Encefalopatía hepática: Visión sobre patogenia, diagnóstico y terapéutica
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Ortiz M, Jacas C, Córdoba J. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: diagnosis, clinical significance and recommendations. J Hepatol. 2005;42(suppl 1):S45-S53.
Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, Weissenborn K and Wong P. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Journal of Hepatology 2014; 61:642–659
Shawcross, D. L., Wright, G., Olde Damink, S. W. & Jalan, R. Role of ammonia and inflammation in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2007. 22, 125-138
Poordad FF. Review article: the burden of hepatic encephalopathy . Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006 ; 25 : 3 – 9.
Bustamante J , Rimola A , Ventura PJ et al. Prognostic significance of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis . J Hepatol 1999; 30: 890 – 5.
Mas A , Rodés J , Sunyer L et al. Comparison of rifaximin and lactitol in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: results of a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled clinical trial. J Hepatol 2003 ; 38 :51 – 8
Qadri, A. M., Ogunwale, B. O. & Mullen, K. D. Can we ignore minimal hepatic encephalopathy any longer? Hepatology 2007; 45, 547-548.
Talwalkar, J. A. & Kamath, P S. Influence of recent advances in medical management on clinical outcomes of cirrhosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005; 80, 1501-1508.
Groeneweg M., Quero J. C., Bruijn I. D., Hartmann I. J. C., Essink‐bot M-L., Hop W. C. J. and Schalm S. W.et al. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy impairs daily functioning. Hepatology 1998;28, 45-49.
Bajaj, J. S., Hafeezullah M., Hoffmann R. G., Varma R. R., Franco J., Binion D. G., Thomas A. Hammeke T. A. and Saeian K.et al. Navigation skill impairment: Another dimension of the driving difficulties in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2008; 47, 596-604.
Bajaj, J. S., Saeian, K., Hafeezullah, M., Hoffmann, R. G. & Hammeke, T. A. Patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy have poor insight into their driving skills. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008; 6, 1135-1139.
Bajaj, J. S.; Hafeezullah, M; Zadvornova, Y; Martin, E; Schubert, C. M.; Gibson, D. P.; Hoffmann, R. G.; Sanyal, A. J.; et al. The effect of fatigue on driving skills in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009; 104, 898-905.
Kircheis, G., Knoche, A., Hilger, N., Manhart, F., Schnitzler, A., Schulze, H. and Häussinger, D. Hepatic encephalopathy and fitness to drive. Gastroenterology 2009; 137, 1706-1715.e9.
Bajaj, J. S., Saeian K., Schubert C. M., Hafeezullah M., Franco J., Varma R. R., Gibson D. P., Hoffmann R. G., Todd Stravitz T., et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy is associated with motor vehicle crashes: the reality beyond the driving test. Hepatology 2009; 50, 1175-1183.
Prakash, R. and Mullen, K. D. Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology&Hepatology 2010; 7: 515–525
Cortez García, Luis. Papel de la nutrición en la encefalopatía hepática: es tiempo de cambiar .Nutr. clín. diet. hosp. 2013; 33(2):89-97
Elwir, Saleh and Rahimi , Robert. Hepatic Encephalopathy: An Update on the Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Options. Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology 2017 vol. 5:142–151
Zieve, L. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 1987; 2, 147-165.
Cooper, A. J. & Plum, F. Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol. Rev.1987; 67, 440-519.
Ytrebø, L. M., Sen S., Rose C., Ten Have, G. A. M., Davies N. A., Hodges S., Nedredal G. I., Romero-Gomez M. and Williams R. Interorgan ammonia, glutamate, and glutamine trafficking in pigs with acute liver failure. Am. J. Physiol.Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006; 291, G373-G381.
Olde Damink, S. W., Jalan, R. & Dejong, C. H. Interorgan ammonia trafficking in liver disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2009; 24, 169-181
Cagnin A., Taylor-Robinson, S. D., Forton, D. M. & Banati, R. B. In vivo imaging of cerebral "peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites" in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Gut 2006; 55, 547-553
Ahboucha, S. & Butterworth, R. F. The neurosteroid system: implication in the pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 2008; 52, 575-587
Baulieu, E. E. Neurosteroids: a novel function of the brain. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1998; 23, 963-987
Papadopoulos, V. , Baraldi M., Guilarte T. R., Thomas B. Knudsen T. B. and Gavish M. Translocator protein (18kDa): new nomenclature for the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor based on its structure and molecular function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006; 27, 402-409.
Papadopoulos, V., Lecanu, L., Brown, R. C., Han, Z. & Yao, Z. X. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor in neurosteroid biosynthesis, neuropathology and neurological disorders. Neuroscience 2006; 138, 749-756
Ahboucha, S. & Butterworth, R. F. The neurosteroid system: an emerging therapeutic target for hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2007; 22, 291-308
Desjardins, P. & Butterworth, R. F. The "peripheral-type" benzodiazepine (omega 3) receptor in hyperammonemic disorders. Neurochem. Int. 2002; 41, 109-114.
Bélanger, M., Desjardins, P, Chatauret, N., Rose, C. & Butterworth, R. F. Mild hypothermia prevents brain edema and attenuates up-regulation of the astrocytic benzodiazepine receptor in experimental acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2005; 42, 694-699
Ahboucha, S., Coyne, L., Hirakawa, R., Butterworth, R. F. & Halliwell, R. F. An interaction between benzodiazepines and neuroactive steroids at GABAA receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurochem. Int. 2006; 48, 703-707
Scott TR, Kronsten VT, Hughes RD, Shawcross DL. Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19: 9240–9255.
Schliess, F., Gorg, B. & Häussinger, D. Pathogenetic interplay between osmotic and oxidative stress: the hepatic encephalopathy paradigm. Biol. Chem. 2006; 387, 1363-1370
Murthy, C. R., Rama Rao, K. V., Bai, G. & Norenberg, M. D. Ammonia-induced production of free radicals in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001; 66, 282-298
Hermenegildo, C., Monfort, P. & Felipo, V. Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat brain in vivo following acute ammonia intoxication: characterization by in vivo brain microdialysi s. Hepatology 2000; 31, 709-715.
Hilgier, W., Anderzhanova, E., Oja, S. S., Saransaari, P. & Albrecht, J. Taurine reduces ammonia- and N-methyl-Daspartate-induced accumulation of cyclic GMP and hydroxyl radicals in microdialysates of the rat striatum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003; 468, 21-25.
Reinehr, R., Görg B., Becker S., Qvartskhava N., Bidmon H. J., Selbach O., Haas H. L., Schliess F., and Häussinge D. Hypoosmotic swelling and ammonia increase oxidative
stress by NADPH oxidase in cultured astrocytes and vital brain slices. Glia 2007; 55, 758-771
Albrecht, J. & Norenberg, M. D. Glutamine: a Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology 2006; 44, 788-794.
Mullen, K. D. & Jones, E. A. Natural benzodiazepines and hepatic encephalopathy. Semin. Liver Dis. 1996; 16, 255-264.
Mullen, K. D., Cole, M. & Foley, J. M. Neurological deficits in "awake" cirrhotic patients on hepatic encephalopathy treatment: missed metabolic or metal disorder? Gastroenterology 1996; 111,256-257 (1996).
Rose, C., Butterworth R. F., Zayed J., Normandin L., Tood K., Michalak A., Spahr L., Huet P-M. and Pomier-Layrargues G. Manganese deposition in basal ganglia structures results from both portal-systemic shunting and liver dysfunction. Gastroenterology 1999; 117, 640-644
Naegele, T., Grodd W., Viebahn R., Seeger U., Klose U., Seitz D., et al. MR imaging and 1H spectroscopy of brain metaboli tes in hepatic encephalopathy: time-course of renormalization after liver transplantation. Radiology 2000; 216, 683-691.
Aggarwal, A., Vaidya S., Shah S., Singh J., Desai S and Bhatt M. Reversible Parkinsonism and T1W pallidal hyperintensities in acute liver failure. Mov. Disord. 2006; 21, 1986-1990.
Krieger, D., Krieger S., Theilmann L., Jansen O., Gasss P. and Lichtnecker H. Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 1995; 346, 270-274.
Merli M, Lucidi C, Pentassuglio I, Giannelli V, Giusto M, Di Gregorio V, et al. Increased risk of cognitive impairment in cirrhotic patients with bacterial infections. J Hepatol 2013; 59:243–250.
Hung TH, Lay CJ, Chang CM, Tsai JJ, Tsai CC, Tsai CC. The effect of infections on the mortality of cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Epidemiol Infect 2013:1–8.
Jones EA, Mullen KD. Theories of the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis 2012;16:7–26.
Córdoba J, García-Martinez R, Simón-Talero M. Hyponatremic and hepatic encephalopathies: similarities, differences and coexistence. Metab Brain Dis 2010; 25:73–80.
Butterworth RF. The liver-brain axis in liver failure: neuroinflammation and encephalopathy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013; 10:522–528.
Rodrigo R, Cauli O, Gomez-Pinedo U, Agusti A, Hernandez-Rabaza V, Garcia-Verdugo JM, et al. Hyperammonemia induces neuroinflammation that contributes to cognitive impairment in rats with hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 2010; 139:675–684.
Wright GA, Sharifi Y, Newman TA, Davies N, Vairappan B, Perry HV, et al. Characterisation of temporal microglia and astrocyte immune responses in bile duct-ligated rat models of cirrhosis. Liver Int 2014; 34:1184–1191.
RangrooThrane V, Thrane AS, Wang F, Cotrina ML, Smith NA, Chen M, et al. Ammonia triggers neuronal disinhibition and seizures by impairing astrocyte potassium buffering. Nat Med 2013; 19:1643–1648.
Odeh M, Sabo E, Srugo I, Oliven A. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha correlate with severity of hepatic encephalopathy due to chronic liver failure. Liver Int 2004; 24:110–116.
Jiang W, Desjardins P, Butterworth RF. Direct evidence for central proinflammatory mechanisms in rats with experimental acute liver failure: protective effect of hypothermia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2009; 29:944–952.
Chang CC, Wang SS, Huang HC, Chan CY, Lee FY, Lin HC, et al. Selective cyclooxygenase inhibition improves hepatic encephalopathy in fulminant hepatic failure of rat. Eur J Pharmacol 2011; 666:226–232.
Odeh M. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: the tumour necrosis factor-alpha theory. Eur J Clin Invest 2007; 37:291–304.
Ginès P, Guevara M. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: pathogenesis, clinical significance, and management. Hepatology 2008;48:1002–1010.
Martín-Llahí M, Guevara M, Torre A, Fagundes C, Restuccia T, Gilabert R, et al. Prognostic importance of the cause of renal failure in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2011; 140:488-496.
Gupta A, Dhiman RK, Kumari S, Rana S, Agarwal R, Duseja A, et al. Role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and delayed gastrointestinal transit time in cirrhotic patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2010; 53:849–855.
Albillos A, de la Hera A. Multifactorial gut barrier failure in cirrhosis and bacterial translocation: working out the role of probiotics and antioxidants. J Hepatol 2002; 37:523–526.
Bellot P, Francés R, Such J. Pathological bacterial translocation in cirrhosis: pathophysiology, diagnosis and clinical implications. Liver Int 2013; 33:31–39.
Lindros KO, Järveläinen HA. Chronic systemic endotoxin exposure: an animal model in experimental hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2005; 20:393–398
Jun DW, Kim KT, Lee OY, Chae JD, Son BK, Kim SH, et al. Association between small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and peripheral bacterial DNA in cirrhotic patients. Dig Dis Sci 2010; 55:1465–1471.
Bajaj JS, Heuman DM, Hylemon PB, Sanyal AJ, White MB, Monteith P, et al. Altered profile of human gut microbiome is associated with cirrhosis and its complications. J Hepatol 2014; 60:940–947.
Bajaj JS, Ridlon JM, Hylemon PB, Thacker LR, Heuman DM, Smith S, et al. Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012; 302:G168–G175.
Palomero-Gallagher N, Zilles K. Neurotransmitter receptor alterations in hepatic encephalopathy: a review. Arch Biochem Biophys 2013; 536:109–121.
Felipo V. Hepatic encephalopathy: effects of liver failure on brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci 2013; 14:851–858.
Elgadi KM, Meguid RA, Qian M, Souba WW, Abcouwer SF. Cloning and analysis of unique human glutaminase
isoforms generated by tissue specific alternative splicing. Physiol Genomics 1999; 1:51–62
Romero-Gómez M, Jover M, Del Campo JA, Royo JL, Hoyas E, Galán JJ, et al. Variations in the promoter region of the glutaminase gene and the development of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med 2010; 153:281–288.
Albrecht J. Hepatic encephalopathy in our genes? Ann Intern Med 2010;153:335–336.
Mayer LB, Gruenhage F, Lammert F. A genetic variant in the promoter of Phosphate Activated Glutaminase (GLS) gene predicts the risk of developing Hepatic Encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2013; 58:216A.
Butt Z, Jadoon NA, Salaria ON, Mushtaq K, Riaz IB, Shahzad A, et al. Diabetes mellitus and decompensated cirrhosis: risk of hepatic encephalopathy in different age groups. J Diabetes 2013;5:449–455.
Kalaitzakis E, Olsson R, Henfridsson P, Hugosson I, Bengtsson M, Jalan R, et al. Malnutrition and diabetes mellitus are related to hepatic encephalopathy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Liver Int 2007; 27: 1194–1201.
Ampuero J, Ranchal I, del Mar Díaz-Herrero M, del Campo JA, Bautista JD, Romero-Gómez M. Role of diabetes mellitus on hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2013; 28:277–279.
Basu S, Zethelius B, Helmersson B, Berne C, Larsson A, Arnlov J. Cytokinemediated inflammation is independently associated with insulin sensitivity measured by the euglycemic insulin clamp in a community-based cohort of elderly men. Int J Clin Exp Med 2011; 4:164–168.
Ampuero J, Ranchal I, Nuñez D, Díaz-Herrero MM, Maraver M, del Campo JA, et al. Metformin inhibits glutaminase activity and protects against hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS One 2012; 7:e49279.
Sigal SH, Stanca CM, Kontorinis N, Bodian C, Ryan E. Diabetes mellitus is associated with hepatic encephalopathy in patients with HCV cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101:1490-1496.
Cordoba J, Ventura-Cots M, Simón-Talero M, Amorós À, Pavesi M, Vilstrup H, et al. Characteristics, risk factors, and mortality of cirrhotic patients hospitalized for hepatic encephalopathy with and without acute-onchronic liver failure (ACLF). J Hepatol 2014; 60:275–281.
Manuel Romero-Gómez M., Montagnese S. and Jalan R. Hepatic encephalopathy in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatology 2015; 62:437–447
Bajaj JS, Wade JB, Sanyal AJ. Spectrum of neurocognitive impairment in cirrhosis: implications for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2009; 50:2014–2021.
Cordoba J. New assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2011;54:1030–1040.
Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P, Shawcross DL, Butterrworth RF, et al. Review article: the design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy—an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011; 33:739–747.
Montagnese S, Amodio P, Morgan MY. Methods for diagnosing hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a multidimensional approach. Metab Brain Dis 2004; 19:281–312.
Hassanein TI, Hilsabeck RC, Perry W. Introduction to the Hepatic Encephalopathy Scoring Algorithm (HESA). Dig Dis Sci 2008; 53:529–538
Guerit JM, Amantini A, Fischer C, Kaplan PW, Mecarelli O, Schnitzler A, et al. Neurophysiological investigations of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int 2009; 29:789–796.
Randolph C, Hilsabeck R, Kato A, Kharbanda P, Li YY, Mapelli D, et al. Neuropsychological assessment of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int 2009; 29:629–635.
Lauridsen MM, Jepsen P, Vilstrup H. Critical flicker frequency and continuous reaction times for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a comparative study of 154 patients with liver disease. Metab Brain Dis 2011; 26:135–139.
Bajaj JS, Pinkerton SD, Sanyal AJ, Heuman DM. Diagnosis and treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy to prevent motor vehicle accidents: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Hepatology 2012; 55:1164–1171
Bajaj JS, Gillevet PM, Patel NR, Ahluwalia V, Ridlon JM, Kettenmann B, et al. A longitudinal systems biology analysis of lactulose withdrawal in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2012; 27:205–215
Weissenborn K, Ennen JC, Schomerus H, Ruckert N, Hecker H. Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2001; 34:768–773
Prakash RK, Brown TA, Mullen KD. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy and driving: is the genie out of the bottle? Am J Gastroenterol 2011; 106:1415–1416
Bajaj JS, Stein AC, Dubinsky RM. What is driving the legal interest in hepatic encephalopathy? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 9:97–98
Dhiman RK, Saraswat VA, Verma M, Naik SR. Figure connection test: a universal test for assessment of mental state. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1995; 10:14–23
Kircheis G, Wettstein M, Timmermann L, Schnitzler A, Haussinger D. Critical flicker frequency for quantification of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2002; 35:357–366.
Romero-Gomez M, Cordoba J, Jover R, del Olmo JA, Ramirez M, Rey R, et al. Value of the critical flicker frequency in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2007; 45:879–885.
Lauridsen MM, Thiele M, Kimer N, Vilstrup H. The continuous reaction times method for diagnosing, grading, and monitoring minimal/covert hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2013; 28:231–234.
Bajaj JS, Hafeezullah M, Franco J, Varma RR, Hoffmann RG, Knox JF, et al. Inhibitory control test for the diagnosis
of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 2008; 135:1591–1600.
Bajaj JS, Thacker LR, Heumann DM, Fuchs M, Sterling RK, Sanyal AJ, et al. The Stroop smartphone application is a short and valid method to screen for minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2013; 58:1122–1132.
Amodio P, Del Piccolo F, Marchetti P, Angeli P, Iemmolo R, Caregaro L, et al. Clinical features and survival of cirrhotic patients with sub-clinical cognitive alterations detected by the number connection test and computerized psychometric tests. Hepatology 1999; 29:1662–1667
Victor M, Adams RD, Cole M. The acquired (non Wilsonian) type of chronic hepatocerebral degeneration. Medicine 1965; 44:345–396.
Montagnese S, Biancardi A, Schiff S, Carraro P, Carla V, Mannaioni G, et al. Different biochemical correlates for different neuropsychiatric abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2010; 53:558–566.
Lockwood AH. Blood ammonia levels and hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2004;19:345–349.
Kramer L, Tribl B, Gendo A, Zauner C, Schneider B, Ferenci P, et al. Partial pressure of ammonia versus ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2000; 31:30–34.
Drolz A, Jäger B, Wewalka M, Saxa R, Horvatits T, Roedl K, et al. Clinical impact of arterial ammonia levels in ICU patients with different liver diseases. Intensive Care Med 2013;39:1227–1237.
Huizenga JR, Gips CH, Conn HO, Jansen PL. Determination of ammonia in ear-lobe capillary blood is an alternative to arterial blood ammonia. Clin Chim Acta 1995; 239:65–70.
Bersagliere A, Raduazzo ID, Schiff S, Gatta A, Merkel C, Amodio P, et al. Ammonia-related changes in cerebral electrogenesis in healthy subjects and patients with cirrhosis. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013; 124:492–496.
Grønbaek H, Johnsen SP, Jepsen P, Gislum M, Vilstrup H, Tage-Jensen U, et al. Liver cirrhosis, other liver diseases, and risk of hospitalization for intracerebral haemorrhage: a Danish population-based case-control study. BMC Gastroenterol 2008; 8:16.
Sherlock S, Summerskill WH, White LP, Phear EA. Portal-systemic encephalopathy; neurological complications of liver disease. Lancet 1954; 267:454–457.
Montagnese S, Schiff S, Amodio P. A quick diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy: fact or fiction? Hepatology 2014; 9:405-406.
Córdoba J, Gottstein J, Blei AT. Chronic hyponatremia exacerbates ammonia-induced brain edema in rats after portacaval anastomosis. J Hepatol 1998; 29:589–594.
Montagnese S, Merkel C, Amodio P. Encephalopathy or hepatic encephalopathy? J Hepatol 2012;57:928–929.].
Rosenberg R, Renvillard SG, Hjerrild S. Organic delirious states and other psychiatric disorders: lessons for the hepatologists. Metab Brain Dis 2013; 28:235–238.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edition (DSM-IV). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
Reade MC, Finfer S. Sedation and delirium in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med 2014; 370:444–454.
Van den Boogaard M, Schoonhoven L, van Achterberg T, van der Hoeven JG, Pickkers P. Haloperidol prophylaxis in critically ill patients with a high risk for delirium. Crit Care 2013; 17:R9.
Van Eijk MM, van Marum RJ, Klijn IA, de Wit N, Kesecioglu J, Slooter AJ. Comparison of delirium assessment tools in a mixed intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 2009; 37:1881–1885.
Van den Boogaard M, Pickkers P, Slooter AJ, Kuiper MA, Spronk PE, van der Voort PH, et al. Development and validation of PRE-DELIRIC (PREdiction of DELIRium in ICu patients) delirium prediction model for intensive care patients: observational multicentre study. BMJ 2012; 344:e420.
Pisani MA, Kong SY, Kasl SV, Murphy TE, Araujo KL, Van Ness PH. Days of delirium are associated with 1-year mortality in an older intensive care unit population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009;180: 1092–1097.
Van den Boogaard M, Schoonhoven L, Evers AW, van der Hoeven JG, van Achterberg T, Pickkers P. Delirium in critically ill patients: impact on long-term health related quality of life and cognitive functioning. Crit Care Med 2012; 40:112–118.
Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 2002;35:716–721
Strauss E, Tramote R, Silva EP, Caly WR, Honain NZ, Maffei RA, et al. Double blind randomized clinical trial comparing neomycin and placebo in the treatment of exogenous hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatogastroenterology 1992; 39:542–545
Riordan SM, Williams R. Gut flora and hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1140–1142. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1000850
Gerber T, Schomerus H. Hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Drugs 2000; 60:1353–1370.
Als-Nielsen B, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Non-absorbable disaccharides for hepatic encephalopathy: systematic review of randomised trials. BMJ 2004; 328:1046.
Riggio O, Varriale M, Testore GP, Di Rosa R, Di Rosa E, Merli M, et al. Effect of lactitol and lactulose administration on the fecal flora in cirrhotic patients. J Clin Gastroenterol 1990; 12:433–436
Huang E, Esrailian E, Spiegel BM. The cost-effectiveness and budget impact of competing therapies in hepatic encephalopathy—a decision analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 26:1147–1161
Camma C, Fiorello F, Tine F, Marchesini G, Fabbri A, Pagliaro L. Lactitol in treatment of chronic hepatic
encephalopathy. A meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci 1993; 38:916–922.
Morgan MY, Hawley KE, Stambuk D. Lactitol vs. lactulose in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind, randomised, cross-over study. J Hepatol 1987; 4:236–244.
Gluud LL, Vilstrup H, Morgan MY. Non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention and lactulose versus lactitol for the prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016 ;4:CD003044. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003044.pub3
Uribe M, Berthier JM, Lewis H, Mata JM, Sierra JG, García-Ramos G, et al. Lactose enemas plus placebo tablets vs. neomycin tablets plus starch enemas in acute portal systemic encephalopathy. A double-blind randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology 1981; 81:101–106.
Uribe M, Campollo O, Vargas F, Ravelli GP, Mundo F, Zapata L, et al. Acidifying enemas (lactitol and lactose) vs. nonacidifying enemas (tap water) to treat acute portal-systemic encephalopathy: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Hepatology 1987; 7:639–643.
Rahimi RS, Singal AG, Cuthbert JA, Rockey DG. A randomized trial of polyethylene glycol 3350-electrolyte solution (PEG) and lactulose for patients hospitalized with acute hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2012; 56:915A–916A, [abstr. 1546]
Wijdicks EF. Hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2016; 375:1660–1670. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1600561.
Bajaj JS, Sanyal AJ, Bell D, Gilles H, Heuman DM. Predictors of the recurrence of hepatic encephalopathy in lactulose-treated patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010; 31:1012–1017.
Patidar KR, Bajaj JS. Antibiotics for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2013; 28:307–312.
Bass NM, Mullen KD, Sanyal A, Poordad F, Neff G, Leevy CB, et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:1071–1081.
Mullen KD, Sanyal AJ, Bass NM, Poordad FF, Sheikh MY, Frederick RT, et al. Rifaximin is safe and well tolerated for long-term maintenance of remission from overt hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 12:1390–1397.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.12.021
Landis CS, Ghabril M, Rustgi V, Di Bisceglie AM, Maliakkal B, Rockey DC, et al. Prospective multicenter observational study of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Dig Dis Sci 2016; 61:1728–1734. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4031-7.
Orr JG, Currie CJ, Berni E, Goel A, Moriarty KJ, Sinha A, et al. The impact on hospital resource utilisation of treatment of hepatic encephalopathy with rifaximin-a. Liver Int 2016; 36:1295–1303. doi: 10.1111/liv.13111.
Kabeshova A, Ben Hariz S, Tsakeu E, Benamouzig R, Launois R. Costeffectiveness analysis of rifaximin-a administration for the reduction of episodes of overt hepatic encephalopathy in recurrence compared with standard treatment in France. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2016; 9:473–482. doi:10.1177/1756283X16644249.
Kimer N, Krag A, Møller S, Bendtsen F, Gluud LL. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effects of rifaximin in hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014; 40:123–132. doi: 10.1111/apt.12803.
Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Lactulose, rifaximin or branched chain amino acids for hepatic encephalopathy: what is the evidence? Metab Brain Dis 2013; 28:221–225.
Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr 2013; 143:1263–1268.
Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Córdoba J, Marchesini G, Borre M, et al. Branchedchain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015; (9):CD001939. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001939.pub3.
Naylor CD, O’Rourke K, Detsky AS, Baker JP. Parenteral nutrition with branched-chain amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. A meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 1989; 97:1033–1042.
Ventura-Cots M, Arranz JA, Simo9n-Talero M, Torrens M, Blanco A, Riudor E, et al. Safety of ornithine phenylacetate in cirrhotic decompensated patients: an open-label, dose-escalating, singlecohort study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2013; 47:881–887.
Rahimi RS, Safadi R, Thabut D, Bajaj J, Bhamidimarri K, Pyrsopoulos N, Potthoff A and Bukofze S. "STOP-HE: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study of OCR-002 in Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy" AASLD 2017; Abstract 502.
Rockey DC, Vierling JM, Mantry P, Ghabril M, Brown Jr RS, Alexeeva O, et al. HALT-HE Study Group. Randomized, double-blind, controlled study of glycerol phenylbutyrate in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2014; 59:1073–1083
Leise MD, Poterucha JJ, Kamath PS, Kim WR. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in the hospital. Mayo Clin Proc 2014 ; 89:241–253.
Kircheis G, Nilius R, Held C, Berndt H, Buchner M, Gortelmeyer R, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate infusions in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy: results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Hepatology 1997; 25:1351–1360.
Bai M, Yang Z, Qi X, Fan D, Han G. l-ornithine-l-aspartate for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013; 28:783–792.
Agrawal A, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sarin SK. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: an open-label, randomized controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics, and no therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 2012; 107:1043–1050.
Patidar KR, Bajaj JS. Covert and overt hepatic encephalopathy: diagnosis and management. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13: 2048–2061.
Lunia MK, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sachdeva S, Srivastava S. Probiotics prevent hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 12:1003–1008.
Saab S, Suraweera D, Au J, Saab EG, Alper TS, Tong MJ. Probiotics are helpful in hepatic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Liver Int 2016; 36:986–993.
Conn, H. O., C.M. Leevy, Z.R Vlahcevic, J.B. Rodgers, W.C. Maddrey, L. Seeff, L.L. Levy. Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy. A double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology 1977; 72, 573-583.
Hawkins RA, Jessy J, Mans AM, Chedid A, DeJoseph MR. Neomycin reduces the intestinal production of ammonia from glutamine. Adv Exp Med Biol 1994; 368:125–134.
Morgan MH, Read AE, Speller DC. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy with metronidazole. Gut 1982; 23:1–7.
Goulenok C, Bernard B, Cadranel JF, Thabut D, Di Martino V, Opolon P, et al. Flumazenil vs. placebo in hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16:361–372.
Garcia-Martinez R, Caraceni P, Bernardi M, Gines P, Arroyo V, Jalan R. Albumin: pathophysiologic basis of its role in the treatment of cirrhosis and its complications. Hepatology 2013; 58:1836–1846.
Jalan R, Kapoor D. Reversal of diuretic-induced hepatic encephalopathy with infusion of albumin but not colloid. Clin Sci (Lond) 2004; 106: 467–474.
Simón-Talero M, García-Martínez R, Torrens M, Augustin S, Gómez S, Pereira G, et al. Effects of intravenous albumin in patients with cirrhosis and episodic hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized double-blind study. J Hepatol 2013;59:1184–1192.
Sen S, Davies NA, Mookerjee RP, Cheshire LM, Hodges SJ, Williams R, et al. Pathophysiological effects of albumin dialysis in acute-on-chronic liver failure: a randomized controlled study. Liver Transpl 2004; 10:1109–1119.
Hassanein TI, Tofteng F, Brown Jr RS, McGuire B, Lynch P, Mehta R, et al. Randomized controlled study of extracorporeal albumin dialysis for hepatic encephalopathy in advanced cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007; 46: 1853–1862.
Bañares R, Nevens F, Larsen FS, Jalan R, Albillos A, Dollinger M, et al. Extracorporeal albumin dialysis with the molecular adsorbent recirculating system in acute-on-chronic liver failure: the RELIEF trial. Hepatology 2013; 57:1153–1162.
Rahimi RS, Singal AG, Cuthbert JA, Rockey DC. Lactulose vs polyethylene glycol 3350–electrolyte solution for treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy: the HELP randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2014; 174: 1727–1733.
Jawaro T, Yang A, Dixit D, Bridgeman MB. Management of hepatic encephalopathy: a primer. Ann Pharmacother 2016; 50:569–577.
Amodio P, Bemeur C, Butterworth R, Cordoba J, Kata A, Montagnese S, et al. The nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: ISHEN practice guidelines. Hepatology 2013; 58:325–336.
Montano-Loza AJ, Meza-Junco J, Prado CM, Lieffers JR, Baracos VE, Bain VG,et al. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10:166–173.
Tandon P, Ney M, Irwin I, Ma MM, Gramlich L, Bain VG, et al. Severe muscle depletion in patients on the liver transplant wait list: its prevalence and independent prognostic value. Liver Transpl 2012; 18:1209–1216.
Tsien CD, McCullough AJ, Dasarathy S. Late evening snack: exploiting a period of anabolic opportunity in cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 27:430–441.
Plauth M, Cabre E, Riggio O, Assis-Camilo M, Pirlich M, Kondrup J, et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Liver disease. Clinl Nutr. 2006;25:285-94.
Mullen, K. D. & Dasarathy, S. Protein restriction in hepatic encephalopathy: necessary evil or illogical dogma? J. Hepatol. 2004; 41: 147-148.
Ndraha S, Hasan I, Simadibrata M. The effect of L-ornithine L-aspartate and branch chain amino acids on encephalopathy and nutritional status in liver cirrhosis with malnutrition. Acta Med Indones 2011; 43:18–22.
Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology 2003; 124:1792–1801.
Marchesini G, Marzocchi R, Noia M, Bianchi G. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in patients with liver diseases. J Nutr 2005; 135:1596S–1601S.
Muto, Y. , Sato S., Watanabe A., Moriwaki H., Suzuki K., Kato A., Kato M., Nakamura T., Higuchi K., Nishiguchi S., Kumada H., Long-Term Survival Study (LOTUS) Group. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin.Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005; 3:705-713.
Als-Nielsen, B., Koretz, R. L., Kjaergard, L. L. & Gluud, C. Branched-chain amino acids for hepatic ncephalopathy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, issue 1. Art. No.: CD001939.doi:10.1002/14651858. CD001939 (2003).
Amodio P., Caregaro L., Pettenó E., Marcon M., Del Piccolo F. and Gatta A. Vegetarian diets in hepatic encephalopathy: facts or fantasies? Dig. Liver Dis. 2001; 33: 492-500
Lynn AM, Singh S, Congly SE, Khemani D, Johnson DH, Wiesner RH, et al. Embolization of portosystemic shunts for treatment of medically refractory hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Transpl 2016; 22:723–731.
Laleman W, Simon-Talero M, Maleux G, Perez M, Ameloot K, Soriano G, et al. Embolization of large spontaneous
portosystemic shunts for refractory hepatic encephalopathy: a multicenter survey on safety and efficacy. Hepatology 2013; 57:2448–2457.
Naeshiro N, Kakizawa H, Aikata H, Kan H, Fujino H, Fukuhara T, et al. Percutaneous transvenous embolization for portosystemic shunts associated with encephalopathy: Long-term outcomes in 14 patients. Hepatol Res 2014; 44:740–749.
Zidi SH, Zanditenas D, Gelu-Siméon M, Rangheard AS, Valla DC, Vilgrain V, et al. Treatment of chronic portosystemic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients by embolization of portosystemic shunts. Liver Int 2007; 27:1389–1393.
Singh S, Kamath PS, Andrews JC, Leise MD. Embolization of spontaneous portosystemic shunts for management of severe persistent hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2014; 59:735–736.
Martin P, DiMartini A, Feng S, Brown Jr R, Fallon M. Evaluation for liver transplantation in adults: 2013 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the American Society of Transplantation. Hepatology 2014; 59:1144–1165.
Lucey MR, Terrault N, Ojo L, Hay JE, Neuberger J, Blumberg E, et al. Long-term management of the successful adult liver transplant: 2012 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the American Society of Transplantation. Liver Transpl 2013; 19:3–26
Herrero JI, Bilbao JI, Diaz ML, Alegre F, Inarrairaegui M, Pardo F, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy after liver transplantation in a patient with a normally functioning graft: treatment with embolization of portosystemic collaterals. Liver Transpl 2009; 15:111–114.
Campagna F, Montagnese S, Schiff S, Biancardi A, Mapelli D, Angeli P, et al. Cognitive impairment and electroencephalographic alterations before and after liver transplantation: what is reversible? Liver Transpl 2014; 20:977–986.
Chavarria L, Alonso J, García-Martínez R, Simón-Talero M, Ventura-Cots M, Ramírez C, et al. Brain magnetic resonance spectroscopy in episodic hepatic encephalopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013; 33:272–277.
Garcia-Martinez R, Rovira A, Alonso J, Jacas C, Simón-Talero M, Chavarria L, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with posttransplant cognitive function and brain volume. Liver Transpl 2011; 17:38–46.
Mechtcheriakov S, Graziadei IW, Mattedi M, Bodner T, Kugener A, Hinterhuber HH, et al. Incomplete improvement of visuo-motor deficits in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2004; 10:77–83.
Sotil EU, Gottstein J, Ayala E, Randolph C, Blei AT. Impact of preoperative overt hepatic encephalopathy on neurocognitive function after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2009; 15:184–192.
Lucero C, Verna EC. The role of sarcopenia and frailty in hepatic encephalopathy management. Clin Liver Dis 2015; 19:507–528 .
Lai JC, Rahimi R, Verna EC, et al. Frailty associated with waitlist mortality independent of ascites and hepatic encephalopathy in a multi-center study. Gastroenterology 2019, 156: 1675–1682
Ney M, Tangri N, Dobbs B, et al. Predicting hepatic encephalopathy-related hospitalizations using a composite assessment of cognitive impairment and frailty in 355 patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2018; 113: 1506–1515
Barritt AS 4th, Fried MW, Hayashi PH. Persistent portosystemic shunts after liver transplantation causing episodic hepatic encephalopathy. Dig Dis Sci 2010; 55:1794–1798.
Abujudeh HH, Samanta AK, Cho KC, Klein KM, Bahramipour P, Koneru B. Images in liver transplantation. Spontaneous portosystemic shunting several years following liver transplantation: successful treatment via percutaneous embolization. Liver Transpl 2004; 10:324–326.
Amodio P, Biancardi A, Montagnese S, Angeli P, Iannizzi P, Cillo U, et al. Neurological complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Dig Liver Dis 2007; 39:740–747.
Cortés-García, L. Papel de la nutrición en la encefalopatía hepática: es tiempo de cambiar. Nutr. clin. diet. Hosp. 2013; 33(2):89-97
Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2016. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2018; 67:1–77
Alsahhar J. S. and Rahimi R. S. Updates on the pathophysiology and therapeutic targets for hepatic encephalopathy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2019, 35:145–154
Angeli P., Bernardi M., Villanueva C. A., Francoz C., Mookerjee R. P., Trebicka J., Krag A., Laleman W. and Gines P. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatology 2018;. 69: 406–460
Morando F, Maresio G, Piano S, Fasolato S, Cavallin M, Romano A, et al. How to improve care in outpatients with cirrhosis and ascites: a new model of care coordination by consultant hepatologists. J Hepatol 2013; 59:257–264.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v74i2.513
IMÁGENES GEN
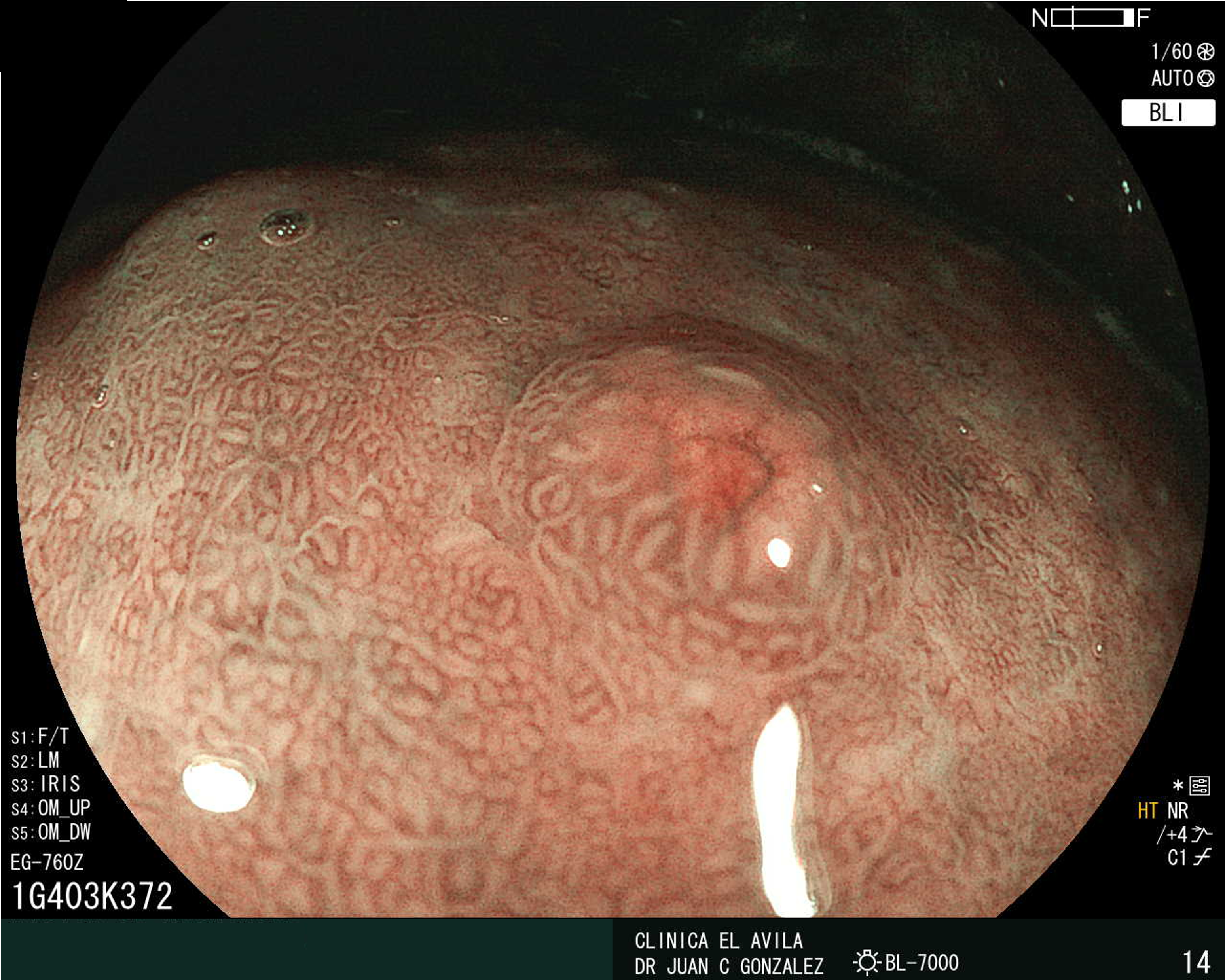
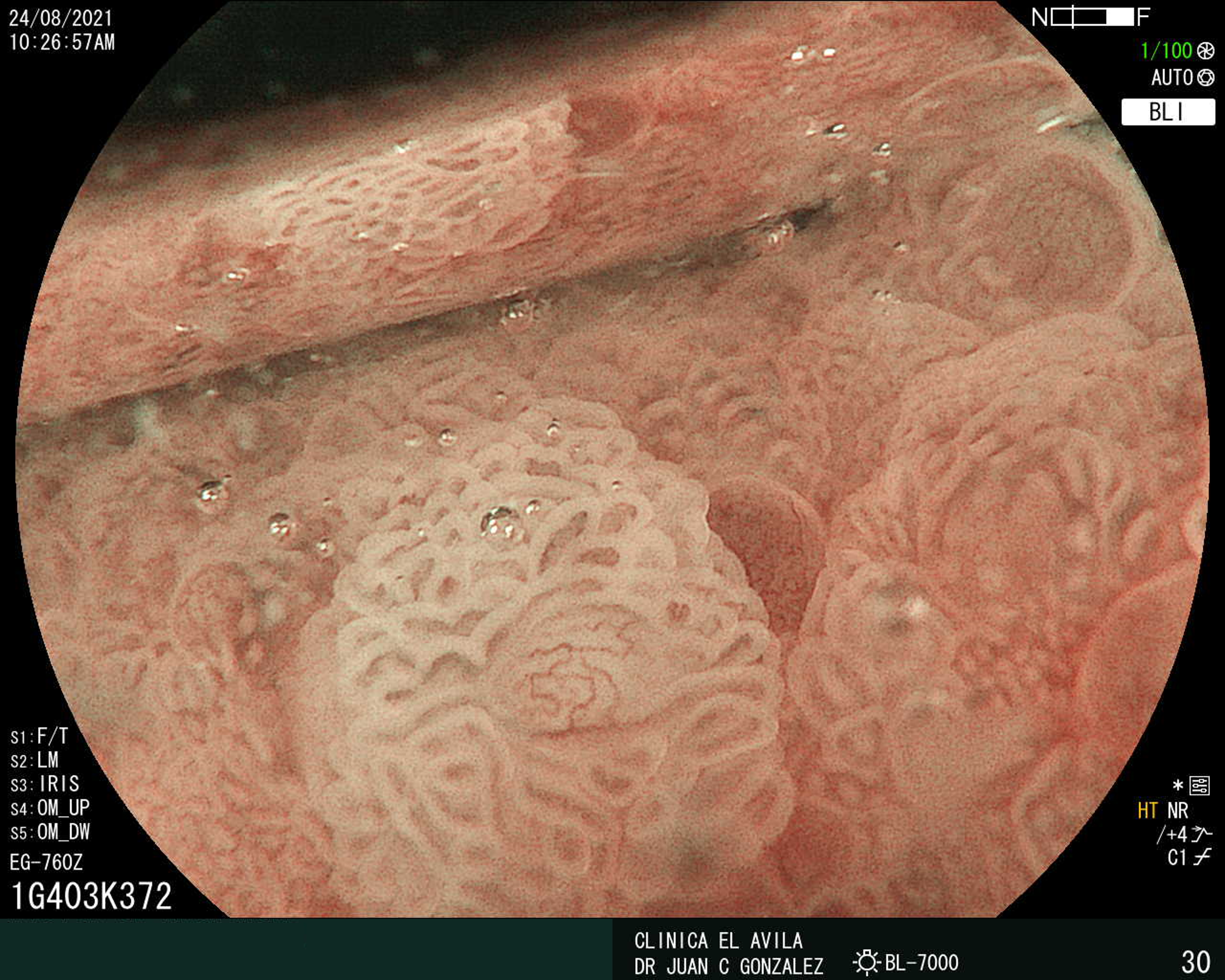
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X