Relación endoscópica entre duodenitis inespecífica y sobrecrecimiento bacteriano del intestino delgado
Resumen
Cuando aparece una proliferación de la flora de tipo colónico en el intestino delgado se producen alteraciones en la digestión y absorción intestinal, que clínicamente conforman el síndrome del Sobrecrecimiento Bacteriano del Intestino Delgado (SBID). En el SBID la concentración bacteriana aumenta hasta 107-109 UFC/ml en intestino delgado. El principio del test de hidrógeno espirado es la administración de un carbohidrato (Lactulosa, dxilosa, glucosa), que al ser degradado por las bacterias produce un aumento de los niveles de hidrógeno espirado en pacientes con SBID.
Hipótesis: Si la duodenitis inespecífica se manifiesta clínicamente de manera similar al (SBID) entonces puede haber una relación entre ambas patologías.
Métodos: Se realizó un estudio clínico descriptivo prospectivo de una muestra seleccionada quienes tuvieron como hallazgo en la endoscopia digestiva superior duodenitis inespecífica. Se usó Video endoscopio Olympus GIF-140, en dicha endoscopia se tomó biopsia del tejido duodenal con pinza. Posteriormente el paciente fue sometido a prueba de hidrógeno en aliento aire espirado con 10 gr de Lactulosa.
Resultados: La prueba de Hidrógeno en aliento resultó positiva en 18 pacientes (29,5%) y negativo en 43 (70,5%) (p=1,000). La sensibilidad fue de 29,6% y Especificidad 71% (IC 95%).
Conclusiones: 1) La prueba de Hidrógeno en aire espirado con Lactulosa es una prueba con poca sensibilidad pero específica para el Diagnóstico de SBID. 2) La prevalencia de duodenitis giardiásica fue del 11,5% en la población estudiada. 3) Los hallazgos histológicos referentes a las alteraciones de las vellosidades intestinales no están correlacionados con el SBID.
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Aparcero M. Duodenitis no específica: Revisión Endoscópica e Histológica. Gen 1992;46:1,49-55.
Bockus Gastroenterology. Fourth edition Berk J. 1985;2:1403.
Cotton P. Preliminary Evaluation of Duodenitis by Endoscopy and Biopsy. Br Med J. 1973;3:430.
Cheli R, Koch H, Marakta Z, Percic V, Shiner M: Limits of normality of the duodenal mucosa. Gut 1969;10:962.
Malagelada J R, Casellas F. Diarrhea due to bacterial overgrowth and motility disorders. Managment of Gastrointestinal disorders Edited by Sidney J. Winawer. Raven Press New York 1992:15,1-15.
Goldstein F, Wirts CW, Kowlessar OD. Diabetic diarrhea and steatorrhea. Microbiologic and clinic observations. Ann Intern Med 1970;72:215-218.
King CE, Toskes PP. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterology 1979;76:1035-1055.
Robert SH, James O, Jarvis EH. Bacterial overgrowth syndrome without "blind loop": a cause for malnutrition in the elderly. Lancet 1977;II:1193-1195.
Quera R, Quigley E, Madrid A M. Small intestinal Overgrowth, An Update. Rev Med Chile 2005;133:1361-1370.
Gasbarini A, Lauritano E, Gabrielli M, Scarpellini E, Lapascu A. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth: diagnosis and treatment. Dig Dis 2007;25:237- 240.
Singh V, Toskes Ph. Small Bowel Bacterial overgrowth: presentation, diagnosis and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2003; 5:365-372.
Gregg CR, Toskes PP. Enteric bacterial flora and small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome. In Sleisenger and Fordtran´s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. Edm 7. Edited By Feeldman Saunders Philadelphia 2002:1783- 1793.
Simon GL, Gorvach SL. The human intestinal microflora. Dig Dis Sci 1986;31:147-62.
Cebra JJ. Influences of microbiota on intestinal immune system development. Am J Cli Nutr 1999;69:1046S-51S.
Walker WA. Role of nutrients and bacterial colonization of intestinal host defense. J Paediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2000; 30: S2-7.
Bouknik Y, Alain S, Attar A, et al. Bacterial populations containing the upper gut in patients with small intestinal overgrowth syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:1327-1331.
Toskes PP. Bacterial overgrowth of the gastrointestinal tract. Adv Int Med 1993;38:387-407.
Bauer TM, Steinbruckner B, Brikmann FE, Ditzen AK, Schwacha II, et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with cirrhosis: prevalence and relation with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:2962-2967.
Kholoussy AM, Yang, Y, Bonacquisti K, Witkowski T, Takenaka K, et al. The competence and bacteriologic effect of the telescoped intestinal valve after small bowel resection. Am Surg 1986;52:555-559.
Riordan SM, Mc Iver CJ, Wakefielf D, Bolin TD, Duncombe et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in the symptomatic elderly. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92:47-51.
Mcevoy A, Dutton J, James OF. Bacterial contamination of the small intestine is an important cause of occult malabsorption in the elderly. BMJ 1983;287:789-793.
Kirch M. Bacterial Overgrowth. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990; 85:231-237.
Wolters M, Sthrole A, Hann A. Cobalamin: a critical vitamin in the elderly. Prev Med 2004;39:1256-1266.
Shindo K, Machida M, Koide K, Fukumura M, Yamezaki R. Deconjugation ability of bacteria isolated from the jejunal fluid patient with progresive systemic sclerosisand its gastric pH. Hepatogastroenterology 1998;45:1643-1650.
Toskes PP, Giannella RA, Jervis HR, Rout WR, Takeuchi A. Small intestinal mucosa injury in the experimental blind loop syndrome. Lights and electron microscopic and histochemical studies. Gastroenterology 1975;68:193-203.
Riordan SM, Mc Iver CJ, Wakefielf D, Bolin TD, Duncombe et al. Mucosal cytokine production in small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Scand J Gastroenterol 1996;31:977-984.
Riordan SM, Mc Iver CJ, Wakefielf D, Bolin TD, et al. Serum immunoglobulin and soluble IL-2 receptors level in small intestinal bacterial overgrowth with indigenous gut flora. Dig Dis Sci 1999; 44:939-944.
Kett K, Baklien K, et al. Intestinal B-cel isotype response in relation to local bacterial load: evidence for immunoglobulin A subclass adaptation. Gastroenterology 1995;109:819-825.
De Boissieu D, Chaussain M, Badoval J, Raymond J, Dupont C. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth in children with chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain or both. J Pediatr 1996;128:203-207.
Kuman A, Forsmark C, Toskes P. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth, the changing face of and old disease. Gastroenterology 1996;110:340.
Di Stephano, Veneto G, Malservisi S, Corazza GR. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth and metabolic bone disease. Dig Dis Sci 2001;46:1077-1082.
Giannella RA, Torkes P. Gastrointestinal bleeding and iron absorption in the experimental blind loop syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 1976;29:754- 757.
Saltzman JR, Kowdley KV, Pedrosa MC, Sepe T, Golner B, et al. Bacterial overgrowth without clinical malabsorption in elderly hypochlorhydric subjects. Gastroenterology 1994;106:615-623.
Corazza GR, Menozzi MG, Strocchi A, Rasciti L, et al. The diagnosis of small bowel bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterology 1990;98:302-309.
Romagnould J, Dan Schiller MSC, Bailey R. Using breath test wisely in a gastroenterology practice: an evidence based review of indications and pitfalls in interpretation. Am J Gastroenterology 2002;97:1113-1126.
Stozter PO, Kilander AF. Comparation of 1 gram (14)C-DXylose breath test and the 50 mg hydrogen glucose breath test for the diagnosis of small intestinal overgrowth. Digestion 2000; 61:165-171.
Riordan SM, Mc Iver CJ, Duncombe V, et al. Factors influencing the 1 gram 14C-D Xylose breath test for bacterial overgrowth. Am J Gastroenterology 1995;90:1455-1460.
Valdovinos M, Camilieri M, Thomforde G, et al. Reduced accuracy of 14C-D-Xylose breath test for detecting bacterial overgrowth in gastrointestinal motility disorders. Scand J Gastroenterology 1993;28:963-968.
Wigg AJ, Roberts-Thompson IC, Dymock RB, Mc Carthy PJ, Grose RH, et al. Role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, intestinal permeability, endotoxaemia, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. Gut 2001;48:206-211.
Pimentel M, Chow EJ, Lin HC. Normalization of lactulosa breath testing correlates with symptoms improvement in irritable bowel syndrome: a doble-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. Am J Gastroenterology 2003; 98:412-419.
Attar A, Flourie B, Rambaud JC, Franchisseur C, et al. Antibiotic efficacy in small intestinal bacterial overgrowth-related diarrhea: a crossover randomized trial. Gastroenterology 1999; 117:794-797.
Madrid AM, Hurtado C, Venegas M, Cumsille E, Defillipi C. Longterm treatment with cisapride and antibiotics in liver cirrhosis: the effects of small intestinal overgrowth, and liver function. Am J Gastroenterology 2001;96:1251-1255.
Dos Reis JC, De Morais MB, García Oliva CA, Fagundes-Neto U. Breath Hydrogen Test in the Diagnosis of Environmental Enteropathy in Childrem Living in an Urban Slum. Dig Dis Sci 2007;52:1253-1258.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v65i3.290
IMÁGENES GEN
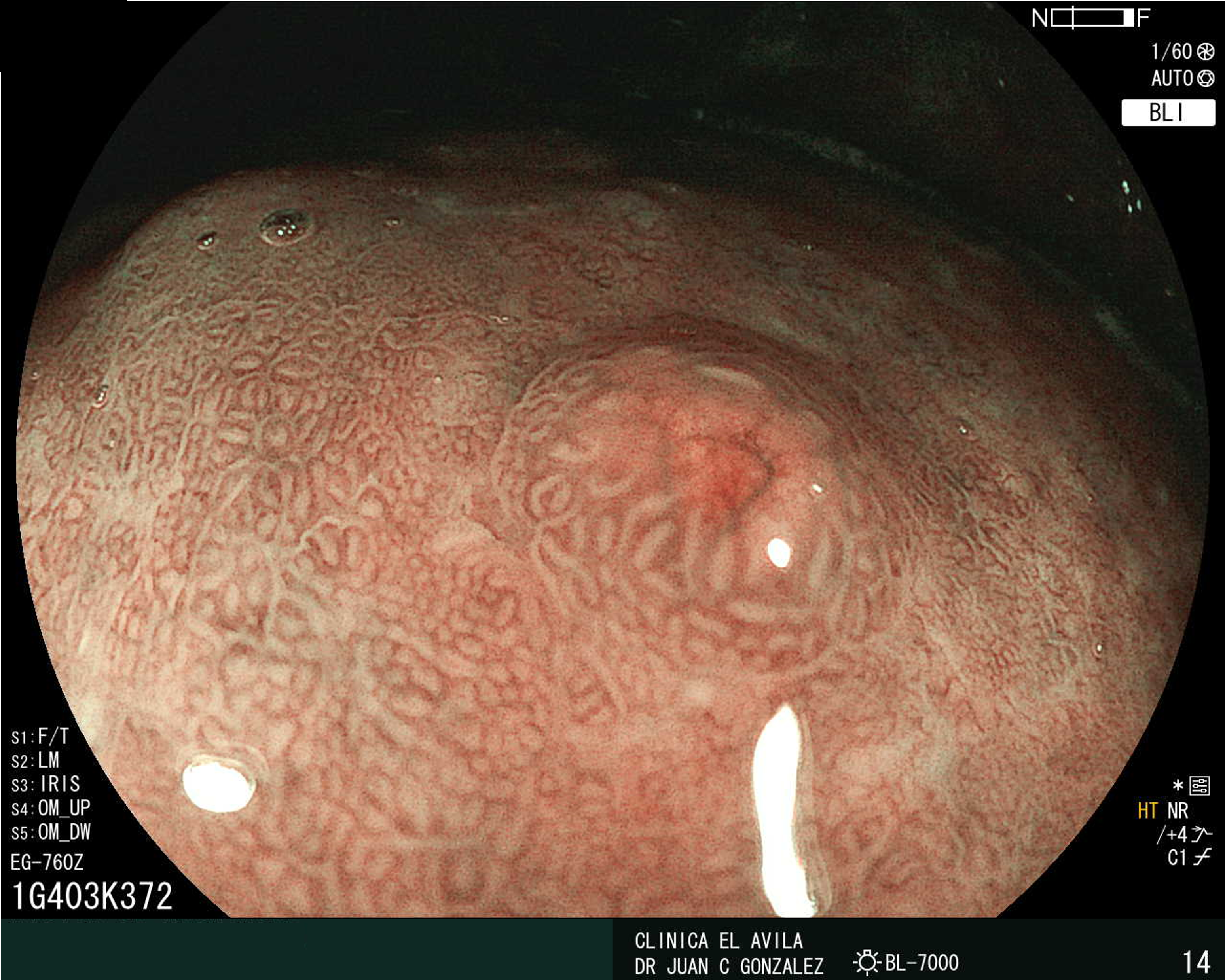
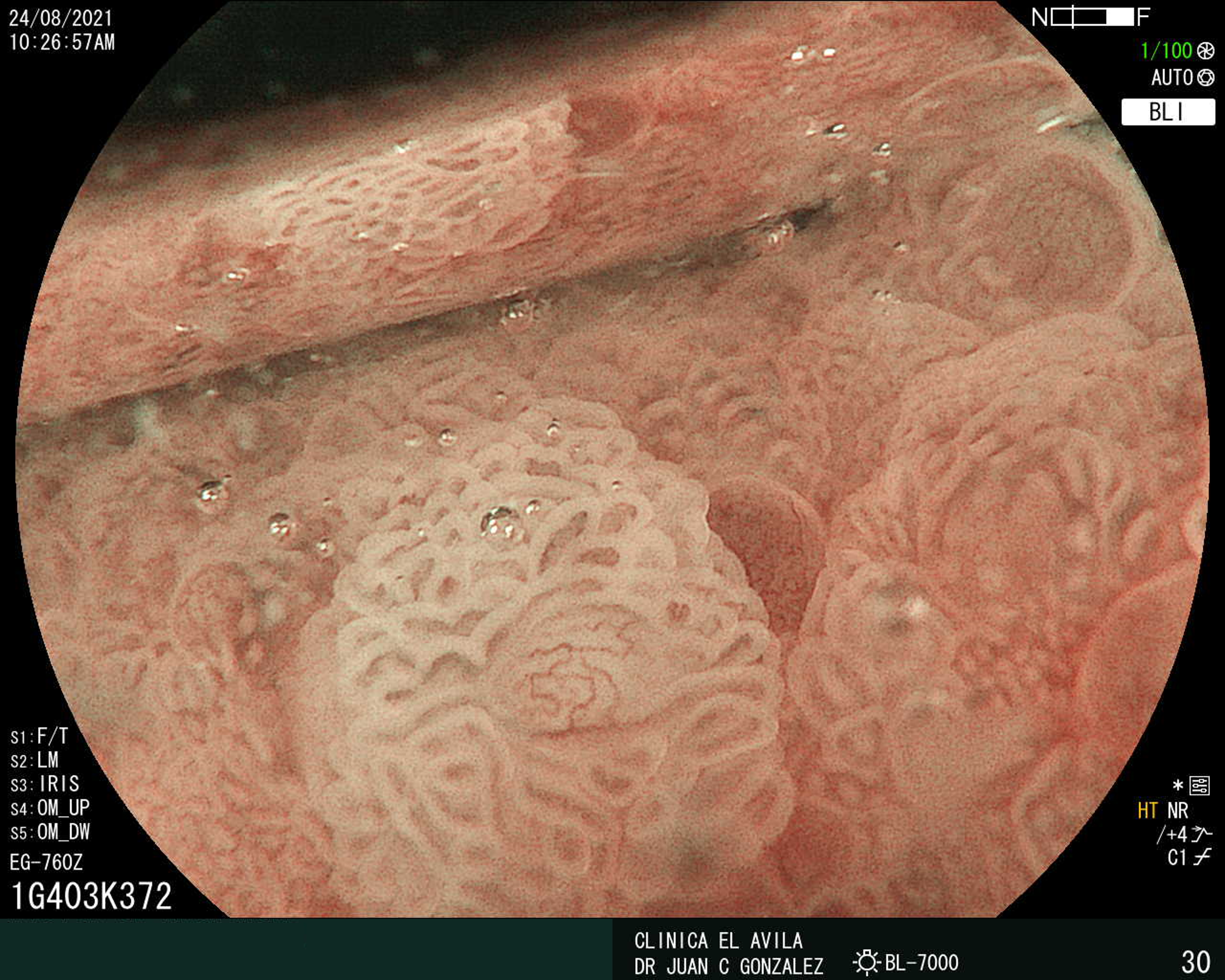
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X