Pautas para la pancreatitis aguda
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Quinlan JD. Acute pancreatitis. Médico Am Fam. 2014; 90: 632-639.
Parniczky A, Kui B, Czentesi A, Mosztbacher D, Szimmer J, et al. Prospective, multicentre, nationwide clinical data from 600 cases of acute pancreatitis. 2016; 11: 1-19.
Cerda, Luis. Análisis de las nuevas clasificaciones de la pancreatitis aguda. Cirujano General. 2013;35: Supl. 1.
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, et al. Classification of acute pan¬creatitis — 2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013; 62:102-11
Bakker OJ, van Santvoort HC, van Brunschot S, et al.: Endoscopic transgastric vs surgical necrosectomy for infected necrotizing pancreatitis: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2012; 307(10): 1053–61.
Van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, et al.: A step-up approach or opennecrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362(16):1491–502.
Dick JF, Gardner TB, Merrens EJ. Acute pancreatitis: New developments and strategies for the hospitalist. J Hosp Med. 2016; 11: 724-729.
Sarr MG. Revision of the Atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2013; 123: 118-124.
Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelinesa IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatol. 2013; 13: 1-15.
Surco Y, Mercado H, Pinto J, Piscoya. Predicción precoz de severidad en pancreatitis aguda. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2012; 32: 241-250.
Portelli M, Jones CD. Severe acute pancreatitis: Pathogenesis, diagnosis and surgical management. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017;16: 155-159.
Pérez Campos A, Paredes Bravo E, Prochazka Zarat R, Bussalleu A, Pinto Valdivia J, et al. BISAP-O y APACHE-O: Utilidad en lapredicción de severidad en la pancreatitis aguda según la clasificaciónmodificada de Atlanta. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2015; 35: 15-24.
Ledesma-Heyer JP, Arias Amara J. Pancreatitis aguda. Med Int Mex. 2009; 25: 285-294.
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1368–1377.
Srinivasan G, Venkatakrishnan L, Sambadam S, Singh G, Kaur M, et al. Current concepts in the management of acute pancreatitis.J Family Med Care Prim. 2016; 5: 752-758.
Abou-Assi S, O’Keefe SJD. Nutrition in acute pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001; 32:203-9.
Ckerwall GE, Tingstedt BB, Bergenzaun PE, et al. Immediate oral feeding in patients with mild acute pancreatitis is safe and may accelerate recovery — a randomized clinical study. Clin Nutr. 2007; 26:758-63.
Chang YS, Fu HQ, Xiao YM, et al. Nasogastric or nasojejunal feeding in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2013; 17:R118.
Al-Omran M, Albalawi ZH, Tashkandi MF, et al. Enteral versus paren¬teral nutrition for acute pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; (1):CD002837.
Crockett SD, Wani S,Gardner TB, et al.: American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis.Gastroenterology.2018; 154(4): 1096–101.
Brattström C, Malmborg AS, Tyden G. Penetration of imipenem into human pancreatic juice following single intravenous dose administra¬tion. Chemotherapy 1989; 35:83-7.
Tse F, Yuan Y: Early routine endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography strategy versus early conservative management strategy in acute gallstone pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; (5): CD009779.
Neoptolemos JP, Carr-Locke DL, London NJ, et al.: Controlled trial of urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic sphincterotomy versus conservative treatment for acute pancreatitis due to gallstones. Lancet.1988; 2 (8678): 979–83.
Van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, Hofker HS, et al. A step-up approach or open necrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 1491-1502 [PMID: 20410514 DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa0908821]
Seewald S, Groth S, Omar S, Imazu H, Seitz U, et al. Aggressive endoscopic therapy for pancreatic necrosis and pancreatic abscess: a new safe and effective treatment algorithm (videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 62: 92-100 [PMID: 15990825]
Ang TL, Kwek AB, Tan SS, Ibrahim S, Fock KM, Teo EK. Direct endoscopic necrosectomy: a minimally invasive endoscopic technique for the treatment of infected walled-off pancreatic necrosis and infected pseudocysts with solid debris. Singapore Med J 2013; 54: 206-211 [PMID: 23624447]
Van Brunschot S, van Grinsven J, van Santvoort HC, Bakker OJ, Besselink MG, Boermeester MA, et al. Endoscopic or surgical step-up approach for infected necrotising pancreatitis: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;391:51–8.
Gurusamy KS, Belgaumkar AP, Haswell A, Pereira SP, Davidson BR. Interventions for necrotising pancreatitis. Cochrane upper GI and pancreatic diseases group. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; 137:201–53.
Yadav D, O’Connell M, Papachristou GI. Natural history following the first attack of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2012; 107:1096–1103.
Van Baal MC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, et al. Timing of cholecystectomy after mild biliary pancreatitis: a systematic review. Ann Surg 2012; 255:860–866.
Leppäniemi et al. World Journal of Emergency Surgery. WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. 2019; 14 1-20
Mandalia A, Wamsteker E-J, DiMagno M. Recent advance in undertanding and managing acute pancreatitis. F1000 Research. 2019;975:1-20
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v73i3.489
IMÁGENES GEN
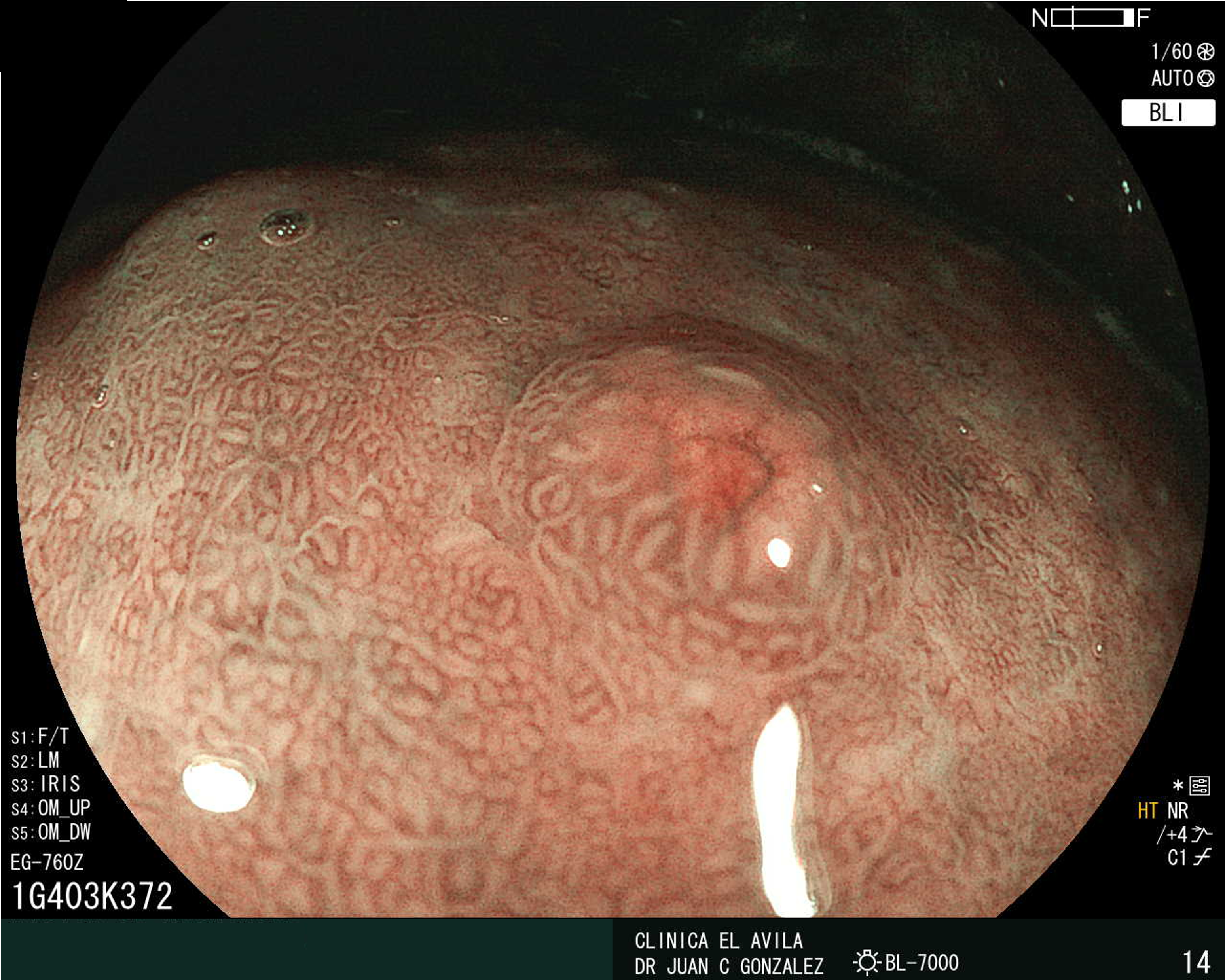
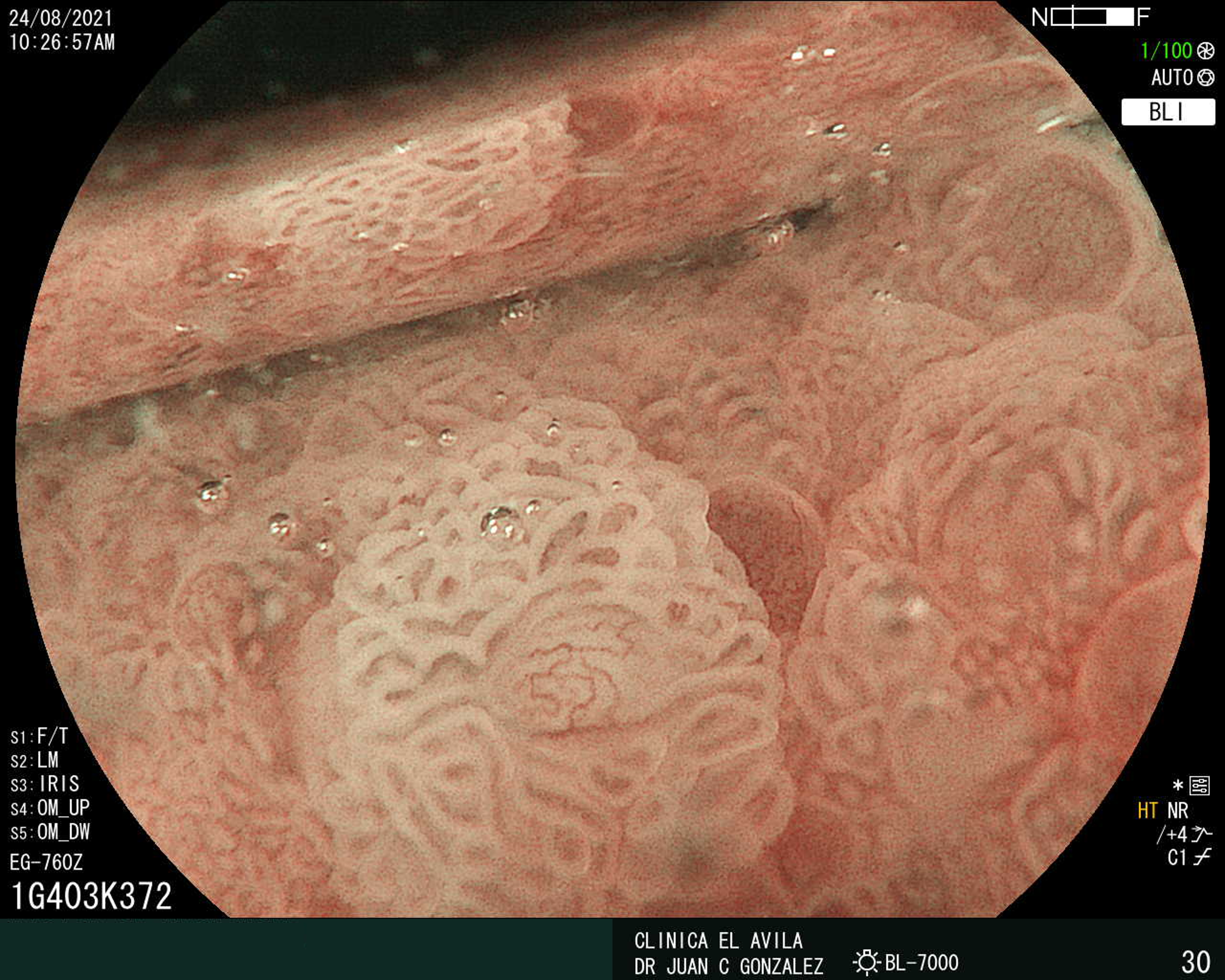
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X