Colitis pseudomembranosa en paciente con COVID-19. A propósito de un caso
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
McDonald LC, et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin Infect Dis 2018; 66: 1-48.
Dubberke ER, Olsen MA. Burden of Clostridium difficile on the healthcare system. ClinInfectDis 2012; 55(2): 88–92
Bagdasarian N, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Clostridium difficile in adults: a systematic review. JAMA 2015; 4: 313-98.
Kelly CP, LaMont JT. Clostridium difficile--more difficult than ever. N Engl J Med 2008; 359(18):1932-40.
Wanahita A, et al. Conditions associated with leukocytosis in a tertiary care hospital, with particular attention to the role of infection caused by clostridium difficile. ClinInfectDis 2002; 34(12):1585-92.
Chitnis AS, et al. Epidemiology of community-associated Clostridium difficile infection, 2009 through 2011. JAMA Intern Med 2013; 173(14):1359-67.
Kulaylat AS, et al. Development and Validation of a Prediction Model for Mortality and Adverse Outcomes Among Patients With Peripheral Eosinopenia on Admission for Clostridium difficile Infection. JAMA Surg 2018; 153 (12):1127-32.
Mattila E, et al. Extraintestinal Clostridium difficile infections. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 57:148-53.
Brown TA, et al. Acute appendicitis in the setting of Clostridium difficile colitis: case report and review of the literature. ClinGastroenterolHepatol 2007; 5(8):969-71.
Tedesco FJ. Antibiotic associated pseudomembranous colitis with negative proctosigmoidoscopy examination. Gastroenterology 1979; 77:295-7.
Zhang W, et al. Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: implication of multiple shedding routes. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2020; 9(1): 386–9.
Lewandowski K, Rosołowski M, Kaniewska M, Kucha P, Meler A, Wierzba W, Rydzewska G. Clostridioides difficile infection in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): an underestimated problem? Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021 Feb 26;131(2):121-127.
Granata G. et al. The Burden of ClostridioidesDifficile Infection during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Case-Control Study in Italian Hospitals J. Clin. Medicina. 2020; 9: 2-11.
Brandt LJ, et al. American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: epidemiology, risk factors, patterns of presentation, diagnosis, and management of colon ischemia (CI). Am J Gastroenterol. 2015; 110 (1):18–45.
K.H. Chan, et al., Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and ischemic colitis: An under-recognized complication, American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2020; 159039: 1-4.
Huang C, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020; 395: 497-506.
Shamsoddin E. A COVID-19 pandemic guideline in evidence-based medicine. Evid Based Dent. 2020; 21: 71-3.
Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382: 1708-1720.
Chen N, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020; 395: 507-513.
Pan L, et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020; 115(5):766–773.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v75i2.565
IMÁGENES GEN
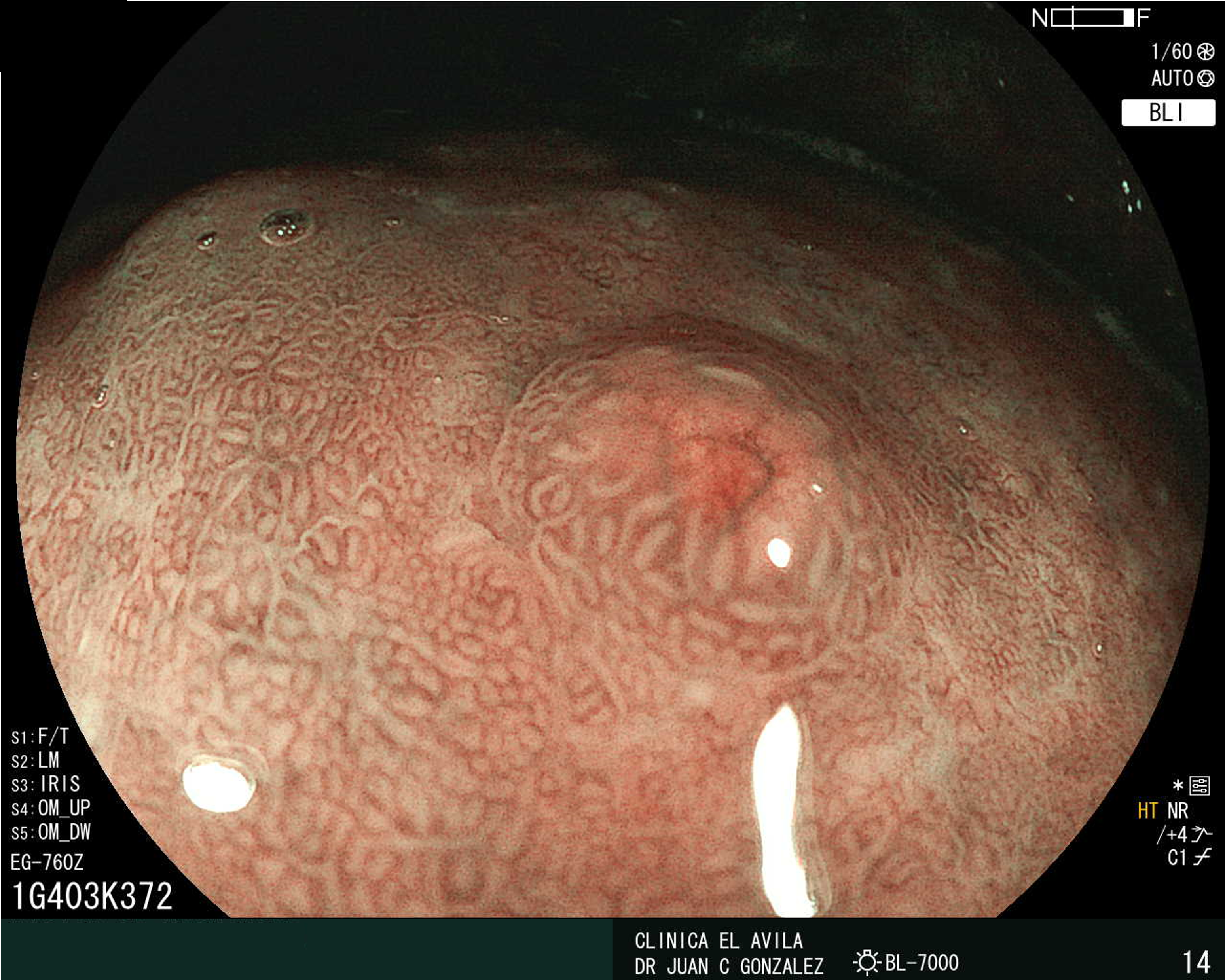
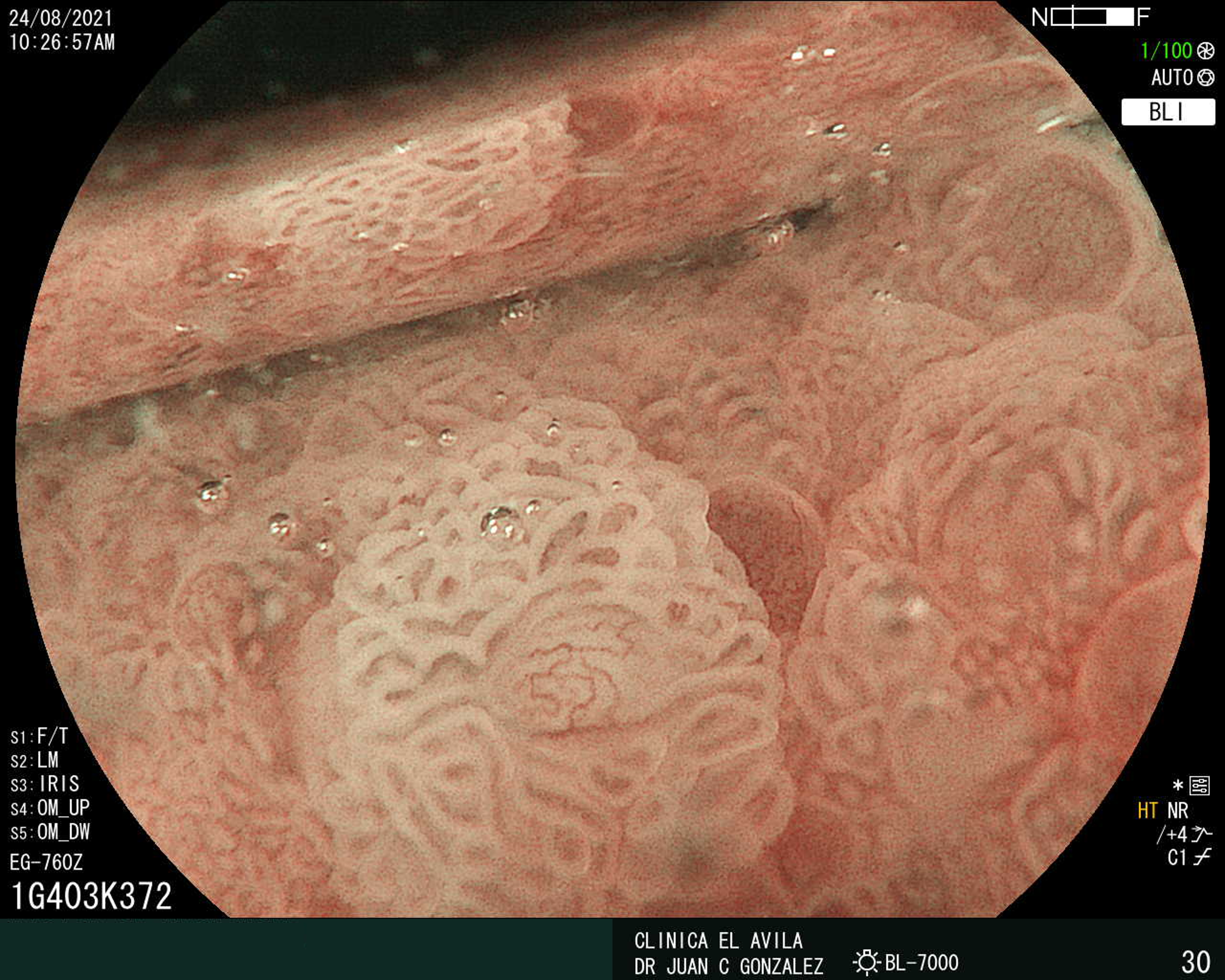
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X