Esófago de Barrett
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Sánchez Fayos P, Martín MJ, González A, et al. El esófago de Barrett: La realidad biológica de una metaplasia columnar premaligna. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002;25:254-266.
Raj A, Jankowski J. Acid suppression and chemoprevention in Barrett oesophagus. Dig Dis 2004;22:171-180.
Winters C, Spurling TJ, Chobanian SJ, et al. Barretts esophagus. A prevalent, occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 1987;92:118-124.
Cameron AJ. Epidemiology of Barretts esophagus and adenocarcinoma. Dis Esoph 2002;15:106-108.
Raj A, Jankowski J. Acid suppression and chemoprevention in Barrett oesophagus. Dig Dis 2004;22:171-180.
Dahms RB, Rothstein FC. Barrett´s esophagus in children: a consequence of chronic gastroeophageal reflux. Gastroenterology 1984;86:318-323.
Borrie J, Golwater L. Columnar cell-lined esophagus: assessment of etiology and treatment. A 22 years experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1976;71:825-834.
Henihan RD, Stuart RC, Nolan N, et al. Barretts esophagus and the presence of Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:542-546.
Malfertheiner P, Lind T, Willich S, et al. Prognostic influence of Barretts oesophagus and Helicobacter pylori infection on healing of erosive gastro-oesophageal (GORD) and symptom resolution in non-erosive GORD: report from the ProGORD Study. Gut 2005; 54:746-751.
Salo J, Kivilaaskso E, Virtanen I. Barretts esophagus originates from squamous esophageal epithelium as judged from its cytokeratin profile. Gastroenterology 1991;100:153A.
Polepalle SC, McCallum RW. Barretts esophagus. Current assessment and future perspectives. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1990;19:733-744.
Parrilla P, Liron R, Martínez de Haro LF, et al. Gastric surgery does nor increase the risk of developing Barrett´s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92:960-963.
Nicolás González,1 Adolfo Parra-Blanco,2 Henry Cohen. Esófago de Barrett. Acta Gastroenterológica Latinoamericana - Vol 42/Nº 4/Diciembre 2012.
Anderson LA, Murphy SJ, Johnston BT, et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric atrophy and the stages of the oesophageal inflammation, metaplasia, adenocarcinoma sequence: results from the FINBAR casecontrol study. Gut 2008;57:734-739.
Spechler SJ. Clinical practice. Barretts Esophagus. N Engl J Med 2002;346:836-842.
Wong DJ, Paulson TG, Prevo LJ, et al. p16 (INK4a) lesions are common, early abnormalities that undergo clonal expansion in Barretts metaplastic epithelium. Cancer Res 2001;61:8284-8289.
Spechler SJ, Robbins AH, Rubins HB, et al. Adenocarcinoma and Barretts esophagus. An overrated risk? Gastroenterology 1984;87:927-933.
Locke GR, Talley NJ, Fett SL, et al. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology 1997;112:1448-1456.
Fitzgerald RC, Triadafilopoulos G. Recent developments in the molecular characterization of Barretts esophagus. Dig Dis 1998; 16:63-80.
Rastogi A, Puli S, El-Serag HB, et al. Incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma in patients with Barretts esophagus and high-grade dysplasia: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 67: 394-398.
Spechler SJ. Managing Barretts oesophagus. BMJ 2003; 326:892-894.
Sampliner RE. Updated guidelines for the diagnosis, surveillance, and therapy of Barretts esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:1888-1895.
Prateek S. The current approach to Barretts esophagus and dysplasia. WGN 2006;11:10-11.
Sharma P, Dent J, Fennerty MB, et al. critical review of the diagnosis and management of Barretts esophagus: The AGA Chicago Workshop. Gastroenterology 2004;127:310-330.
Peuchmaur M, Potet F, Goldfain D. Mucin histochemistry of the columnar epithelium of the esophagus (Barretts esophagus): a prospective study. J Clin Pathol 1984;37:607-610.
Canto MI. Staining in gastrointestinal endoscopy: the basics. Endoscopy 1999;31:479-486.
Rezende L, Parra-Blanco A. Utilidad de la cromoendoscopía como método auxiliar de la colonoscopía. Gastr Latinoam 2005;16:192-204.
Curvers WL, Bansal A, Sharma P, Bergman JJ. Endoscopic work-up of early Barretts neoplasia. Endoscopy 2008;40:1000-1007.
Pohl J, May A, Rabenstein T, et al. Comparison of computed virtual chromoendoscopy and conventional chromoendoscopy with acetic acid for detection of neoplasia in Barretts esophagus. Endoscopy 2007;39:594-598.
Canto MI, Setrakian S, Willis J, et al. Methylene-blue directed biopsies improve detection of intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia in Barretts esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2000;51:560-568.
Ngamruengphong S, Sharma VK, Das A. Diagnostic yield of methylene blue chromoendoscopy for detecting specialized intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia in Barretts esophagus: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;69:1021-1028.
Shailender S, Prateek S. Magnifying endoscopy in upper GI tract and lower GI tract. Digest Endosc 2005;17(suppl):S17-S19.
Kara MA, Peters FP, Rosmolen WD, et al. High-resolution endoscopy plus chromoendoscopy or narrow-band imaging in Barretts esophagus: a prospective randomized crossover study. Endoscopy 2005;37:929-936.
Vázquez-Iglesias JL, Alonso-Aguirre P, Diz-Lois MT, et al. Acetic acidallows effective selection of areas for obtaining biopsy samples in Barretts esophagus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;19:187-193.
Yamamoto H, Sekine Y, Higashizawa T, et al. Successful en bloc resection of a large superficial gastric cancer by using sodium hyaluronate and electrocautery incision forceps. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;54:629-632.
Curvers WL, Singh R, Song LM, et al. Endoscopic tri-modal imaging for detection of early neoplasia in Barretts oesophagus: a multi-center feasibility study using high-resolution endoscopy, autofluorescence imaging and narrow band imaging incorporated in one endoscopy system. Gut 2008;57:167-172.
Ouatu-Lascar R, Triadafilopoulos G. Complete elimination of reflux symptoms does not guarantee normalization of intraesophageal acid reflux in patients with Barretts esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:711-716.
Breumelhof R, Smout AJ. The symptom sensitivity index: a valuable additional parameter in 24-hour esophageal pH recording. Am J Gastroenterol 1991;86:160-164.
Fennerty MB. Endoscopic suturing for treatment of GERD. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;57:390-395.
Mahmood Z, McMahon BP, Arfin Q, et al. Endocinch therapy for gastrooesophageal reflux disease: a one year prospective follow up. Gut 2003;52:34-39.
Chen YK, Raijman I, Ben-Menachem T, et al. Long-term outcomes of endoluminal gastroplication: a U.S. multicenter trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2005;61:659-667.
Arts J, Lerut T, Rutgeerts P, et al. A one-year follow-up study of endoluminal gastroplication (Endocinch) in GERD patients refractory to proton pump inhibitor therapy. Dig Dis Sci 2005;50: 351-356.
McDonald ML, Trastek VF, Allen MS, et al. Barrett´s esophagus: does and antireflux procedure reduce the need for endoscopic surveillance?. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1996;111:1135-1140.
Katz PO, Anderson C, Khoury R, Castell DO. Gastrooesophageal reflux associated with nocturnal gastric acid breakthrough on proton pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1998;12:1231-1234.
McDonald ML, Trastek VF, Allen MS, et al. Barrett´s esophagus: does and antireflux procedure reduce the need for endoscopic surveillance?. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1996;111:1135-1140.
Sagar PM, Ackroyd R, Hosie KB, et al. Regression and progression of Barrett´s esophagus after antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 1995;82:806-810.
Gossner L, May A, Stolte M, Seitz G, Hahn EG, Ell C. KTP laser destruction of dysplasia and early cancer in colunnarlined Barrett´s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc 1999;49:8-12.
Ye W, Chow WH, Lagergren J, Yin L, Nyrén O. Risk of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and after antireflux surgery. Gastroenterology 2001;121:1286-1293.
Sikkema M, Kerkhof M, Steyerberg EW, et al. Aneuploidy and overexpression of Ki67 and p53 as markers for neoplastic progression in Barretts esophagus: a case-control study. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:2673-2680.
Peters FP, Kara MA, Curvers WL, et al. Multiband mucosectomy for endoscopic resection of Barretts esophagus: feasibility study with matched historical controls. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;19:311-315.
Miyamoto S, Muto M, Hamamoto Y, et al. A new technique for endoscopic mucosal resection with an insulated-tip electrosurgical knife improves the completeness of resection of intramucosal gastric neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;55:576-581.
Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Boku N, Ohtu A, Tajiri H, Yoshida S. New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy 2001;33:221-226.
Schnell TG, Sontag SJ, Chejfec G, et al. Long term nonsurgical management of Barrets esophagus with high-grade dysplasia. Gastroenterology 2001;120:1607-1619.
Gossner L, Stolte M, Sroka R, Hahn EG, Ell C, et al. Photodynamic therapy of high-grade dysplasia and early stage carcinomas by means of 5-aminolaevulinic acid. Gastroenterology 1998;22:239-245.
González M, De Ascencao M. Síndrome de intestino irritable. Aspectos psicológicos. Revista de la facultad de medicina de la Universidad Central de Venezuela 2005; 28(2): 139-145
Ackroyd R, Brown NJ, Davis MF, et al. Photodynamic therapy for dysplastic Barretts oesophagus: a prospective, double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial. Gut 2000;47:612-617.
Ganz RA, Utley DS, Stern RA, et al. Complete ablation of esophageal epithelium with a balloon-based bipolar electrode: a phased evaluation in the porcine and in the human esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;60:1002-1010.
Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barretts esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med 2009;360:2277-2288.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v67i1.119
IMÁGENES GEN
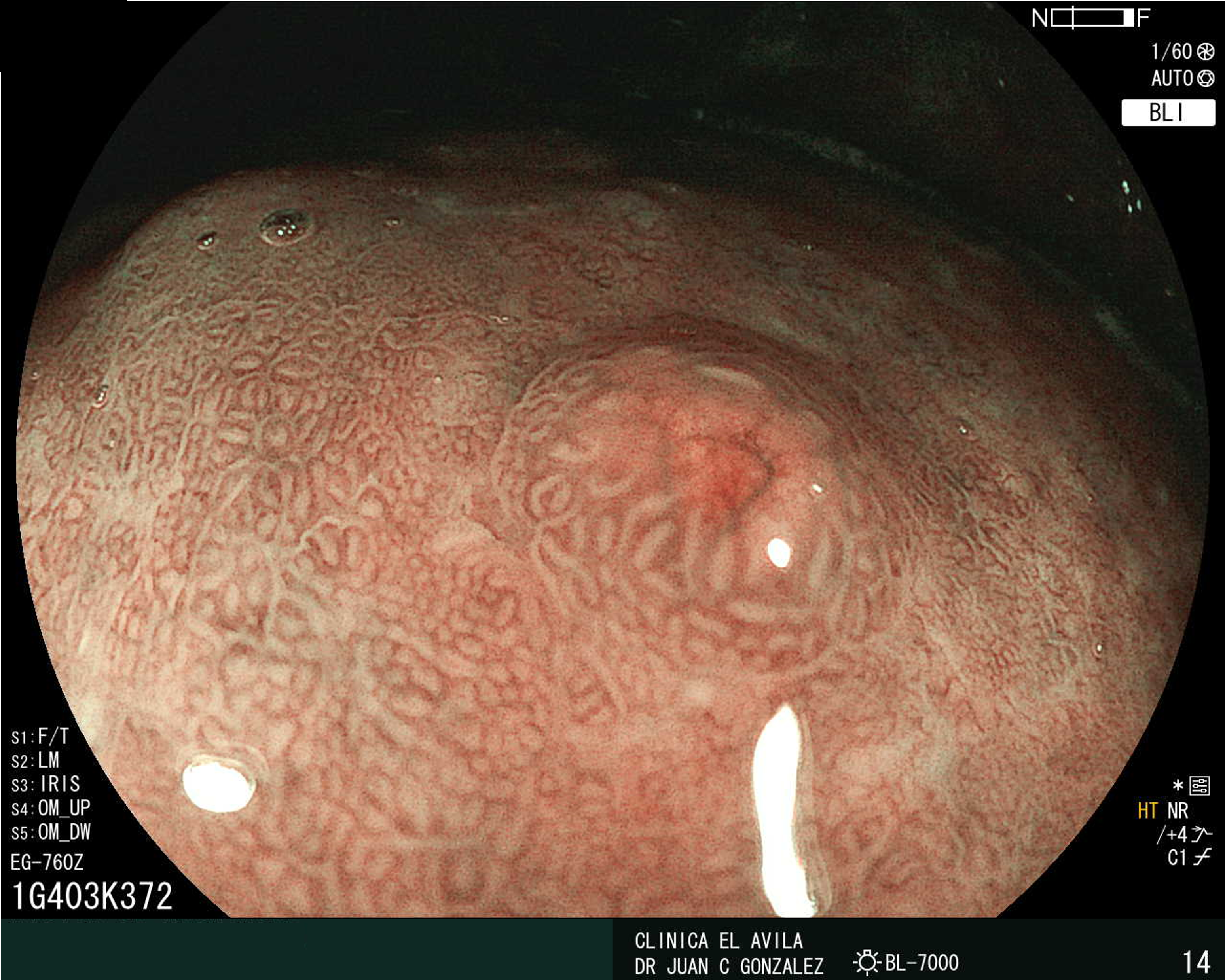
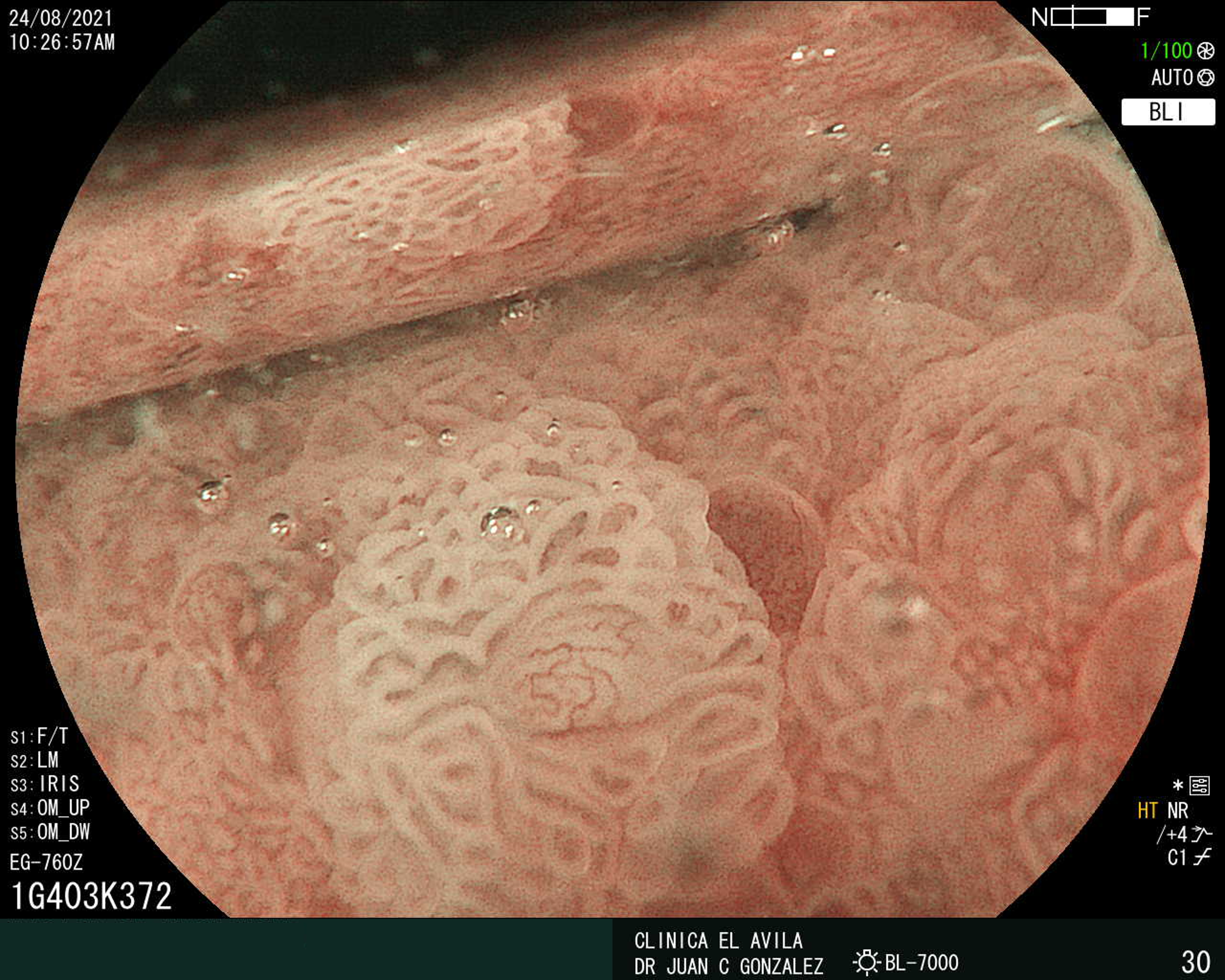
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X