspreading-type arid penetrating-type gastric carcinoma. Kurume Med J. Jan2001; 48(3):197-200. [ Links ]
Ougolkov A. Altered Expression of Beta-Catenin arid c-erb B-2 in Early Gastric Cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer 2000;19(3): 349-55. [ Links ]
Dursun A, Poyraz A, Cetik B, Akkol G. Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in gastric carcinoma: correlation eith histopathologic characteristic and analysis of Ki-67. Pathol Oncol Res 1999;5(2): 104-6. [ Links ]
Correa P. Human gastric carcinogenesis: A multistep and multifactorial process First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 6735-40. [ Links ]
Brenes E, Correa P, et al. Helicobacter pylori causes hyperprotiferation of gastric epithelium. Pre-and post-eradication indices of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Am J Gastroenterology 1993;88:1870-5. [ Links ]
Tsujii M, Kawano S, et al. Ammonia, a possible promoter in Helicobacter pylori related gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 1992;65:15-18. [ Links ]
Zhong Zhang, Yuan Yuan, et al. Apoptosis, proliferation and P53 gene expression of H. pylori associated gastric epithelial lesions. World J. Gastroenterology 2001;7(6): 779-782. [ Links ]
Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma. Japanese Research Society for Gastric Cancer. First English Edition. Kanehara y Co., LTD., Tokyo. 1995. [ Links ]
Sobin LR, Fleming ID. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, Fifth edition (1997). Union Internationale Contre le Cancer and the American Joint Committee on Cancer 1997 Nov 1; 80(9): 1803-1804. [ Links ]
Linden MD, Torres FX, et al. Clinical application of morphologic and immunochemical assessment of cell proliferation. Am J Clin Pathology 1990; 162:285-94. [ Links ]
Filipe MI, Muñoz N, Matko I, et al. Intestinal Metaplasia Types and the Risk of Gastric cancer: A Cohort Study in Slovenia. Int. J. Cancer 1994; 57: 324-5. [ Links ]
Lui XP, Tsushimi K, et al. Expression of P53 protein as a prognostic indicator of reduced survival time in diffuse type gastric carcinoma. Pathol int 2001Jun; 51(6): 440-4. [ Links ]
Xu A, Li S, Liu J. Correlation between apoptosis and proliferation in gastric-pre carcinoma. Zhongliua Yi Xue ZA Zhi 01Mar1999; 79(3): 185-6. [ Links ]
Sugay T, Nakamura S. Role of DNA aneuploidy, over expression of P53 gene product and cellular proliferation in the progression of gastric cancer. Cytometry 15Jun1999; 38(3): 111-7. [ Links ]
Roviello F, Marrelli D, et al. P53 accumulation is prognostic factor in intestinal type gastrinoma but not in diffuse type. Ann Surg Oncol 01Dec1999; 6 (8):739-45. [ Links ]
Ikeguchi M, Saito H, et al. Mutated P53 protein expression and proliferative activity in advanced gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 1999Jul-Aug; 46(28): 2648-53. [ Links ]
Carreño Luz y Col. P53 en la Carcinogénesis Gástrica. Centro de Control de Cáncer Gastrointestinal "Dr. Luis Anderson".(No publicado. Datos aportados por el Autor) [ Links ]
Wang J. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Oncogene Expression in Gastric Carcinoma and its Precursor Lesions. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2002;47 (1): 107-113. [ Links ]
Nakajima M. The prognostic significance of amplification and overexpression of c-met and cerb B-2 inhuman gastric carcinoma. Cancer 1999; 85(9): 1894-902. [ Links ]
Polkowski W, et al. Prognostic Value of Lauren Classification and c-erb B 2 Oncogene Overexpression in adenocarcinoma of esophagus and Gastroesophageal Junction. Ann Surg. Oncol. 1999; 6(3): 290-7. [ Links ]
Jorlic N, Kovac K, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor expressions correlate with tumor cell prolileration and prognosis in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 1997Sep-Oct; 17(59):3883-8. [ Links ]
Márquez R, Gutierrez Y, Peraza S, Castro D, et al. Marcadores inmunohistoquímicos en lesiones gástricas premalignas. Centro de Control de Cáncer Gastrointestinal "Dr. Luis Anderson". (No publicado. Datos aportados por el Autor) [ Links ]
Peraza S, Castro D, Oliver WE, et al. Investigación histológica del Helicobacter pylori en 265 biopsias gástricas consecutivas. GEN 1991;45:163-66. [ Links ]
Muñoz N, Kato I, et al. Prevalence of Precancerous Lesions of Stomach in Venezuela. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention, 1996;5:41-46. [ Links ]
Tsuji N, Ishiguro S, et al. Time Trends for small gastric cancer in Japan. Gastric Cancer 2000Dec27; 3(3): 123-127. [ Links ]
Ruschoff J, Mehringer S, et al. Correlation between histological and molecular mechanism of carcinogenesis in stomach cancer. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 01Jan1999; 83: 71- 8. [ Links ]
Fiocca IT, Luinelti O, et al. Molecular mechanism involved in the pathogenesis of gastric carcinoma: Interactions between genetics alterations, cellular phenotype and cancer histotype. Hepatogastroenterology 2001Nov-Dec; 48 (42): 1523-30. [ Links ]
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v60i3.772
IMÁGENES GEN
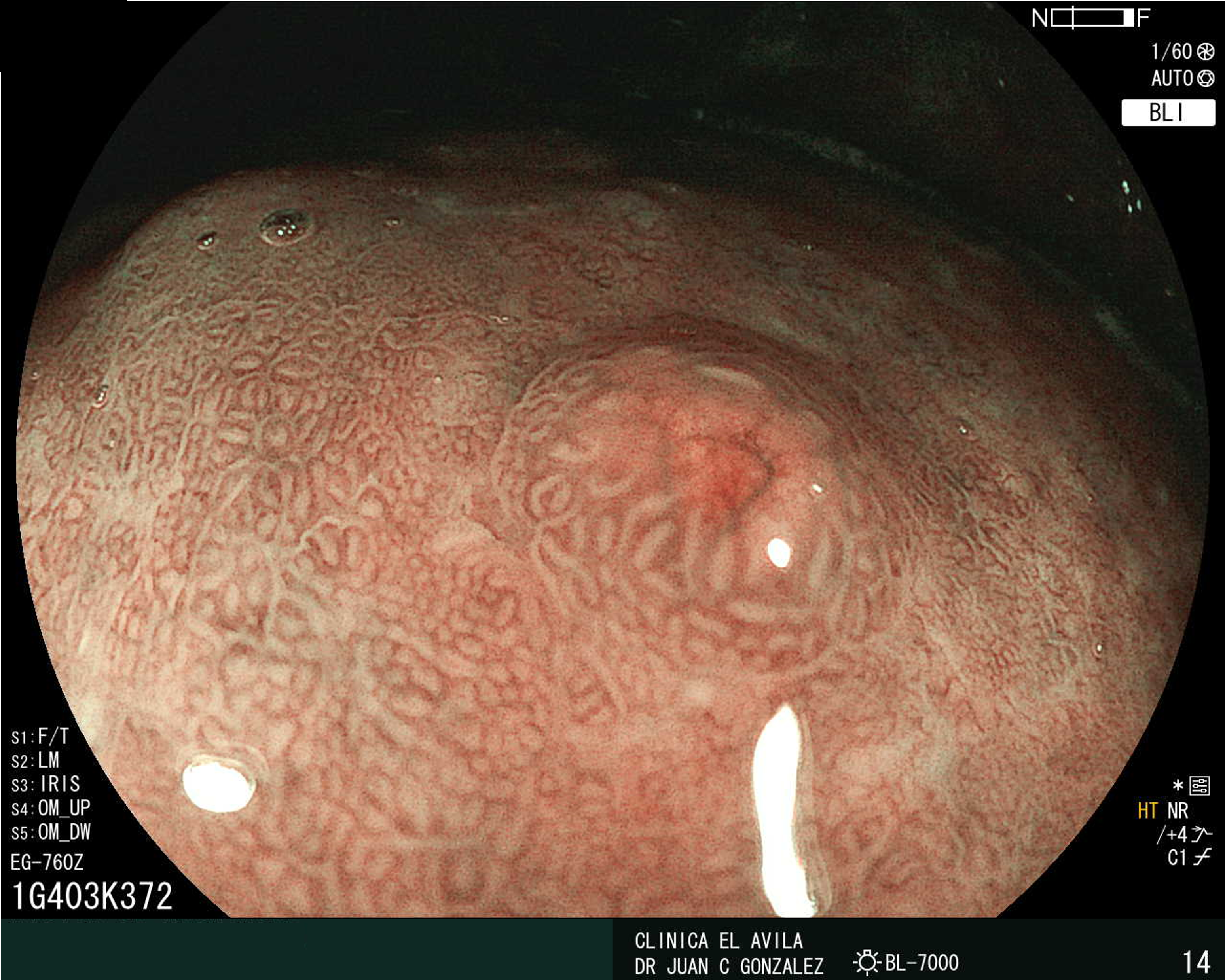
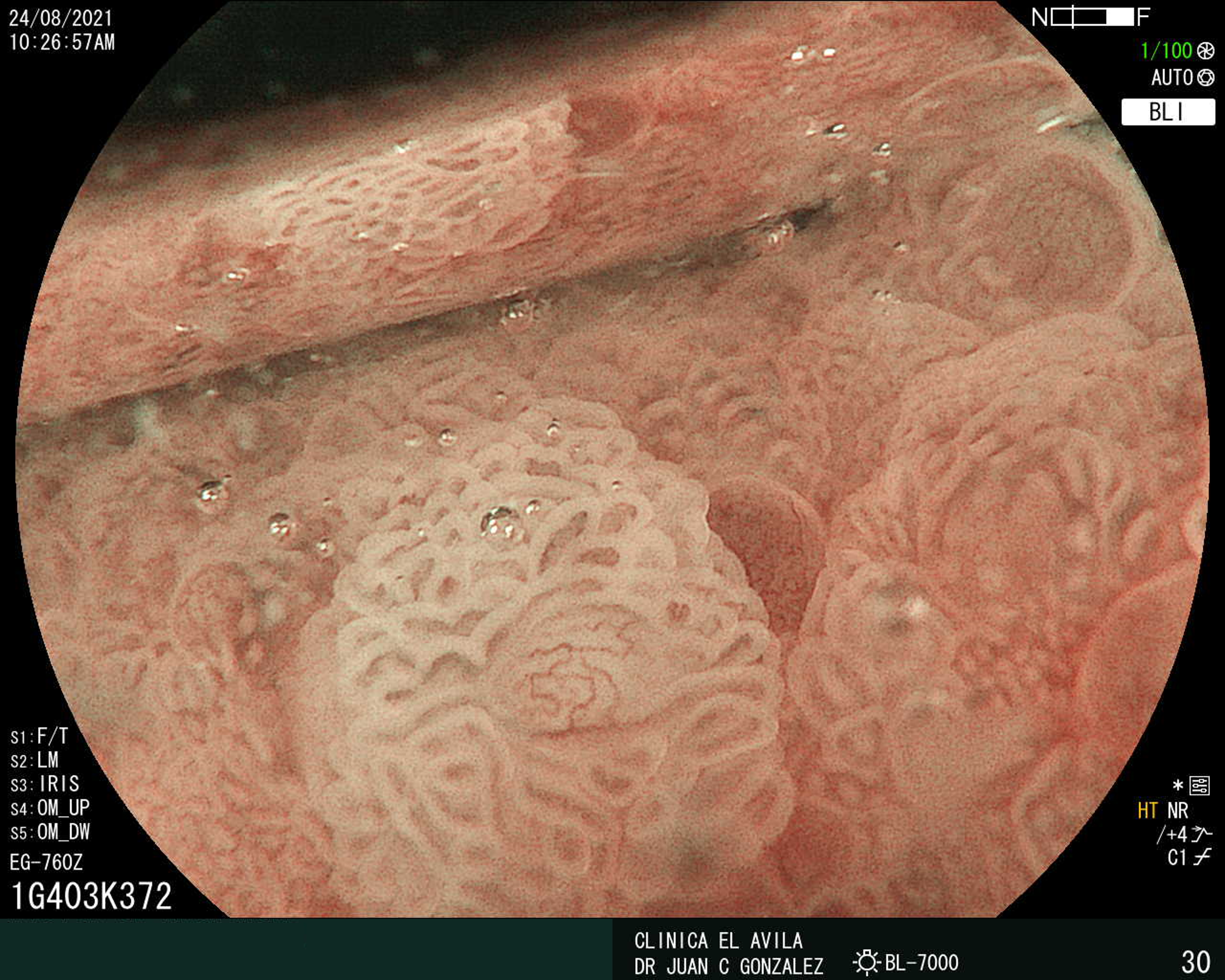
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X