Pruebas diagnósticas en la enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Carlsson R, Dent J, Bolling-Sternevald E, et al. The usefulness of a structured questionnaire in the assessment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 1998; 33:1023-9.
Jones R y cols. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009;30:1030-1038.
Gomez-Escudero O, Remes-Troche JM, Ruiz JC, Pelaez-Luna M, Schmulson MJ, Valdovinos Diaz MA. Diagnostic usefulness of the Carlsson-Dent questionnaire in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2004;69(1):16-23.
Lundell L, Backman L, Ekström P, et al. Omeprazole or high dose of ranitidine in the treatment of patients with reflux esophagitis not responding to standard doses of H2-receptor antagonist. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1990;4:145-55.
Schenk BE, Kuipers EJ, Klinkenberg-Knol EC, et al. Omeprazole as a diagnostic tool in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92:1997-2000.
Fass R, Ofman JJ, Gralnek IM, et al. Clinical and economic assessment of the omeprazole test in patients with symptoms suggestive of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Intern Med 1999; 159:2161-68.
Neville PM, Moayyedi P, Edwards A. Response to pantoprazole is an effective diagnostic test for gastroesophageal reflux disease: results of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study (abstract). Gastroenterology 1998; 114 (suppl): A242.
Remes-Troche JM, Carmona-Sánchez R, Soto Pérez J, González M, Icaza ME, Valdovinos-Díaz MA. Diagnóstico de las diferentes variedades de la enfermedad por reflujo no erosiva (ERNE) mediante pHmetría y prueba de rabeprazol. Estudio Multicéntrico Nacional. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 2005.
Dent J, Brun J, Fendrick AM, et al. An evidence based appraisal of reflux disease management The Genval Workshop report. GUT 1999;44:S1-S6.
Uscanga L, Nogueira JR, Gallardo E y cols. Enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico. Resultados del consenso del Grupo Mexicano para el Estudio de la ERGE. Asociación Mexicana de Gastroenterología. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 2002, Vol. 67, Núm. 3. 215-22.
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. GUT 1999;45:172-80.
Sharma P. Gastroenterology 2007; 133: 454–464.
Lind T, Havelund T, Carlsson R, et al. Heartburn without oesophagitis: efficacy of omeprazole therapy and features determining therapeutic response. Scand J Gastroenterol 1997;32: 974-9.
Fass R, Fennerty MB, Vakil N. Nonerosive reflux disease current concepts and dilemmas. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96(2): 303-14.
DeMeester TR, Wang C-I, Wernly JA, et al. Technique, indications and clinical use of 24-hour esophageal pH monitoring. J Thorac CArdiovasc Surg 1980;79:656-70.
Galmiche JP, Clouse RE, Bálint A. et al. Functional esophageal disorders. In: Drosssman DA, Corazziari E, Spiller RC, Thompson WG, Delvaux M, Talley NJ, Whitehead W. Rome II: The functional gastrointestinal disorders., 3rd edition, Lawrence KS: Allen Press 2006: 369-418.
Teramoto Matsubara O. utilización de un sistema inalámbrico para medición del ph esofágico ¿es realmente necesario?. Rev Mex Cir Endoscop 2004;5(3):127-130.
Carmona-Sanchez R, Solana-Senties S. Efficacy, diagnostic utility and tolerance of intraesophageal pH ambulatory determination with wireless pH-testing monitoring system. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2004;69(2):69-75.
Valdovinos Diaz MA, Remes Troche JM, Ruiz Aguilar JC, Schmulson MJ, Valdovinos-Andraca F. Successful esophageal pH monitoring with Bravo capsule in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2004;69(2):62-.
Remes-Troche JM, Ibarra-palomino J, Carmona-Sánchez RI, Valdovinos-Díaz MA. Performance, tolerability and symptoms related to prolonged pH monitoring using the Bravo system in Mexico. Am J Gastroenterol 2005 (In press).
Sifrim D, Castell D, Dent J, Kahrilas PJ. Gastro-oesophageal reflux monitoring: review and consensus report on detection and definitions of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut 2004;53:1024-1031.
Vela MF, Camacho-Lobato L, Srinivasan R, Tutuian R, Katz PO, Castell DO. Intraesophageal Impedance and pH measurement of acid and non-acid reflux: effect of omeprazole. Gastroenterology 2001;120:1599-1606.
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Shay S, Vela M, Zhang X, Sifrim D, Castell DO. Acid and non-acid reflux in patients with persistent symptoms despite acid suppressive therapy: a multicenter study using combined ambulatory impedance-pH monitoring. Gut 2006;55:1398-1402.
AGA Technical review on the clinical use of esophageal manometry. Gastroenterology 2005;128:209-24.
Murray JA, Clouse RE, Conklin JL. Components of the standard oesophageal manometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2003; 15:591-606.
Sifrim D, Blondeau K. New techniques to evaluate esophageal function. Dig Dis. 2006;24:243-51.
Dogan I, Mittal RK. Esophageal motor disorders: recent advances. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2006;22:417-22.
Pandolfino JE, Kim H, Gosh SK, Clarke JO, Zhank Q, Kahrilas PJ. High-resolution manometry of the EGJ: an analysis of crural diaphragm function in GERD. Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102:1056-63.
Tobey NA, Carson JL, Alkiek RA, Orlando RC. Dilated intercellular spacies: a morphological feature of acid-refluxed damaged human esophageal epithelium. Gastroenterology 1996;111:1200-1205.
Calabrese C, Fabbri A, Bortolotti M, et al. Dilated intercellular spacies as a marker of esophageal damage: comparative results in gastroesophageal reflux disease with or without bile reflux. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003;18:525-32.
Vela MF, Craft BM, Sharma N, et al. Intercellular space distance is increased in refractory heartburn patients with positive symptom index regardless of whether symptoms are caused by acid or nonacid reflux: A study using impedance-pH and electron microscopy. Gastroenterology 2009; 136 (Suppl 1): A426.
Remes-Troche JM. The hypersensitive esophagus: pathophysiology, evaluation, and treatment options. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2010;12(5):417-26.
Fass R. Sensory testing of the esophagus. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38:628-41.
Remes-Troche JM, Maher J, Mudipalli R, Rao SS. Altered esophageal sensory-motor function in patients with persistent symptoms after Nissen fundoplication. Am J Surg 2007;193:200-5.
Drewes AM, Gregersen H. Multimodal pain stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:2477-86.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v67i4.172
IMÁGENES GEN
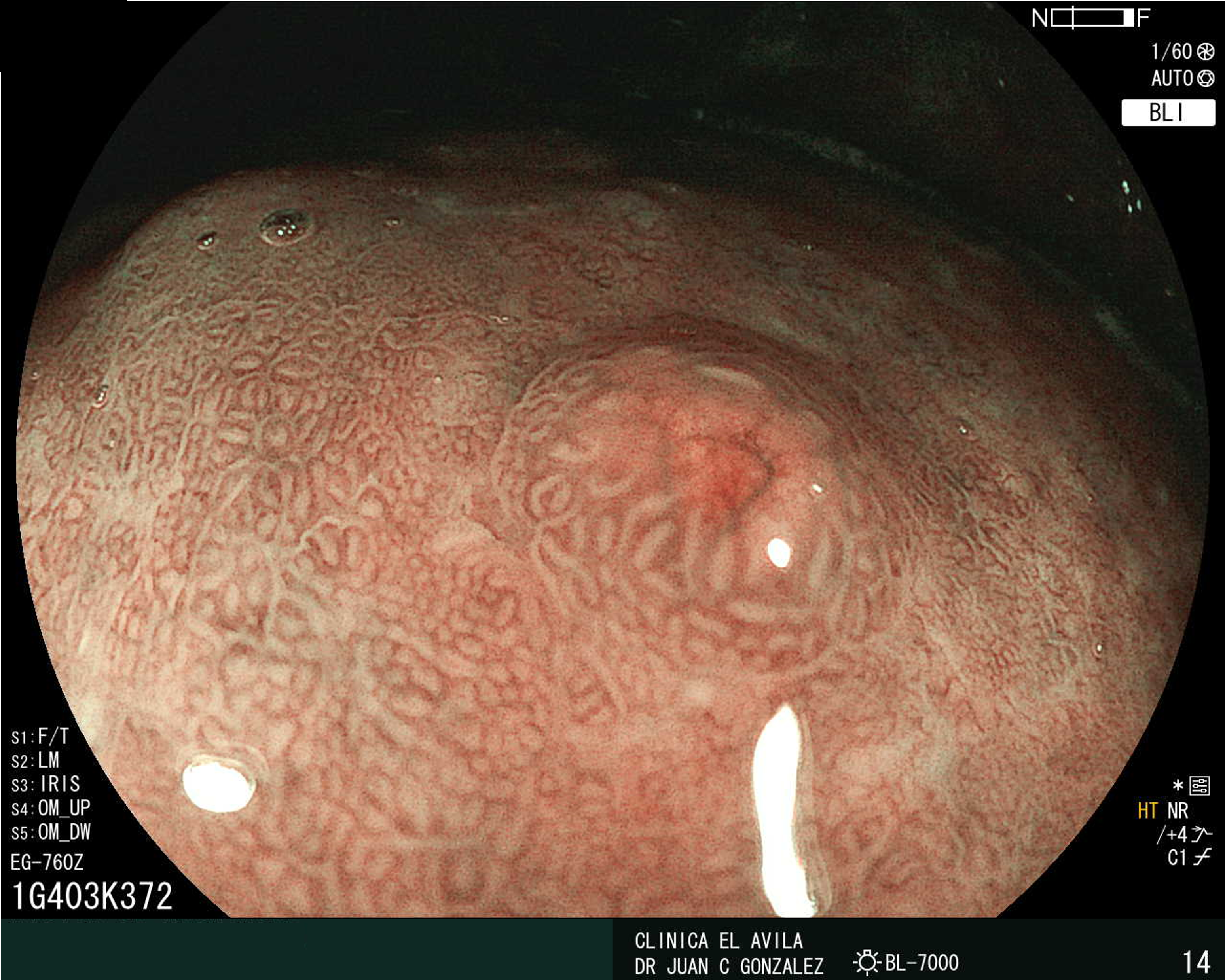
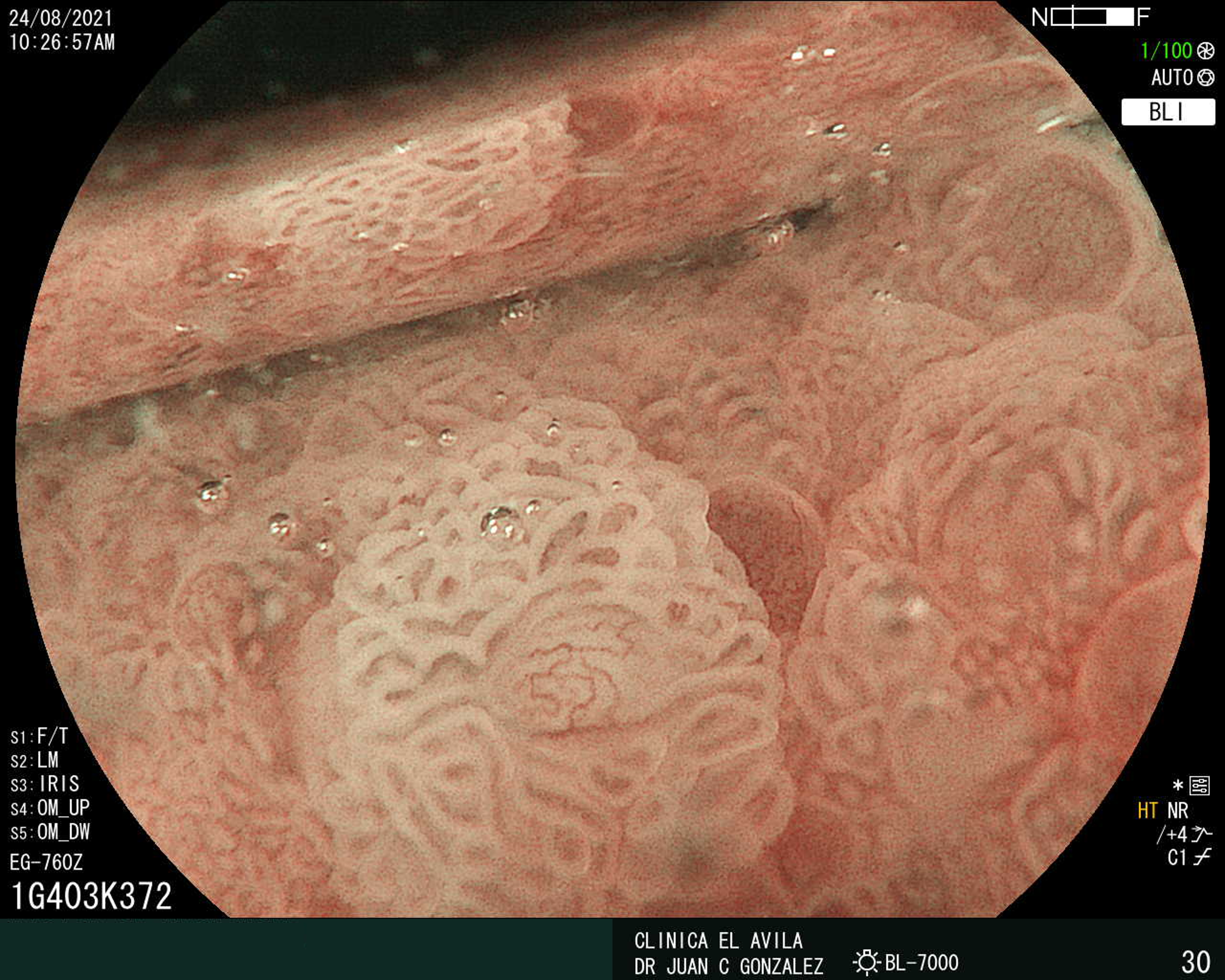
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X