Comparación de Vonoprazan y Esomeprazol en el tratamiento de la Esofagitis Erosiva por Enfermedad de Reflujo Gastroesofágico
Resumen
La esofagitis erosiva (EE) se trata habitualmente con inhibidores de la bomba de protones (IBPs), aunque una proporción de pacientes no alcanza una curación completa. Los bloqueadores ácido-competitivos de potasio (P-CABs) ofrecen una inhibición más potente y sostenida del ácido gástrico. Objetivo: El objetivo del presente estudio fue comparar directamente la probabilidad de curación con Vonoprazan y Esomeprazol en el tratamiento de la esofagitis erosiva asociada a enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico, evaluando tanto la resolución de los síntomas como la curación endoscópica. Metodología: Estudio observacional prospectivo con 60 pacientes entre 18 y 75 años, divididos en dos grupos de 30. Un grupo recibió Vonoprazan 20 mg dos veces al día (BID) y el otro Esomeprazol 20 mg BID durante 8 semanas. Se realizaron endoscopias al inicio y al final, y se registró diariamente la presencia de pirosis y regurgitación. Resultados: Vonoprazan mostró mayores tasas de curación endoscópica en todos los grados de severidad (A–D). En el Grado D logró un 50% de curación, mientras Esomeprazol no resolvió ningún caso. Alivio sintomático: Vonoprazan logró desaparición total de síntomas desde el día 2 hasta la semana 8 en todos los pacientes, mientras que con Esomeprazol persistieron síntomas leves en algunos casos. No se observaron efectos adversos relevantes. Conclusión: Vonoprazan es superior a Esomeprazol en curación endoscópica y control sintomático rápido en el tratamiento de la EE.
ESCUCHE EL RESUMEN HANCIENDO CLIC EN EL IDIOMA DE SU PREFERENCIA:
EspañolEnglish
Portugués
Japones
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Richter JE, Rubenstein JH. Presentation and epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:267–276.
El-Serag HB, Sweet S, Winchester CC, Dent J. Update on the epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 2014;63:871–880.
González JC, Louis CE, Piñero RE, et al. Primer Consenso Venezolano de Enfermedad por Reflujo Gastroesofágico. Arch Venez Farmacol Ter. 2011;30(1):1–13.
Soumekh A, Schnoll-Sussman FH, Katz PO. Reflux and acid peptic diseases in the elderly..Clin Geriatr Med. 2014;30(1):29-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2013.10.006.
Moole H, Patel J, Ahmed Z, et al. Progression from low-grade dysplasia to malignancy in patients with Barrett’s esophagus diagnosed by two or more pathologists. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:8831–8843.
Tsoi EH, Williams RA, Christie M, et al. Not all low-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s oesophagus is the same: using specific histological criteria in predicting progression to neoplasia. Pathology. 2021;53:700–704.
Antunes C, Aleem A, Curtis SA. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025.
Chapelle N, Ben Ghezala I, Barkun A, Bardou M. The pharmacotherapeutic management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22:219–227.
Yadlapati R, Hubscher E, Pelletier C, et al. Induction and maintenance of healing in erosive esophagitis in the United States. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;16:967–980.
Shah SC, Tepler A, Pimentel C, et al. Host genetic determinants associated with Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2021;161(5):1443–1459.
Yang JC, Wang HL, Chern HD, et al. Role of omeprazole dosage and cytochrome P450 2C19 genotype in patients receiving omeprazole-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Pharmacotherapy. 2011;31:227–238. doi:10.1592/phco.31.3.227.
Robinson M. New-generation proton pump inhibitors: overcoming the limitations of early-generation agents. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13(Suppl 1):S43–S47.
Yang X, Li Y, Sun Y, et al. Vonoprazan: a novel and potent agent in the treatment of acid-related diseases. Dig Dis Sci. 2018;63:302–311. doi:10.1007/s10620-017-4866-6.
Echizen H. The first-in-class potassium-competitive acid blocker, vonoprazan fumarate: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(4):409–418. doi:10.1007/s40262-015-0326-7.
Scarpignato C, Hunt RH. Potassium-competitive acid blockers: current clinical use and future developments. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2024;26:273–293.
Stewart J. Voquezna FDA approval history [Internet]. 2024. Disponible en: Drugs.com.
Anik AH, Proma FA, Saha P, Sarker S. Tegoprazan as a new remedy for gastrointestinal diseases compared to its therapeutic predecessors: a mini-review. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024;16:11–17.
Mermelstein J, Mermelstein AC, Chait MM. Tegoprazan for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Drugs Today. 2020;56:715–721.
Ramani A, Merchant A, Cash BD. Review of the clinical development of fexuprazan for gastroesophageal reflux-related disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2023;79:1023–1029.
Kang C. Keverprazan hydrochloride: first approval. Drugs. 2023;83:639–643.
Seicean R. Vonoprazan versus conventional proton pump inhibitor in the therapeutic armamentarium of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease. In: Chai J, editor. Peptic Ulcer Disease – What’s New? 2021. doi:10.5772/intechopen.101349.
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999;45:172–180.
Iwakiri K, Fujiwara Y, Manabe N, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for gastroesophageal reflux disease 2021. J Gastroenterol. 2022;57:267–285.
Johnson DA, Benjamin SB, Vakil NB, et al. Esomeprazole once daily for 6 months is effective therapy for maintaining healed erosive esophagitis and for controlling gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(1):27–34. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03443.
Dimenäs E, Glise H, Hallerbäck B, et al. Well-being and gastrointestinal symptoms among patients referred to endoscopy owing to suspected duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995;30(11):1046–1052. doi:10.3109/00365 529509101605.
Katz PO, Dunbar KB, Schnoll-Sussman FH, et al. ACG clinical guideline for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:27–56.
Gyawali CP, Fass R. Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:302–318.
Sakurai K, Suda H, Fujie S, et al. Correction to: Short-term symptomatic relief in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:1724. doi:10.1007/s10620-019-5464-6.
Oshima T, Arai E, Taki M, et al. Randomised clinical trial: vonoprazan versus lansoprazole for the initial relief of heartburn in patients with erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49(2):140–146.
Xiao YL, Zhang ST, Dai N, et al. Phase III randomized, double-blind, multicentre study of vonoprazan versus lansoprazole in Asian patients with erosive oesophagitis. Gut. 2019;69:224–230.
Ashida K, Iwakiri K, Hiramatsu N, et al. Maintenance therapy for healed erosive esophagitis: phase III comparison of vonoprazan with lansoprazole. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:1550–1561.
Ashida K, Sakurai Y, Hori T, et al. Randomised clinical trial: vonoprazan vs lansoprazole for the healing of erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43(2):240–251.
Ashida K, Sakurai Y, Nishimura A, et al. Randomised clinical trial: dose-ranging study of vonoprazan vs lansoprazole for erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42(6):685–695.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v80i1.794
IMÁGENES GEN
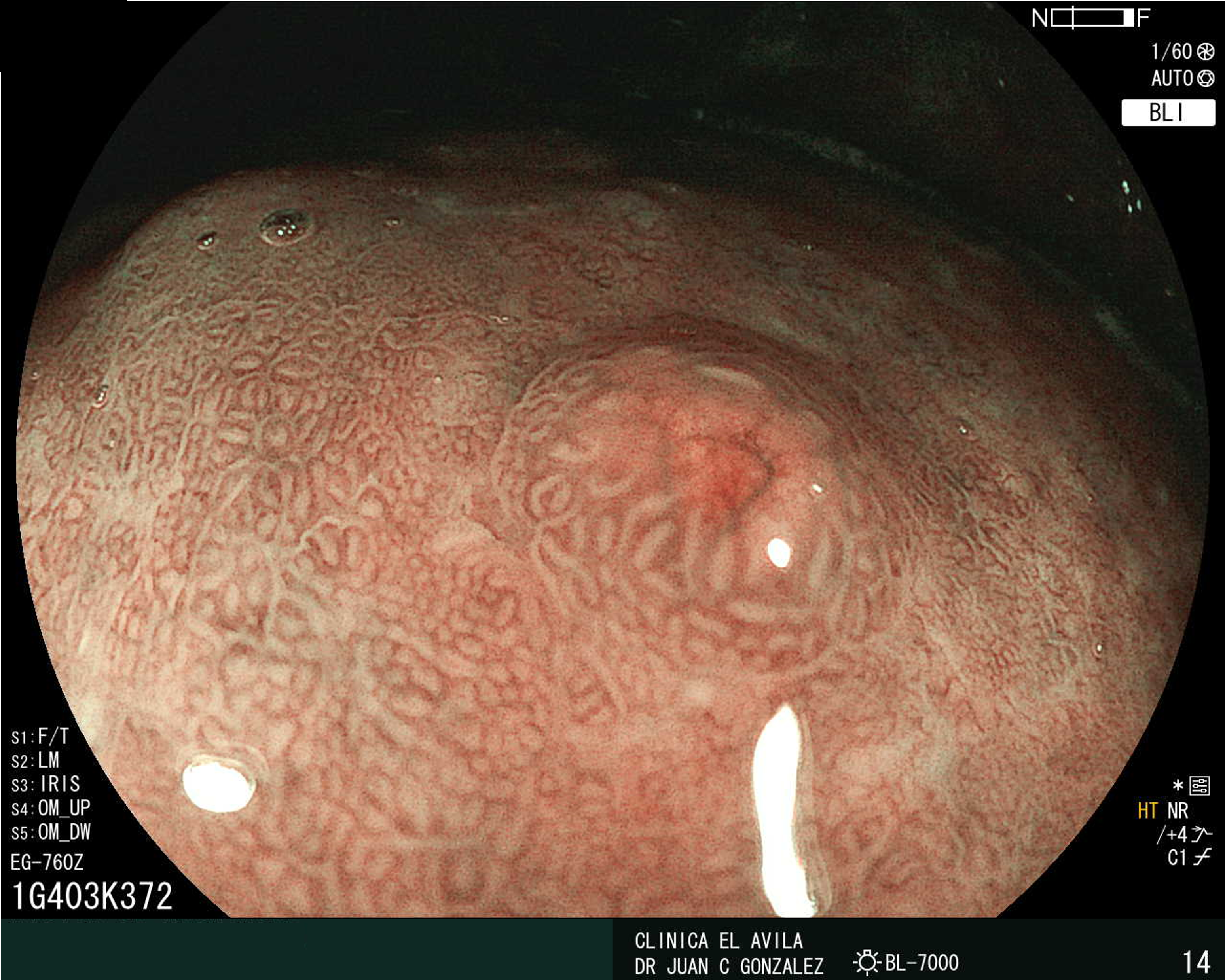
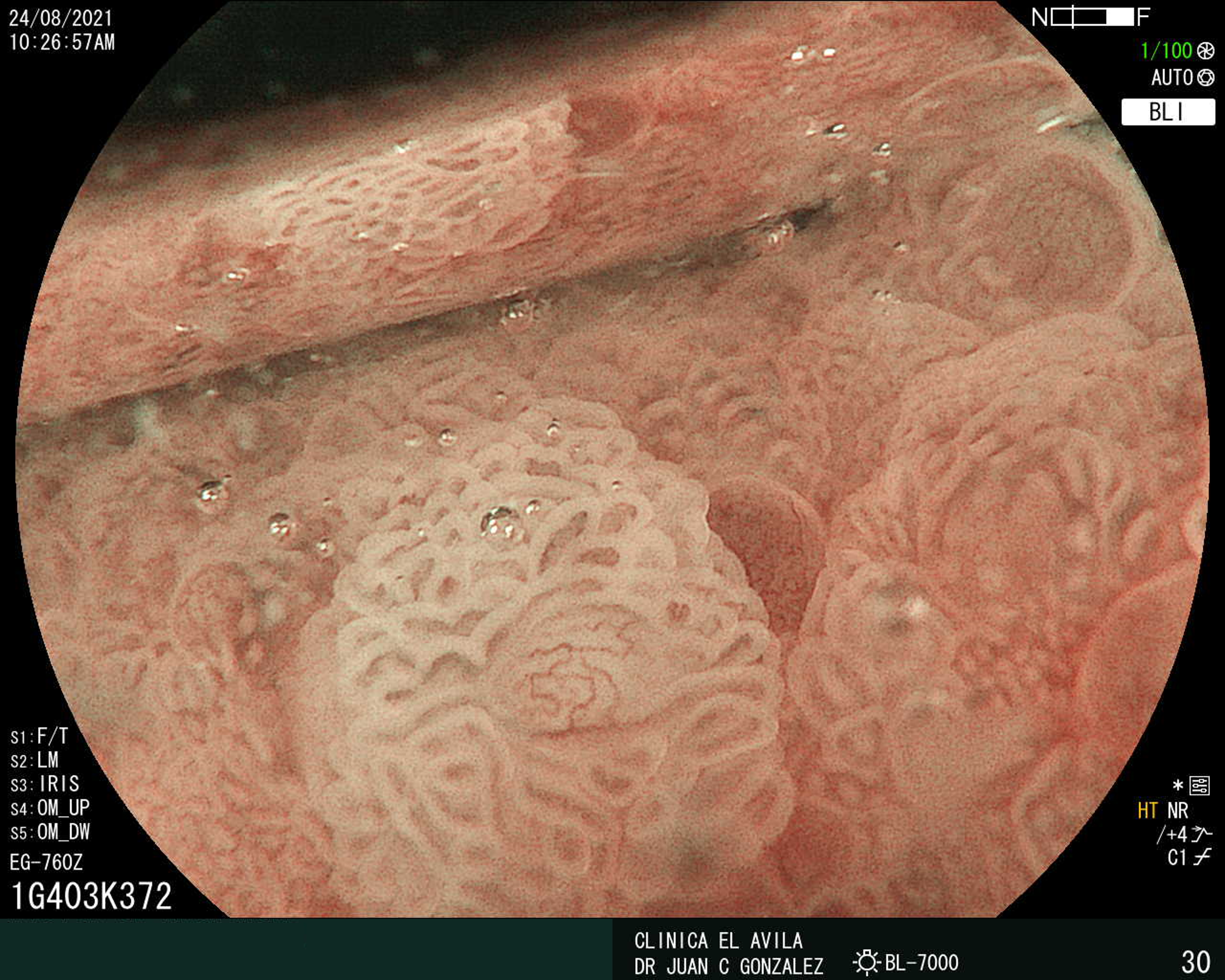
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X