Laringitis por reflujo: Mito o realidad?
Resumen
Referencias
Vaezi MF. Laryngitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: increasing prevalence or poor diagnostic tests?. Am J Gas-troenterol 2004; 99:786-788.8.
McNally PR, Maydonovitch CL, Prosek RA, Collette RP, Wong RKH. Evaluation of gastroesophageal reflux as a cause of idiopathic hoarseness. Dig Dis Sci 1989; 34: 1900-1904.9.
Vaezi M, Hicks DM, Abelson TI, Richter JE. Laryngeal signs and symptoms and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): A critical assessment of cause and effect association. Clinical Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003; 1: 333-44.10.
Irwin RS, Rosen MJ, Braman SS.Cough: a comprehensive review. Arch Intern Med 1977; 137:1186-1191. 11.
Irwin RS, Corrao WM, Pratter MR. Chronic persistent cough in the adult: the spectrum and frequency of causes and suc-cessful outcome of specific therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis 1981; 123:413-417.12.
Curren JA, Barry MK, Callanan V, Gormely PK. A prospective study of acid reflux and globus pharyngeus using a modified symptom index. Clin Otolaryngol 1995; 20:552-554.13.
Ward PH, Hanson DG. Reflux as an etiological factor of carcinoma of the laryngopharynx. Laryngoscope 1998; 98: 1195-1199.14.
Walters JF, Vaezi M. Extraesophageal GERD. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2008; 37: 845-858.15.
Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestation of gastroe-sophageal reflux disease. Laryngoscope. 1991;101:1-7816.
Little FB, Kohut RI, Koufman JA, Marshall RB. Effect of gas-tric acid on the pathogenesis of subglottic stenosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1985;94:516-519.17.
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Shay S, et al. Acid and non-acid reflux in patients with persistent symptoms despite acid suppressive therapy: a multicentre study using combined ambulatory impedance-pH monitoring. Gut 2006; 55:1398-1402.18.
Patterson N, Mainie I, Rafferty G, et al. Nonacid Reflux Epis-odes Reaching the Pharynx are Important Factors Associated With Cough. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009 [Epub ahead of print].19.
Belafsky PC, Rees CJ, Rodriguez K, Pryor JS, Katz PO. Esophagopharyngeal reflux. Otol Headn Neck Surg 2008; 138: 57-61.20.
González M, De Ascencao M. Síndrome de intestino irritable. Aspectos psicológicos. Revista de la facultad de medicina de la Universidad Central de Venezuela 2005; 28(2): 139-145.
Vaezi MF. Are there specific laryngeal signs for gastroesopha-geal reflux disease?. Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102:723-724.21.
Delahunty JE, Cherry J. Experimentally produced vocal cord granulomas. Laryngoscope 1968; 78:1941-1947.22.
Ahmed TF, Abelson TI, Hicks DM, et al. Chronic laryngitis associated with GERD: prospective assessment of differences in practice patterns between gastroenterologists and ENT physicians. Gastroenterology 2005; 128 (Suppl 2).23.
Vavricka SR, Storck C, Wildi SM, et al: Limited diagnostic value of laryngopharyngeal lesions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux during routine upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102:716-722.24.
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and re-liability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope 2001; 111: 1313-1317.25.
Oelschlager BK, Eubanks TR, Hillel A, et al. Laryngoscopy and pharyngeal pH are complementary in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal laryngeal reflux. J Gastroenterol Surg 2002; 6: 189-194.26.
Hicks DM, Vaezi MF, Ours TM, et al. ENT signs of GERD. J Voice 2002; 16: 564-579
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v64i2.407
IMÁGENES GEN
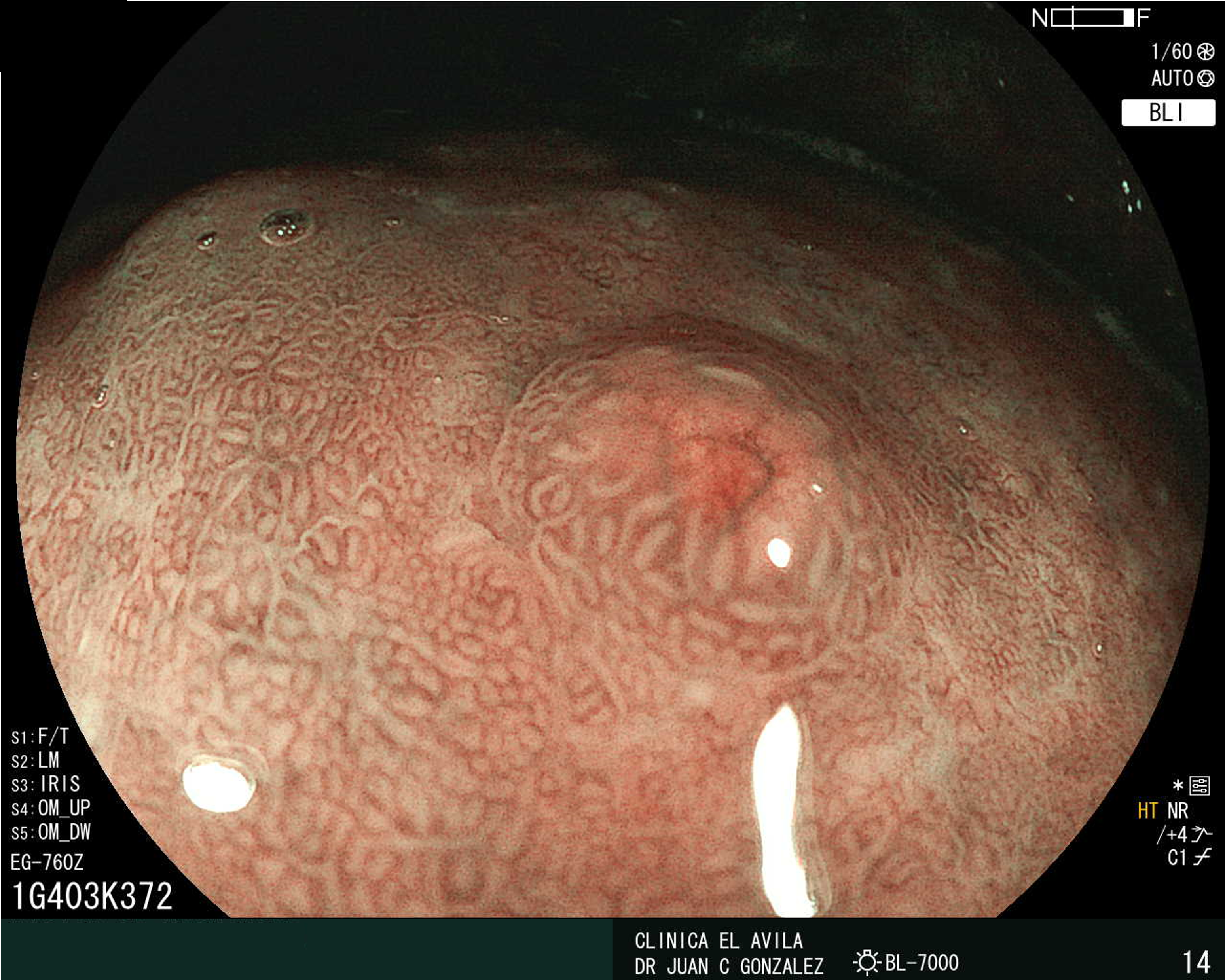
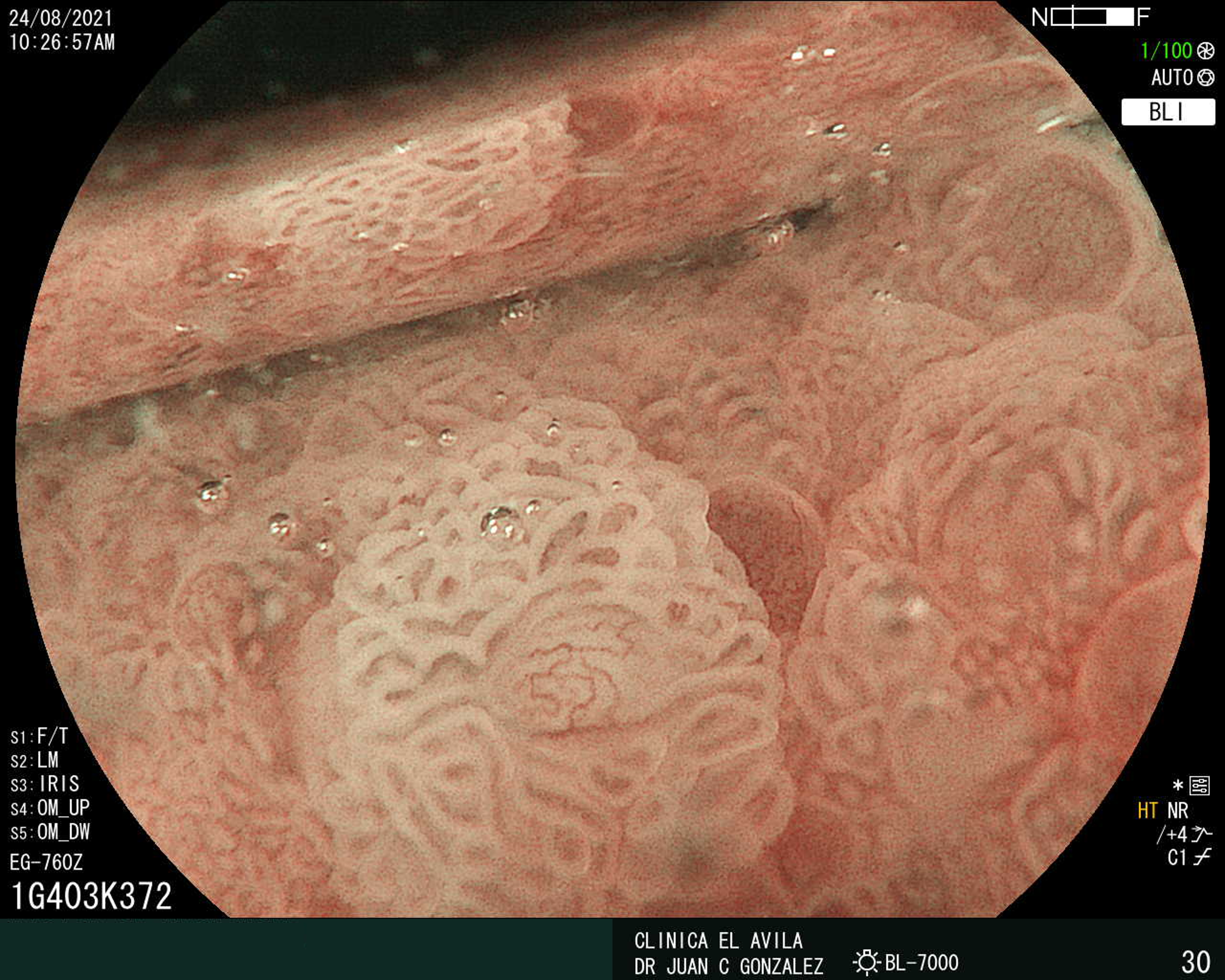
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X