Segundo Balón Intragástrico para el Tratamiento de la Obesidad. Experiencia Preliminar
Resumen
El balón intragástrico bioenteric (BIB) es un procedimiento endoscópico, no quirúrgico indicado para el tratamiento temporal de la obesidad, que favorece la disminución de la capacidad gástrica, ocupando gran parte del fundus. Poca experiencia se ha publicado en la colocación de segundo balón intragástrico.
Objetivo: Analizar la eficacia, seguridad y tolerabilidad de la colocación de segundo balón intragástrico.
Métodos: Estudio retrospectivo, descriptivo y longitudinal, de Abril 2007 hasta Abril 2010, 10 pacientes, 7 mujeres, 3 hombres, con edad promedio de 39.4 en mujeres y 35,7 en hombres, con un rango desde 18 hasta 52 años y de intervalo de colocación de 10,4 meses.
Resultados: La pérdida de peso promedio con el primer balón fue de 21.4 kg y la pérdida de peso con el segundo balón fue de 7.7 kg, con una diferencia de 13.7 kg en promedio. No hubo complicaciones severas.
Conclusión: El segundo BIB no demostró en este grupo preliminar ser efectivo para la pérdida de peso
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Mc Dowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States.1999-2004. JAMA 2006;295:1549-1555.
Peña M, Bacalao J. La Obesidad y sus Tendencias en la Región. Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública. 2001;10(2). http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/paho/pajph/2001/00000010/00000002/art00001.
Dias C, Gonzalez O, y col. Balón intragástrico: Una alternativa para el tratamiento de la obesidad. GEN 2010;64(2):93-96.
Dumonceau JM. Evidence based review of the Bioenterics Intragastric Balloon for Weight Loss. Obes Surg 2008;18:18111617.
Imaz I, Martínez C, y col. Safety and Effectiveness of the Intra-gastric Balloon for Obesity. A Meta Analysis. Obes Surg. 2008; 18(7):841-6.
Roman S, Napoleon B, Mion F, et al. Intragastric balloon for "non-morbid" obesity: a retrospective evaluation of tolerance and efficacy. Obes Surg. 2004;14(4):539-44.
Sallet JA, Marchesini JB, Paiva DS, et al. Brazilian multicenter study of the intragastric balloon. Obes Surg. 2004;14(7):991-8.
Martinez-Brocca MA, Belda O, Parejo J, et al. Intragastric balloon induced satiety is not mediated by modification in fasting or postprandial plasma ghrelin levels in morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2007;17(5):649-57.
Zago S, Kornmuller AM, Agagliati D, et al. Benefit from bioenteric Intra-gastric balloon (BIB) to modify lifestyle and eating habits in severely obese patients eligible for bariatric surgery. Minerva Med. 2006;97(1):51-64.
National Institutes of Health. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adultsthe evidence report. Obes Res. 1998;6 Suppl 2:51S-209.
Herve J, et al. What Becomes of Patient one year after the Intra-gastric Balloon has been removed? Obes Surg. 2005;15(6):864-70.
Dumonceau JM, et al. Single vs Repeated Treatment with the Intragastric Balloon: A 5-year weight loss study. Obes Surg. 2010;20(6):692-7.
Bispo M, Ferreira M.J., Bana T, et al. O balao intra-gastrico no tratamento da obesidade: avaliação da sua eficácia, segurança e tolerabilidade. GE-J Port. Gastrenterol 2008;15:103-109.
Blasco C, Jiménez M, Campos G, et al. Balón intragástrico para el tratamiento temporal de la obesidad. Endoscopia 2007; (4)19:315-321.
Lopez-Nava G, Rubio MA, et al. BioEnterics Intragastric Balloon. (BIB). Single Ambulatory Center Spanish Experience with 714 consecutive patients treated with one or two consecutive balloons. Obes Surg. 2011;21(1):5-9.
De Waele B, Reynaert H, Urbain D, et al. Intragastric balloons for preoperative weight reduction. Obes Surg. 2000;10(1):58-60.
Nieben OG, Harboe H. Intragatric balloon as an artificial bezoar for treatment of obesity. Lancet 1982 Jan 23;1(8265):198-9. [ Links ]
McFarland RJ, Grundy A, Gazet JC, et al. The intragastric ballon: a novel idea proved ineffective. Br J Surg. 1987 Feb;74(2):137-9.
Ramhamadany EM, Fowler J, Baird IM. Effect of the gastric balloon versus sham procedure on weight loss in obese subjects. Gut.1989;30(8):1054-7.
Benjamin SB, Maher KA, Cattau EL, et al. Double blind controlled trial of the Garren-Edward gastric bubble: an adjunctive treatment for exogenous obesity. Gastroenterology. 1988; 95(3):581-8.
Hogan RB, Johnston JH, Long BW, et al. A double blind, randomised, sham controlled trial of the gastric bubble for obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 1989;35(5):381-5.
Meshkinpour H, Hsu D, Farivar S. Effect of gastric bubble as a weight reduction device: a controlled, crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1988;95(3):589-92.
Douketis JD, Macie C, Thabane L, et al. Systematic review of long-term weight loss studies in obese adults: clinical significance and applicability to clinical practice. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005; 29(10):1153-67.
Dansinger ML, Tatsioni A, Wong JB, et al. Meta-analysis: the effect of dietary counseling for weight loss. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147(1):41-50.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v66i3.214
IMÁGENES GEN
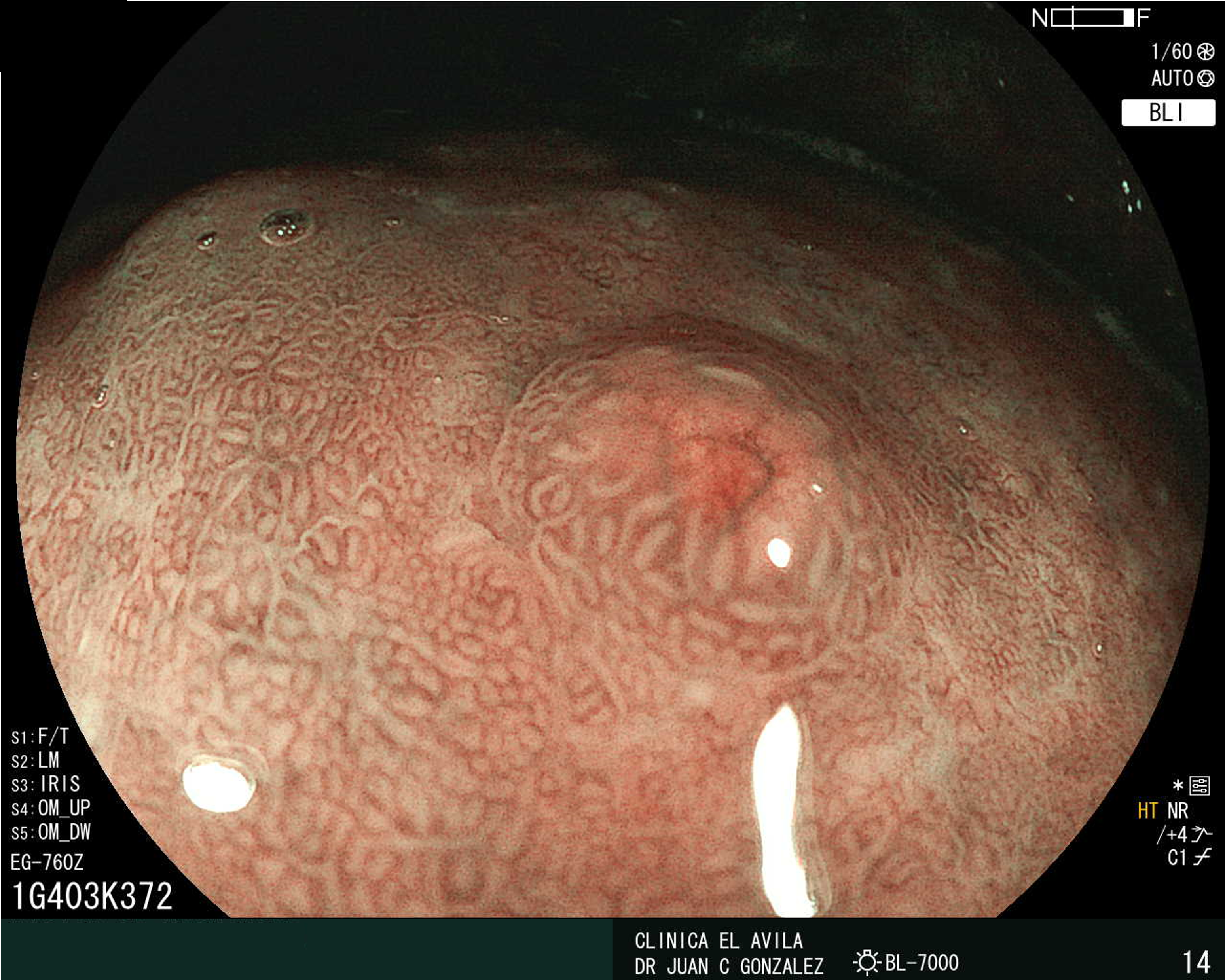
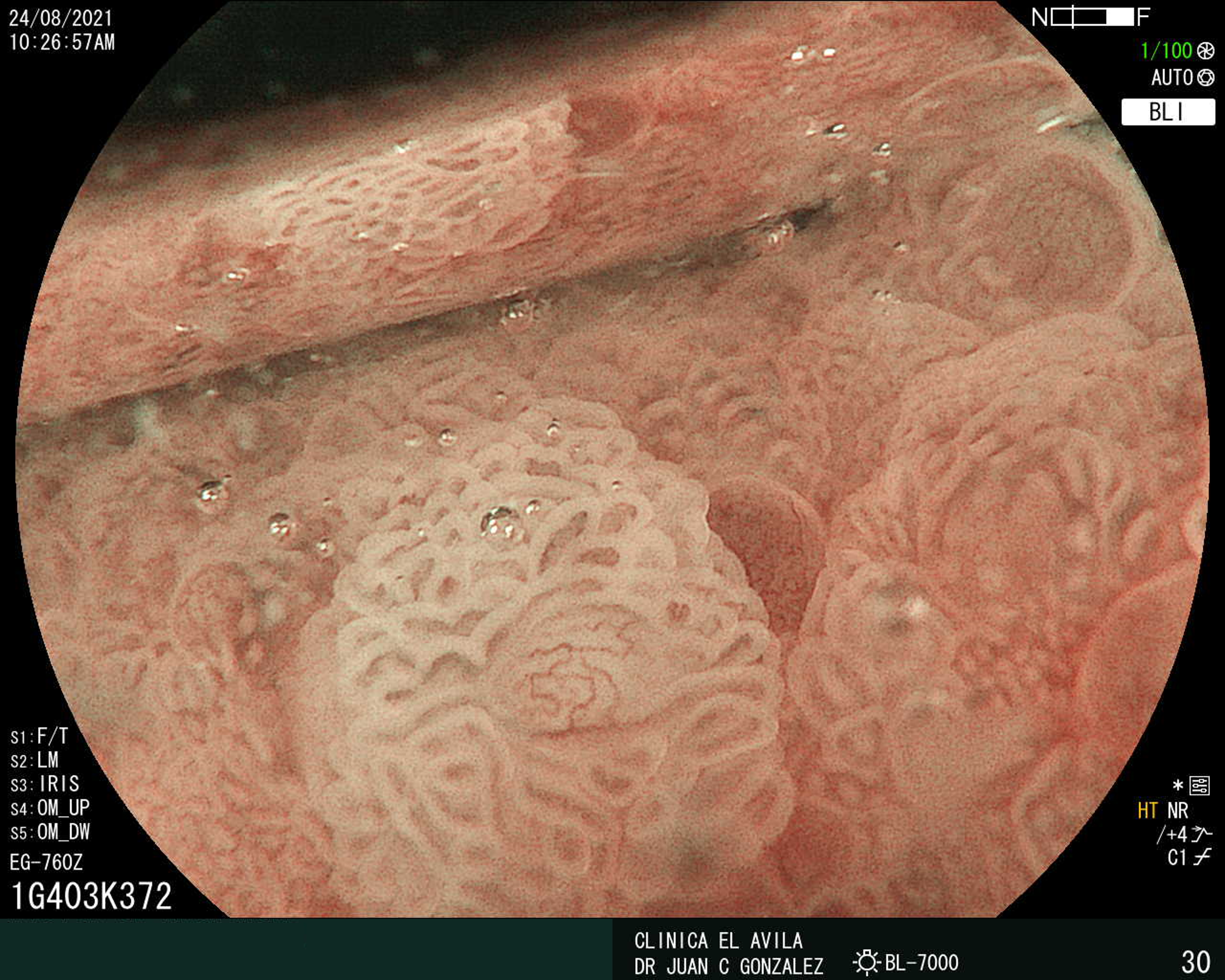
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X