Esófago en cascanueces: relación entre la presentación clínica y los hallazgos manométricos
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Coss-Adame E, Rao Satish S. C, MD. A Review of Esophageal Chest Paint. Gastroenterol & Hepatol. 2015;11(11):459-766.
Wong WM, Beeler J, Risner-Adler S, Habib S, Bautista J, Fass R. Attitudes and referral patterns of primary care physicians when evaluating subjects with noncardiac chest pain a national survey. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50(4):656-61.
Groarke J, O’Brien J, Go G, Susanto M, Owens P, Maree AO. Cost burden of non-specific chest pain admissions. Ir J Med Sci. 2013;182(1):57-61.
Waterman D, Dalton CB, Ott DJ, Castell JA, Bradley LA, Castell DO et al. Hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter: what does it mean?. J ClinGastroenterol 1989;11:139-146.
Katz PO, Dalton CB, Richter JE, Wu WC, Castell DO. Esophageal testing of patients with noncardiac chest pain or dysphagia. Results of three years experience with 1161 patients. Ann Intern Med 1987;106:593-597.
Nelson JB, Castell DO. Esophageal motility disorders. Dis Mon 1988;34:297-389.
Rencoret G, Csendes A, Henríquez A. Estudio manométrico de
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v75i1.554
IMÁGENES GEN
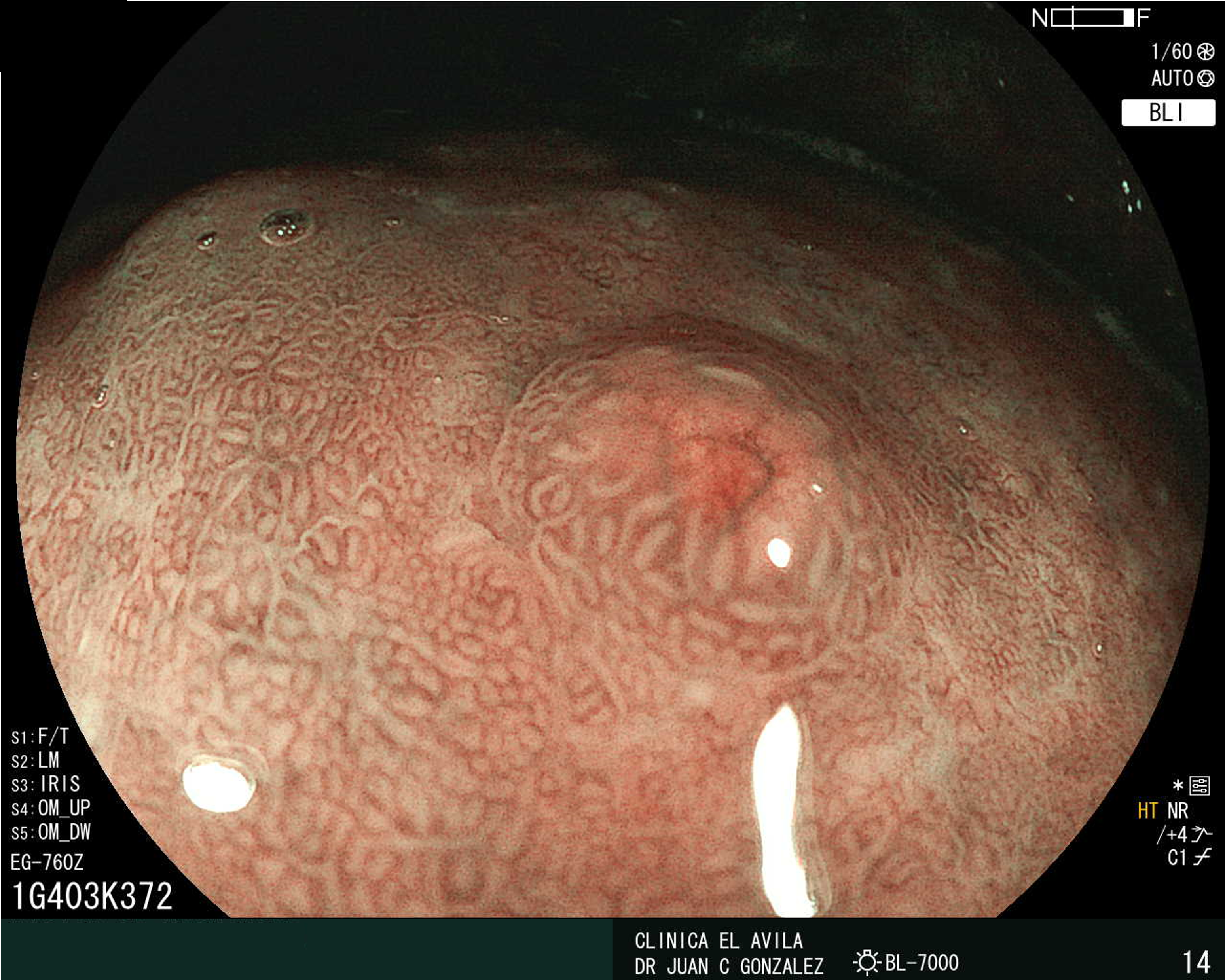
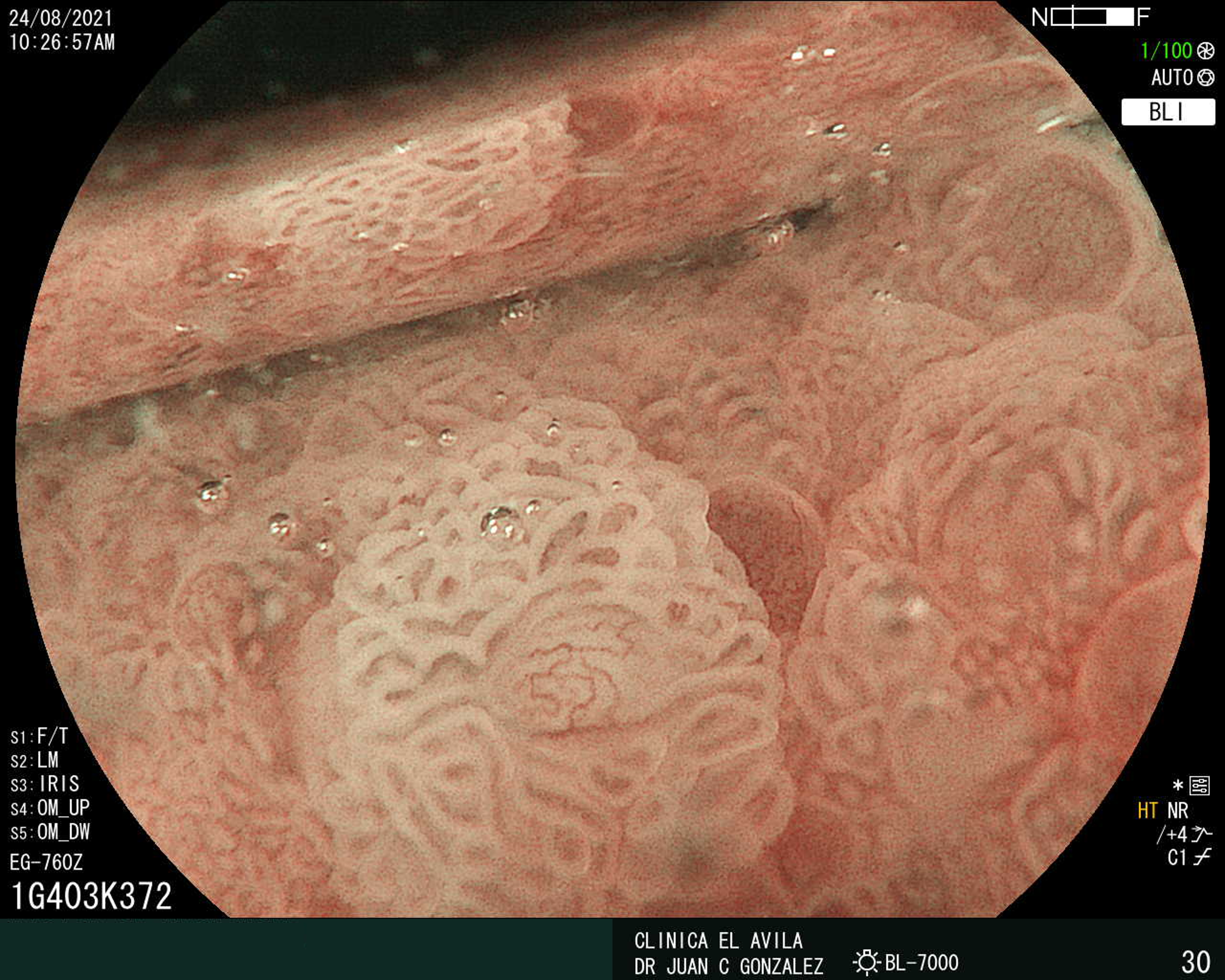
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X