ASOCIACIÓN DEL POLIMORFISMO DEL GEN PTPN22 (C1858T) CON HEPATITIS AUTOINMUNE TIPO 1 EN LA POBLACIÓN MESTIZA VENEZOLANA
Resumen
Introducción: La Hepatitis Autoinmune (HAI) tipo 1 es una enfermedad hepática progresiva en la cual se demuestra susceptibilidad genética asociada a determinantes compartidos de moléculas HLA clase II. Sin embargo, 30 a 50% de estos pacientes, no asocian alelos HLA de susceptibilidad por lo que otros promotores genéticos que pudiesen predisponer a la ruptura de inmunotolerancia están siendo investigados. La Proteína Linfoide Tirosina Fosfatasa (LYP) codificada por el gen PTPN22, ejerce una potente inhibición en el linfocito T activado. El polimorfismo de este gen en la posición 1858 (sustitución de citosina (C) por una timina (T)) se describe asociada a múltiples patologías autoinmunes pero aún no se ha reportado en HAI tipo 1.
Objetivo: Determinar la posible asociación del polimorfismo del gen PTPN22 en mestizos venezolanos con HAI tipo 1.
Material y Métodos: Nuestra población consistió de 62 pacientes con HAI tipo 1 y 107 individuos sanos, ambos grupos venezolanos de tercera generación. La determinación del polimorfismo se realizó mediante la amplificación de la región en estudio (posición 1850 del codón 620) con la técnica de PCR estandarizada seguida por digestión de enzimas de restricción (Xcm I).
Resultados: El genotipo más frecuente fue el genotipo homocigoto silvestre (C/C) tanto en pacientes (90.3%) como en controles (98.1%,) sin diferencia significativa. El polimorfismo C1858T (genotipo C/T) del gen PTP22 se identificó con mas frecuencia en los pacientes con diferencia estadísti-camente signifi cativa al relacionarlo con el grupo control (p= 0.029, OR=5,6). El genotipo homocigoto TT no se observó en ninguno de los individuos estudiados.
Conclusión: El polimorfismo del gen PTPN22 a nivel C1858T descrito en otras enfermedades de origen au-toinmune también se detecta en HAI tipo 1, probable-mente confiriendo susceptibilidad a esta enfermedad en la población mestiza venezolana.
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Czaja AJ, Donaldson PT. Genetic susceptibilities for immune expression and liver cell injury in autoimmune hepatitis. Immunol Rev 2000;174:250-9.
Donaldson PT. Genetics in autoimmune hepatitis. Semin Liver Dis 2002; 22 ( 4): 353-63.
Goldberg AC, Bittencourt PL, Mougin B, Cancado ELR, Porta G, Carrilho F, et al. Analysis of HLA haplotypes in autoimmune hepati-tis type 1: identifying the major susceptibility locus. Hum Immunol 2001; 62: 165-9.
Wen L, Peakman M, Lobo-Yeo A, McFarlane BM, Mowat AP, Mieli-Vergani G, et al. T-cell directed hepatocyte damage in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Lancet 1990; 336: 1527-30.
Lohr H, Manns M, Hyriatsoulis A, Lohse AW, Trautwein C, Buschenfelde K-H, et al. Clonal analysis of liver-infiltrating T cells in patients with LKM-1 antibody-positive autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol 1991; 84: 297-302.
Mustelin T, Alonso A, Bottini N, Huynh H, Rahmouni S, Nika K, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in T cell physiology. Mol Im-munol 2004; 41: 687-700.
Chow LM, Fournel M, Davidson D, Veillette A, et al. Negative regulation of T-cell receptor signaling by tyrosine protein kinase p50csk. Nature 1993; 365; 156-60.
Cohen S, Dadi H, Shaoul E, Sharfe N, Roifman CM. Cloning and characterization of a lymphoid-specific, inducible human protein tyrosine phosphatase. Lyp Blood 1999; 93: 2013-24.
Gjorloff-Wingren A, Saxena M, Han S, Wang X, Alonso A, Renedo M, et al. Subcellular localization of intracellular protein tyrosine phosphatases in T cells. Eur J Immunol 2000; 30: 2412-21.
Cloutier JF, Veillete A. Cooperative inhibition of T-cell antigen receptor signaling by a complex between a kinase and a phospha-tase. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 111-21.
Hill RJ, Zozulya S, Lu Yl, Ward K, Gishizhy M, Jallal. The liymphoid protein tyrosine phosphatase LYP interacts with the adaptor molecule GRb2 and functions as a negative regulator of T-cell activation. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 237-44.
Ota Y, Samelson LE. The product of the proto-oncogene c-cbl: a negative regulator of the Syk tyrosine kinase. Science 1997; 276: 418.
Lupher ML, Songyang Z, Shoelson SE, Cantley LC, Band H. The Cbl phosphotyrosine-binding domain selects a D(N/D)XpY motif and binds to the Tyr292 negative regulatory phosphorylation site of ZAP-70. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 33140-44.
Bottini N, Musumci L, Alonso A, Ralumouni S, Nika K, Rostam-khani M, et al. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phospha-tase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 337-8.
Yokoi N, Komeda K, Wang HY, Yano H, Kitada K, Saitoh Y, et al. Cblb is major susceptibility gene for rat type diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet 2002; 31: 391-4.
Criswell LA, Pfeiffer KA, Lum RF, Gonzales B, Novitzke J, Kern M, et al. Analysis of families in the multiple autoimmune genetics consortium (MADGC) collection: the PTPN22620W allele associates with multiple autoimmune phenotypes. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 561-71.
Orozco G, Sanchez E, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Lopez-Nevot Ma, Tor-res B, Caliz R, et al. Association of a functional single-nucleotide polymorphism of PTPN22, encoding lymphoid protein phosphatase, with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 219-24.
Brand O, Gough S, Heward J. HLA, CTLA-4 and PTPN22: the shared genetic master-key to autoimmunity? Expert rev 2005; 7 ( 23): 1-15.
Johnson PJ, McFarlane IG. Meeting report: international autoimmune hepatitis group. Hepatology 1993; 18: 998-1005.
Fortes MP, Machado IV, Gil G, Fernández-Mestre M, Dagher L, León R et al. Genetic Contribution of MHC class II region to Type 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis Susceptibility in Venezuela. Liver Internat 2007; 27 ( 10): 1409-1.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v65i1.251
IMÁGENES GEN
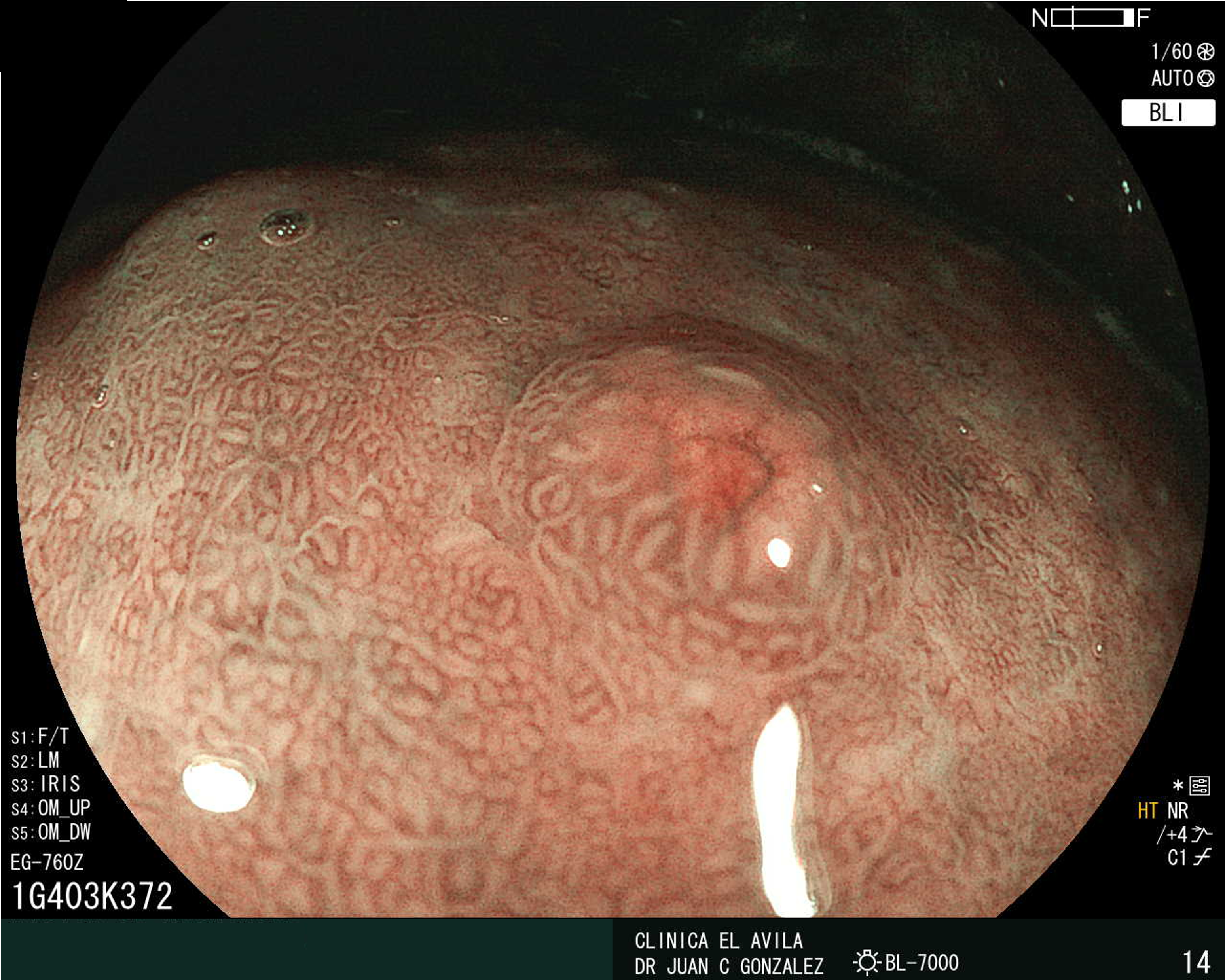
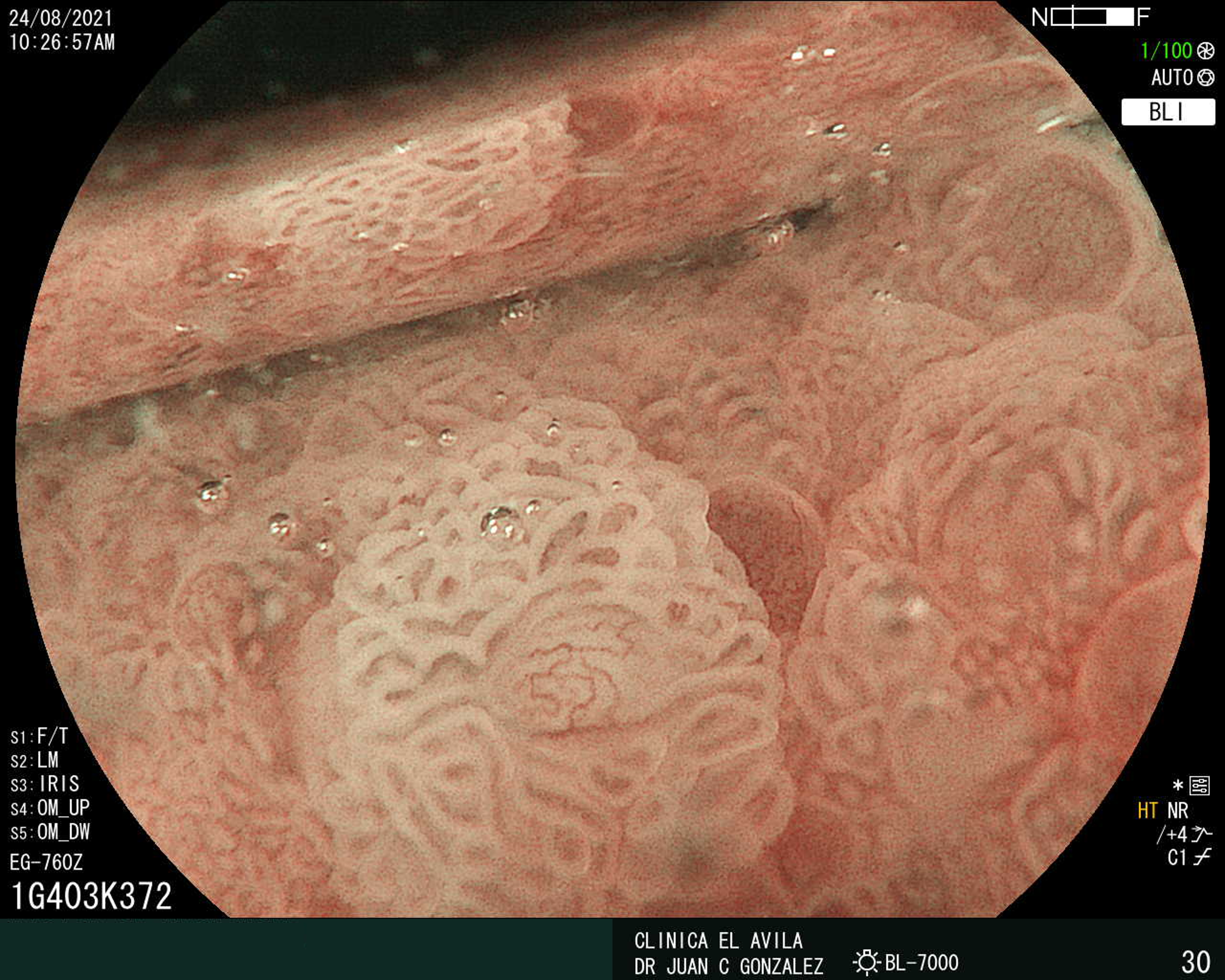
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X