Factores psicosociales asociados con la calidad de vida en las enfermedades inflamatorias del intestino
Resumen
Introducción y objetivos: En los últimos años ha existido el interés en saber cómo las enfermedades inflamatorias del intestino (EII), influyen en la calidad de vida de quienes la padecen. El objetivo de la presente revisión teórica, trata de subrayar la importancia de indagar cuáles factores psicosociales podrían estar asociados a la calidad de vida que reportan estas personas. Método: Para llevar a cabo esta investigación, se realizó una revisión bibliográfica de publicaciones en varias bases de datos online consultadas. Se seleccionaron 71 artículos, que cumplieron un conjunto de criterios de inclusión. Resultados: Existe evidencia acerca de la influencia de los factores psicosociales en diversos ámbitos de las EII, primordialmente en la afectación de la calidad de vida de quienes las padecen, al ser enfermedades que alteran no sólo la funcionalidad de la persona sino también su bienestar psicológico. Conclusiones: Al plantear terapias para mejorar la calidad de vida de quienes padecen estar enfermedades, es necesario reconocer la característica multifactorial de las mismas, para de esa forma contribuir a anticipar su aparición, mejorar el diagnóstico y su tratamiento.
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Castillo D, Rosas J, Serrano A, Amezcua L. Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Revista de especialidades médico-quirúrgicas. 2005; 10(2): 10-20.
Podolsky D. Inflammatory bowel disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002; 347(6): 417-429. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra020831
Tobón S, Vinaccia S, Quiceno J, Sandín B, Nuñez A. Aspectos psicopatológicos en la enfermedad de Crohn y en la colitis ulcerosa. Avances en Psicología Latinoamericana. 2007; 25(2): 83-97.
Ortigosa L. Concepto actual y aspectos clínicos de la enfermedad de Crohn y la colitis ulcerosa. Colombia Médica. 2005; 36(2): 16-24.
Andres P, Friedman, A. Epidemiology and the natural course of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology Clinics of North American. 1999; 28(2): 255-81. doi: 10.1016/S0889-8553(05)70056-X
Casati J, Toner B. Psychosocial aspects of inflammatory bowel disease. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2000; 54(7): 388-393. doi: 10.1016/S0753-3322(01)80006-8
Moyer M. A collaborative effort to define the epidemiology of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: what can we learn from children with early-onset disease? Journal of Pediatrics. 2005; 146(1): 7-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.10.068
Kugathasan S, Judd R, Hoffman R, Heikenen J, Telega G, Khan F. et al. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of children with newly diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease in Wisconsin: A statewide population-based study. Journal of Pediatrics. 2003; 143(4): 525-531. doi: 10.1067/S0022-3476(03)00444-X
Ouyang R, Tandon R, Goh K, Ooi C, Ogata H, Fiocchi C. The emergence of inflammatory bowel disease in the Asian Pacific region. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 2005; 21(4): 408-413.
Thia K, Loftus E, Sandborn W, Yang S. An update on the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2008; 103(12): 3167-3182. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.02158.x.
González R. Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. En: Weitz J, Berger Z, Sabah S, Silva H, editores. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de las enfermedades digestivas. Chile: Editorial IKU; 2002.p. 148-154.
Anton P, Shanahan F. Neuroimmunomodulation in inflammatory bowel disease. How far from bench to bedside?. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1998; 840(1): 723-734. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09611.x
Díaz M, Comeche M, Mas B, Díaz M, Vallejo M. Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal: depresión y estrategias de afrontamiento. Apuntes de Psicología. 2008; 26(1): 91-102.
Loftus EV. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126(6): 1504-1517. doi: 10.1053/j.gastr o.2004.01.063
Varona L, Collado E, Pinillos A. Terapia cognitivo-conductual en la enfermedad de Crohn. Norte de salud mental. 2009; 8(34): 117-123.
Bennebroek F, Thijssens N, Stokkers P, Grootenhuis M, Bockting C, Nieuwkerk P. et al. Do inflammatory bowel disease patients with anxiety and depressive symptoms receive the care they need?. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2012; 16(1): 68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.c rohns.2011.07.006
Graff L, Walker J, Bernstein C. La depresión y la ansiedad en la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal: una revisión de la comorbilidad y la gestión. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2009; 15(7): 1105-18. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20873.
García E, Fernández C. Algunos factores predictores en la enfermedad de Crohn. Psicothema. 1998; 10(1): 143-151.
Kurina L, Goldacre M, Yeates D, Gill L. Depression and anxiety in people with inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health. 2001; 55(10): 716-20. doi: 10.1136/jech.55.10.716
Danzi J. Extraintestinal manifestation of idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1998; 148(2): 297-302. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.2.297
Krunpnick A, Morris J. The long-term results of resection and multiples resections in Crohn’s diseaase. Seminars in Gastroenterology Disease. 2000; 11(1): 41-51.
Hungin A, Whorwell P, Tack J, Mearin F. The prevalence, patterns and impact of irritable bowel syndrome: an international survey of 40000 subjets. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 17:643-650.
Brandtzaeg P. Inflammatory bowel disease: clinics and pathology. Do inflammatory bowel disease and periodontal disease have similar immunopathogeneses?. Acta Odontol Scand. 2001; 59(4): 235-243.
Nikolaus S, Schreiber, S. Diagnostics of inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133: 1670-1689.
Quera R, Palma R. Enfermedades inflamatorias intestinales: colitis ulcerosa y enfermedad de Crohn. Revista Médica Clínica Las Condes. 2008; 19(4): 331-341.
Ekbom A. The epidemiology of IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2004; 10(1): 32-34.
Slimming J, Álvarez M, Carvajal S, Lubascher J, Quera R, Vergara M. et al. Aproximación a la realidad nacional en enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Gastr latinoam. 2007; 18: 451-463.
Carter MJ, Lobo AJ, Travis S. On behalf of the IBD Section of the British Society of Gastroenterology. Guidelines for the management of IBD in adults. Gut. 2004; 53(5): 1-16.
Vatn MH. Natural history and complications of IBD. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2009; 11(6): 481-487.
Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, et al. Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of infl ammatory bowel disease: report of a working party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005; 19(1): 5-36.
Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Inflammatory Bowel disease: Clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. The Lancet. 2007; 369: 1641-1657.
Lichtenstein GR, Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ. Management of Crohns Disease in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2008.
Figueroa C, Quera R, Valenzuela J, Jensen C. Enfermedades Inflamatorias Intestinales: experiencia en dos centros chilenos. Rev Med Chile. 2005; 133: 1295-1304.
Pappa HM, Semrin G, Walker TR, Grand RJ. Pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opi Gastroenterol. 2004; 20: 333-340.
Yepes I, Carmona R, Díaz F, Marín I. Prevalencia y características demográficas de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal en Cartagena, Colombia. Revista Colombiana de Gastroenterología. 2010; 25(2).
Danese S, Fiocchi C. Ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365(18): 1713-1725.
López F, Godoy, J. Estrategias cognitivo-conductuales para el tratamiento de la obesidad. Psicothema. 1994; 6(3): 333-345.
Oblitas L. Psicología de la Salud y Calidad de Vida. México: Thomson; 2003.
Morales D. Efecto predictivo del afrontamiento y frecuencia de crisis sobre la calidad de vida en epilepsia. [Tesis Magister]. Venezuela: Universidad Simón Bolívar. Magister en Psicología; 2009.
Ruiz F. Calidad de vida en medicina: problemas conceptuales y consideraciones éticas. Revista Electrónica de Psicología. 2007; 11(2).
Schwartzmann L. Calidad de vida relacionada con la salud: aspectos conceptuales. Ciencia y Enfermería. 2003; 9(2): 9-21
Irvine EJ. Quality of life issness in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92: 8-24.
Maunder R, Levenstein S. The Role of Stress in the Development and Clinical Course of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Epidemiological Evidence. Current Molecular Medicine. 2008; 8(4): 247-252. doi: 10.2174/156652408784533832
Schmulson M. Síndrome de colon irritable: ¿Hay una terapéutica eficaz? En Valdovinos M, Milke P, Uscanga L. Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Basadas en Evidencias. México: Masson; 2002.
Vinaccia S, Fernández H, Amador O, Tamayo R, Vázquez A, Contreras F. et al. Calidad de vida, ansiedad y depresión en pacientes con diagnóstico de colon irritable. Terapia psicológica. 2005; 23(2): 65-74.
Corney R, Stanton R. Physical symptom severity, psychological and social dysfunction in a series of outpatients with irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1990; 34(5): 483-491. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(90)90022-V
Sánchez V, Comeche M, Mas Hesse B. Resumen de Entrenamiento en inoculación de estrés en un caso de Síndrome de Intestino Irritable. Acción Psicológica. 2002; 1(1): 71-80.
Whitehead W, Schuster, M. Gastrointestinal disorders. Londres: Academic Press; 1985.
Drossman D. Irritable bowel syndrome: The role of psychosocial factors. Stress Medicine. 1994;10: 49-55.
Dalton C, Drossman D. Diagnostic and treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome. American Family Physician. 1998; 5(3): 140-149.
Fowlie S, Eastwood M, Ford M. Irritable bowel syndrome: The influence of psychological factors on the symptom complex. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1992; 2(36): 169-173.
Hashem M, El-Serag, H. Impact of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Prevalence and Effect on Health-related Quality of Life. Gastroenterological Disorders. 2003; 3(2): S-3-S11.
Guyatt G, Feeny D, Patrick D. Measurement health-related quality of life. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 118.
Tanimoto M, Schmulson M, Ramírez D, Valdovinos M. Prevalencia de trastornos funcionales digestivos en estudiantes de medicina. Rev.Gastroenterol Mex. 1995; 60(3): 57.
Tobón S, Sadin B, Vinaccia S. Trastornos gastrointestinales: psicopatología y tratamientos psicológicos. Madrid: Klinik; 2005.
González M, De Ascencao M. Síndrome de intestino irritable. Aspectos psicológicos. Revista de la facultad de medicina de la Universidad Central de Venezuela 2005; 28(2): 139-145.
Molano J. Calidad de vida en el síndrome de intestino irritable. Asociación Colombiana de gastroenterología. 2003; 18(3): 25-27.
Hahn BA, Kirchdoerfer LJ, Fullerton S, Mayer E. Patient-perceived severity of irritable bowel syndrome in relation to symptoms, health resource utilization and quality of life. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Jun; 11(3):553–559.
Glanek I, Hays R, Kilbourne A, Naliboff B, Mayer, E. The impact of irritable bowel syndrome on health-related quality of life. Gastroenterology. 2000; 119: 654-660.
Naliboff B, Balice G, Mayer E. Psychosocial moderators of quality of life in irritable bowel syndrome. European Journal Surgery Supplement. 1998; 583: 57-59.
Whitehead W, Bosmajian L, Zonderman A, Costa P, Schuster M. Symptoms of Psychologic Distress Associated With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Comparison of Community and Medical Clinic Samples. Gastroenterology. 1988; 95: 709-714.
Hardt J, Conrad S, Muche-Borowski C, Raspe H. Epidemiology of depression and distress in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and validation of an indicator scale of perceived stress for psychosocial impairments. European Psychiatry. 2011; 26(1): 2217-2218
Duffy L, Zielezny M, Marshall J, Byers T, Weiser M., Phillips J. et al. Relevance of major stress events as an indicator of disease activity prevalence in inflammatory bowel disease. Behav Med. 1991; 17:101-110.
Levenstein S, Prantera C, Varvo V, Scribano M, Andreoli A, Luzi C. et al. Stress and exacerbation in ulcerative colitis: a prospective study of patients enrolled in remission. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95: 1213-1220.
Sewitch M, Abrahamowicz M, Bitton A, Daly D, Wild G, Cohen A. et al. Psychological distress, social support, and disease activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96: 1470-1479.
Iglesias M, Barreiro M, Vázquez I, Piñeiro M, Figueiras A, Nieto L. et al. Psychologic stress in Crohn’s disease an ulcerative colitis: role of gender and clinical activity of the disease. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140(1): S-787.
Mawdsley J, Rampton D. The role of psychological stress in inflammatory bowel disease. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2006; 13(5-6): 327-336.
Ringel Y, Williams RE, Kalilani L, Cook SF. Prevalence, characteristics, and impact of bloating symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7(1): 68-72.
Casellas F, López J, Malagelado J. Experiencia previa y calidad de vida en pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal durante los brotes de actividad. Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas. 2003; 95(7): 471-475.
Vidal A, Gómez E, Sans M, Portella M, Salamero M, Piqué J. et al. Life events and inflammatory bowel disease relapse: a prospective study of patients enrolled in remission. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006; 101(4): 775-781. doi: 10.1111/j.1 572-0241.2006.00476.x
Yacavone R, Locke G, Provenzale D, Eisen G. Quality of life measurement in gastroenterology: what is available? The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2001; 96(2): 285-297. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9270(00)02302-9
Drossman D, Whitehead W, Toner BB, Diamant N, Hu Y, Bandiwala SI. et al. What determines severity among patients with painful functional bowel disorders? Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95: 974-980.
DeLegge M. Nutrition and Gastrointestinal Disease. Humana Press Inc; 2008.
Veitía G, Pernalete B, Cachima L, Manuitt J, La Cruz M, Da Farias A, et al. Prevalencia del síndrome intestino irritable en la población adulta venezolana. GEN 2013; 67(3): 139-144.
Moskovitz DN, Maunder RG, Cohen Z, McLeod RS, MacRae H. Coping behavior and social support contribute independently to quality of life after surgery for inflammatory bowel disease. Disease Colon Rectum. 2000; 43(4): 517-521.
Crane C, Martin M. Social learning, affective state and passive coping in irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. General Hospital Psychiatry. 2004; 26(1): 50-58.
García H, Calvanese N. Calidad de vida percibida y locus de control en pacientes con tratamiento sustitutivo de la función renal: diálisis y trasplante renal. Anales de la Universidad Metropolitana. 2007; 7(1): 205-222.
Han K, Lee P, Lee S, Park E. Factors influencing quality of life in people with chronic illness in Korea. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2003; 35(2): 139-144.
Rose M, Fliege H, Hildebrandt M, Schirop T, Klapp B. The network of psychological variables in patients with diabetes and their importance for quality of life and metabolic control. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25(1): 35-42.
Urzúa A. Calidad de Vida y Factores Biopsicosociales en patologías médicas crónicas. Terapia Psicológica. 2008; 26(2): 207-214.
Kohler C, Fish L, Greene P. The relationship of perceived self-efficacy to quality of life in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Health Psychology. 2002; 21(6): 610-614.
Navarro A, Bueno B, Delgado J, Mayoral P. Percepción de autoeficacia en el afrontamiento de los problemas y su contribución en la satisfacción vital de las personas muy mayores. Revista española de geriatría y gerontología. 2006; 41(4): 222-227.
Sánchez JJ, González, AL. Evaluación de la calidad de vida desde la perspectiva psicológica. En: Caballo VE. Manual para la evaluación clínica de los trastornos psicológicos. Madrid: Pirámide; 2006. p. 473-492.
Wahl A, Rustoen T, Hanestad B, Gjengedal E, Moum T. Selfefficacy, pulmonary function, perceived health and global quality of life of cystic fibrosis patients. Social Indicators Research. 2005; 72: 239-261.
Collins P, Rhodes J. Ulcerative colitis: diagnosis and management. BM. 2006; 333(7): 501-507.
Avendaño M, Barra M. Autoeficacia, Apoyo Social y Calidad de Vida en Adolescentes con Enfermedades Crónicas. Terapia Psicológica. 2008; 26(2): 165-172.
Vallejo M, Comeche M, Ortega J, Rodríguez M, Díaz M. Las expectativas de autoeficacia y el ajuste emocional en el afrontamiento de la fibromialgia. Escritos de Psicología. 2009; 2(2):28-34.
Rotter J. Generalized Expectancies for internal versus external control reinforcerment. Psychological Monographs. 1966; 80(609).
Michalos A, Zumbo B, Hubley A. Health and the quality of life. Social Indicators research. 2000; 51:245 - 286.
Pucheu S, Consoli S, D'Auzac C, Francais P, Issad B. Do Health causal attributions and coping strategies act as moderators of quality oflife in peritoneal dialysis patients? Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2004; 56: 317-322.
Vinaccia S, Contreras F, Bedoya M, Carrillo L, Cuartas M, López N. et al. Conducta anormal de enfermedad en pacientes con enfermedades gastrointestinales. Psicología y Salud. 2004; 14(1):31-41.
Koloski N, Beyce P, Talley N. Vínculo entre somatización y síndrome de intestino irritable. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 18(10): 1101-1109.
Blanchard E, Lackner J, Gusmano R, Gudlesky G, Sanders K. et al. Prediction of treatment outcome among patients with irritable bowel syndrome treated with group cognitive therapy. Behavior Research and Therapy. 2004; 44: 317-337.
Mahvi-Shirazi M, Fathi-Ashtiani A, Rasoolzade-Tabatabaei SK, Amini M. Irritable bowel syndrome treatment: cognitive behavioral therapy versus medical treatment. Archives of Medical Science : AMS. 2012;8(1):123-129. doi:10.5114/aoms.2012.27292.
Toner B. Cognitive-Behavioral Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. CNS Spectrums. 2005; 10: 883-890 doi:10.1017/S1092852900019854
Rey E. La dieta y el síndrome de intestino irritable ¿no pero sí? ¿sí pero no?. Anales de Medicina Interna. 2004; 21(12): 575-576.
Huerta I, Valdovinos M, Schmulson M. Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Mexico. Digestive Diseases. 2001; 19: 251-257.
Smith GD, Watson R, Roger D, McRorie E, Hurst N, Luman W. et al. Impact of a nurseled couselling service on quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2002; 38:152-160.
Nordin K, Pahlman L, Larsson K, Sundberg-Hjelm M, Loof L. Health-related quality of life and psychological distress in a population-based sample of Swedish patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 2002; 37: 450-457.
Vavricka S, Rogler G. Fistula treatment: The unresolved challenge. Dig Dis. 2010; 28(3):556-564. doi: 10.1159/000320416
Vázquez I, Romero R, Aguilar J, García I. Trastorno del afecto. ¿Factor de riesgo para padecer trastornos funcionales digestivos?. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2000; 65(1): 50.
Stolorow R, Atwood G. Contexts of Being: The Intersubjective Foundations of Psychological Life. Hillsdale: The Analytic Press; 1992.
Porcelli P, Taylor G, Bagby R, De Carne M. Alexithymia and functional gastrointestinal disorders: a comparison with inflammatory bowel disease. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics. 1999; 69: 263-269.
Bouma G, Strober W. The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003; 3:521-33.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v70i1.31
IMÁGENES GEN
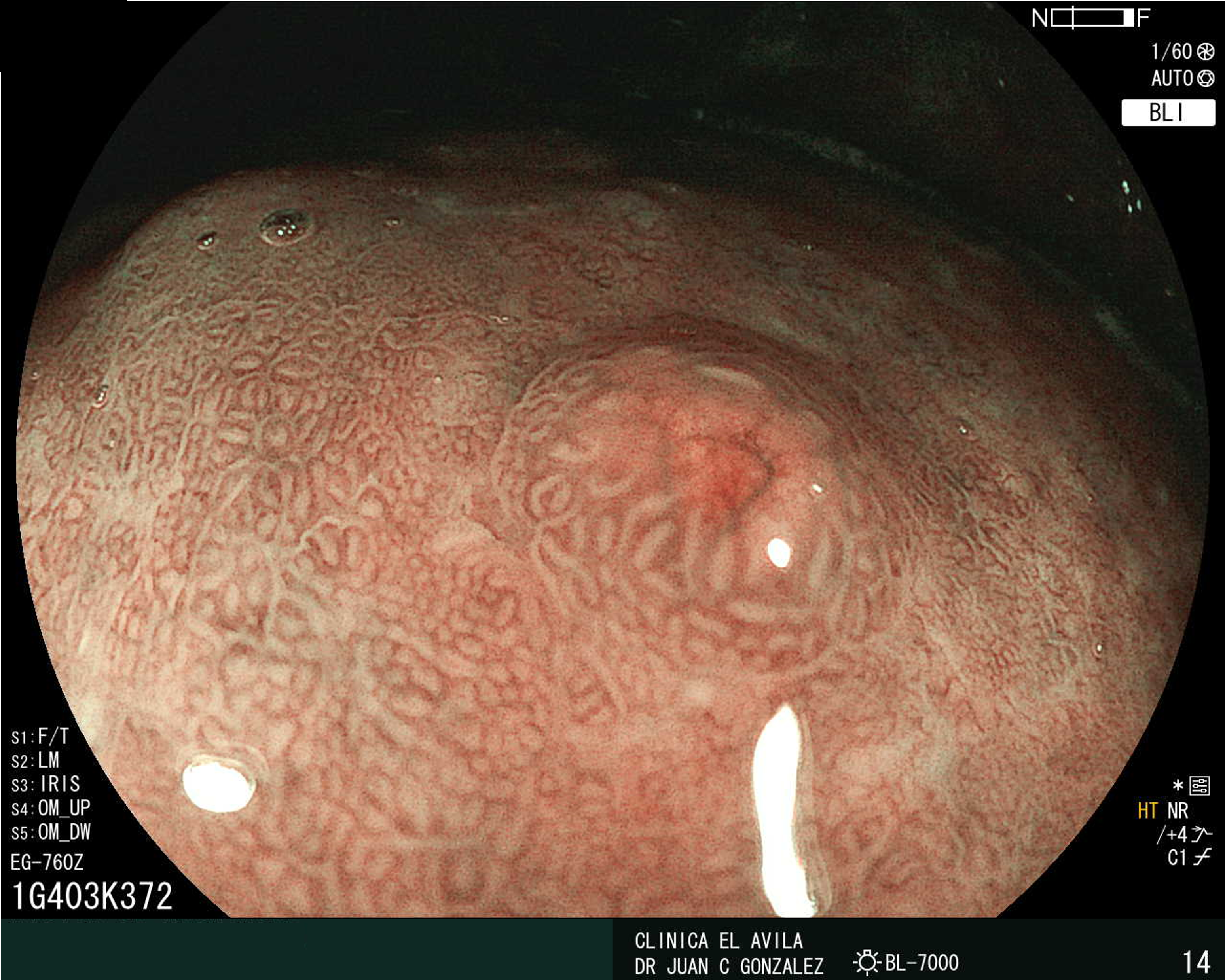
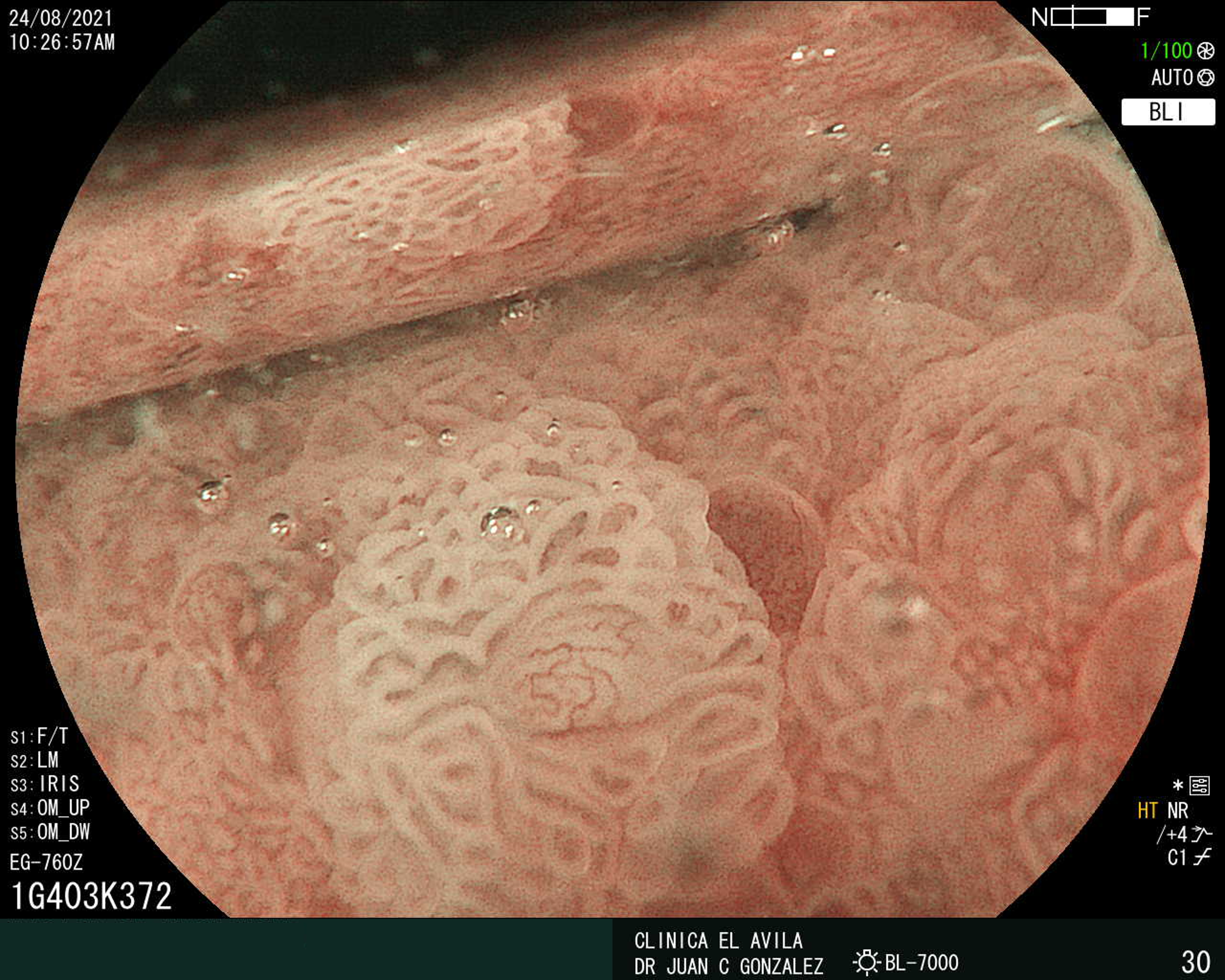
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X









 ESCUCHAR RESUMEN DEL ARTICULO
ESCUCHAR RESUMEN DEL ARTICULO