Transportadores de lípidos biliares: una revisión actualizada
Resumen
Palabras clave
Texto completo:
PDFReferencias
Chan J, Vandeberg JL. Hepatobiliary transport in health and disease. Clin Lipidol 2012;7(2):189-202.
Nawroth T, Buch P, Buch K, Langguth P, Schweins R. Liposome formation from bile salt-lipid micelles in the digestion and drug delivery model FaSSIF(mod) estimated by combined time-resolved neutron and dynamic light scattering. Mol Pharm 2011;8(6): 2162-2172.
Stokes CS, Lammert F. Transporters in cholelithiasis. Biol Chem 2011;393(1-2):3-10.
Halilbasic E, Claudel T, Trauner M. Bile acid transporters and regulatory nuclear receptors in the liver and beyond. J Hepatol 2012. PMID:22885388.
Nicolau M, Andress EJ, Zolnerciks JK, Dixon PH, Williamson C, Linton KJ. Canalicular ABC transporters and liver disease. J Pathol 2012;226(2):300-315.
Gadaleta RM, van Mil SW, Oldenburg B, Sierseman PD, Klomp LW, van Erpecum KJ. Bile acids and their nuclear receptor FXR: relevance for hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010;1801(7):683-692.
Dawson PA, Lan T, Rao A. Bile acid transporters. J Lipid Res 2009;50(12):2340-2357.
María J, Perez MJ, Briz O. Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol 2009;15(14):1677-1689.
Mukhopadhyay S, Uday M. Chemistry and biology of bile acids. Curr Scien 2004;87(12):1666-1683.
Cole LK, Vance JE, Vance DE. Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and lipoprotein metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011; 1821(5):754-761.
Dikkers A, Tietge UJ. Biliary cholesterol secretion: more than a simple ABC. World J Gastroenterol 2010;16(47): 5936-5945.
Köck K, Brouwer KL. A perspective on efflux transport proteins in the liver. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2012;92(5):599-612.
Trauner M, Boyer JL. Bile salt transporters: molecular characterization, function, and regulation. Physiol Rev 2003;83(2): 633-671.
Pramfalk C, Jiang ZY, Parini P. Hepatic Niemann-Pick C1-like 1. Curr Opin Lipidol 2011;22(3):225-230.
Kubitz R, Dröge C, Stindt J, Weissenberger K, Häussinger D. The bile salt export pump (BSEP) in health and disease. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2012. PMID:22795478.
Müllenbach R, Weber SN, Krawczyk M, Zimmer V, Sarrazin C, Lammert F, et al. A frequent variant in the human bile salt export pump gene ABCB11 is associated with hepatitis C virus infection, but not liver stiffness in a German population. BMC Gastroenterol 2012;12(1):63.
Henkel AS, Kavesh MH, Kriss MS, Dewey AM, Rinella ME, Green RM. Hepatic overexpression of ABCB11 promotes hypercholesterolemia and obesity in mice. Gastroenterology 2011; 141(4):1404-1411.
Stieger B. Role of the bile salt export pump, BSEP, in acquired forms of cholestasis. Drug Metab Rev 2010;42(3):437-445.
Stieger B, Beuers U. The canalicular bile salt export pump BSEP (ABCB11) as a potential therapeutic target. Curr Drug Targets 2011;12(5):661-670.
Lam P, Soroka CJ, Boyer JL. The bile salt export pump: clinical and experimental aspects of genetic and acquired cholestatic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 2010;30(2):125-133.
Zhang Y, Li F, Patterson AD, Wang Y, Krausz KW, Neale G, et al. Abcb11 deficiency induces cholestasis coupled to impaired β-fatty acid oxidation in mice. J Biol Chem 2012; 287(29): 24784-24794.
Tougeron D, Fotsing G, Barbu V, Beauchant M. ABCB4/MDR3 gene mutations and cholangiocarcinomas. J Hepatol 2012;57(2):467-468.
Groen A, Romero MR, Kunne C, Hoosdally SJ, Dixon PH, Wooding C, et al. Complementary functions of the flippase ATP8B1 and the floppase ABCB4 in maintaining canalicular membrane integrity. Gastroenterology 2011;141(5):1927-1937.
Oude Elferink RP, Beuers U. Targeting the ABCB4 gene to control cholesterol homeostasis. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2011; 15(10):1173-1182.
Groen A, Kunne C, Jongsma G, van den Oever K, Mok KS, Petruzzelli M, et al. Abcg5/8 independent biliary cholesterol excretion in Atp8b1-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 2008;134(7): 2091-2100.
Paulusma CC, Folmer DE, Ho-Mok KS, de Waart DR, Hilarius PM, Verhoeven AJ, et al. ATP8B1 requires an accessory protein for endoplasmic reticulum exit and plasma membrane lipid flippase activity. Hepatology 2008;47(1):268-278.
Hirata T, Okabe M, Kobayashi A, Ueda K, Matsuo M. Molecular mechanisms of subcellular localization of ABCG5 and ABCG8. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2009;73(3):619-626.
Yamanashi Y, Takada T, Yoshikado T, Shoda J, Suzuki H. NPC2 regulates biliary cholesterol secretion via stimulation of ABCG5/G8-mediated cholesterol transport. Gastroenterology 2011;140(5):1664-1674.
Abumrad NA, Davidson NO. Role of the gut in lipid homeostasis. Physiol Rev 2012;92(3):1061-1085.
Nguyen TM, Sawyer JK, Kelley KL, Davis MA, Kent CR, Rudel LL. ACAT2 and ABCG5/G8 are both required for efficient cholesterol absorption in mice: evidence from thoracic lymph duct cannulation. J Lipid Res 2012;53(8):1598-1609.
Grenier E, Garofalo C, Delvin E, Levy E. Modulatory role of PYY in transport and metabolism of cholesterol in intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS One 2012;7(7):e40992.
Betters JL, Yu L. NPC1L1 and cholesterol transport. FEBS Lett. 2010;584(13):2740-2747.
Deffieu MS, Pfeffer SR. Niemann-Pick type C1 function requires lumenal domain residues that mediate cholesterol-dependent NPC2 binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2011;108(47):18932-18936.
Pramfalk C, Jiang ZY, Parini P. Hepatic Niemann-Pick C1-like 1. Curr Opin Lipidol 2011;22(3):225-230.
Davis HR Jr, Altmann SW. Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 (NPC1L1) an intestinal sterol transporter. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1791(7): 679-683.
Wang LJ, Song BL. Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 and cholesterol uptake. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012;1821(7):964-972.
Wang LJ, Wang J, Li N. Molecular characterization of the NPC1L1 variants identified from cholesterol low absorbers. J Biol Chem 2011;286(9):7397-7408.
Tang W, Jia L, Ma Y, Xie P, Haywood J, Dawson PA, et al. Ezetimibe restores biliary cholesterol excretion in mice expressing Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 only in liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011; 1811(9):549-555.
Yamanashi Y, Takada T, Shoda JI, Suzuki Y. A novel function of NPC1L1 as a negative regulator of NPC2 protein. Hepatology 2011;55(3):953-964.
Ge L, Qi W, Wang LJ, Miao HH, Qu YX, Li BL, et al. Flotillins play an essential role in Niemann-Pick C1-like 1-mediated cholesterol uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011;108(2):551-556.
De Bario O, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Liu M, Portincasa P, Wang DQ. Ezetimibe: its novel effects on the prevention and the treatment of cholesterol gallstones and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Lipids 2012. PMID: 22132342.
Alrefai WA, Gill RK. Bile acid transporters: structure, function, regulation and pathophysiological implications. Pharm Res 2007; 24(10):1803-1823.
Stieger B. The role of the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) in physiology and pathophysiology of bile formation. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2011;(201):205-259.
Lionarons DA, Boyer JL, Cai SY. Evolution of substrate specificity for the bile salt transporter ASBT (SLC10A2). J Lipid Res 2012;53(8):1535-1542.
Hu NJ, Iwata S, Cameron AD, Drew D. Crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of the bile acid sodium symporter ASBT. Nature 2011;478(7369):408-411.
Geyer J, Wilke T, Petzinger E. The solute carrier family SLC10: more than a family of bile acid transporters regarding function and phylogenetic relationships. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2006;372(6):413-431.
Lange Y, Ye J, Steck TL. Activation mobilizes the cholesterol in the late endosomes-lysosomes of Niemann Pick type C cells. PLoS One 2012;7(1):e30051.
Blazquez AG, Briz O, Romero MR, Rosales R, Monte MJ, Vaquero J, et al. Characterization of the role of ABCG2 as a bile acid transporter in liver and placenta. Mol Pharmacol 2012; 81(2):273-283.
Jemnitz K, Heredi-Szabo K, Janossy J, Ioja E, Vereczkey L, Krajcsi P. ABCC2/Abcc2: a multispecific transporter with dominant excretory functions. Drug Metab Rev 2010;42(3):402-436.
Fahrmayr C, Fromm MF, König J. Hepatic OATP and OCT uptake transporters: their role for drug-drug interactions and pharmacogenetic aspects. Drug Metab Rev 2010;42(3):380-401.
Cui JY, Aleksunes LM, Tanaka Y, Fu ZD, Guo Y, Guo GL, et al. Bile acids via FXR initiate the expression of major transporters involved in the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in newborn mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;302(9):G979-996.
Jonker JW, Liddle C, Downes M. FXR and PXR: potential therapeutic targets in cholestasis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2012; 130(3-5):147-158.
Modica S, Gadaleta RM, Moschetta A. Deciphering the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR paradigm. Nucl Recept Signal 2010; 8: e005.
Modica S, Petruzzelli M, Bellafante E, Murzilli S, Salvatore L, Celli N, et al. Selective activation of nuclear bile acid receptor FXR in the intestine protects mice against cholestasis. Gastroenterology 2012;142(2):355-365.
Van Straten EM, Huijkman NC, Baller JF, Kuipers F, Plösch T. Pharmacological activation of LXR in utero directly influences ABC transporter expression and function in mice but does not affect adult cholesterol metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2008;295(6):E1341-1348.
Matsubara T, Li F, Gonzalez FJ. FXR signaling in the enterohepatic system. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2012. PMID: 22609541.
Li T, Matozel M, Boehme S, Kong B, Nilsson LM, Guo G, et al. Overexpression of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase promotes hepatic bile acid synthesis and secretion and maintains cholesterol homeostasis. Hepatology 2011;53(3):996-1006.
Anzivino C, Odoardi MR, Meschiari E, Baldelli E, Facchinetti F, Neri I, et al. ABCB4 and ABCB11 mutations in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in an Italian population. Dig Liver Dis 2012; (In press).
Castro-Torres IG. Cholesterol gallstones formation: new scientific advances. Rev GEN (Gastroenterología Nacional) 2012; 66(1):57-62.
Acalovschi M, Tirziu S, Chiorean E, Krawczyk M, Grünhage F, Lammert F. Commons variants of ABCB4 and ABCB11 and plasma lipid levels: a study in sib pairs with gallstones, and controls. Lipids 2009;44(6):521-526.
Tyson GL, El-Serag HB. Risk factors of cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2011;54(1):173-184.
Shneider BL. ABCB4 Disease presenting with cirrhosis and copper overload-potential confusion with Wilson Disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2011;1:115-117.
Méndez-González J, Julve J, Rotllan N, Llaverias G, Blanco-Vaca F, Escolà-Gil JC. ATP-binding cassette G5/G8 deficiency causes hypertriglyceridemia by affecting multiple metabolic pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011;1811(12):1186-1193.
Castro-Torres IG, Naranjo-Rodríguez EB, Domínguez-Ortíz MA, Gallegos-Estudillo MA, Saavedra-Vélez MV. Antilithiasic and hypolipidaemic effects of Raphanus sativus L. var niger in mice fed with a lithogenic diet. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012. PMID: 23093836.
Von Kampen O, Buch S, Nothnagel M, Azocar L, Molina H, Brosch M, et al. Genetic and functional identification of the likely causative variant for cholesterol gallstone disease at the ABCG5/8 lithogenic locus. Hepatology 2012. PMID: 22898925.
Poirier J, Cockell KA, Scoggan KA, Ratnayake WM, Rocheleau H, Gruber H, et al. High-dose supplemental selenite to male Syrian hamsters fed hypercholesterolaemic diets alters Ldlr, Abcg8 and Npc1l1 mRNA expression and lowers plasma cholesterol concentrations. Br J Nutr 2012;108(2):257-266.
Krawczyk M, Wang DQ, Portincasa P, Lammert F. Dissecting the genetic heterogeneity of gallbladder stone formation. Semin Liver Dis 2011;31(2):157-172.
Renner O, Harsch S, Schaeffeler E, Winter S, Schwab M, Krawczyk M, et al. A variant of the SLC10A2 gene encoding the apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter is a risk factor for gallstone disease. PLoS One 2009;4:e7321.
Miura T, Kimura N, Yamada T, Shimizu T, Nanashima N, Yamana D, et al. Sustained repression and translocation of Ntcp and expression of Mrp4 for cholestasis after rat 90 % partial hepatectomy. J Hepatol 2011;55(2):407-414.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.61155/gen.v67i1.120
IMÁGENES GEN
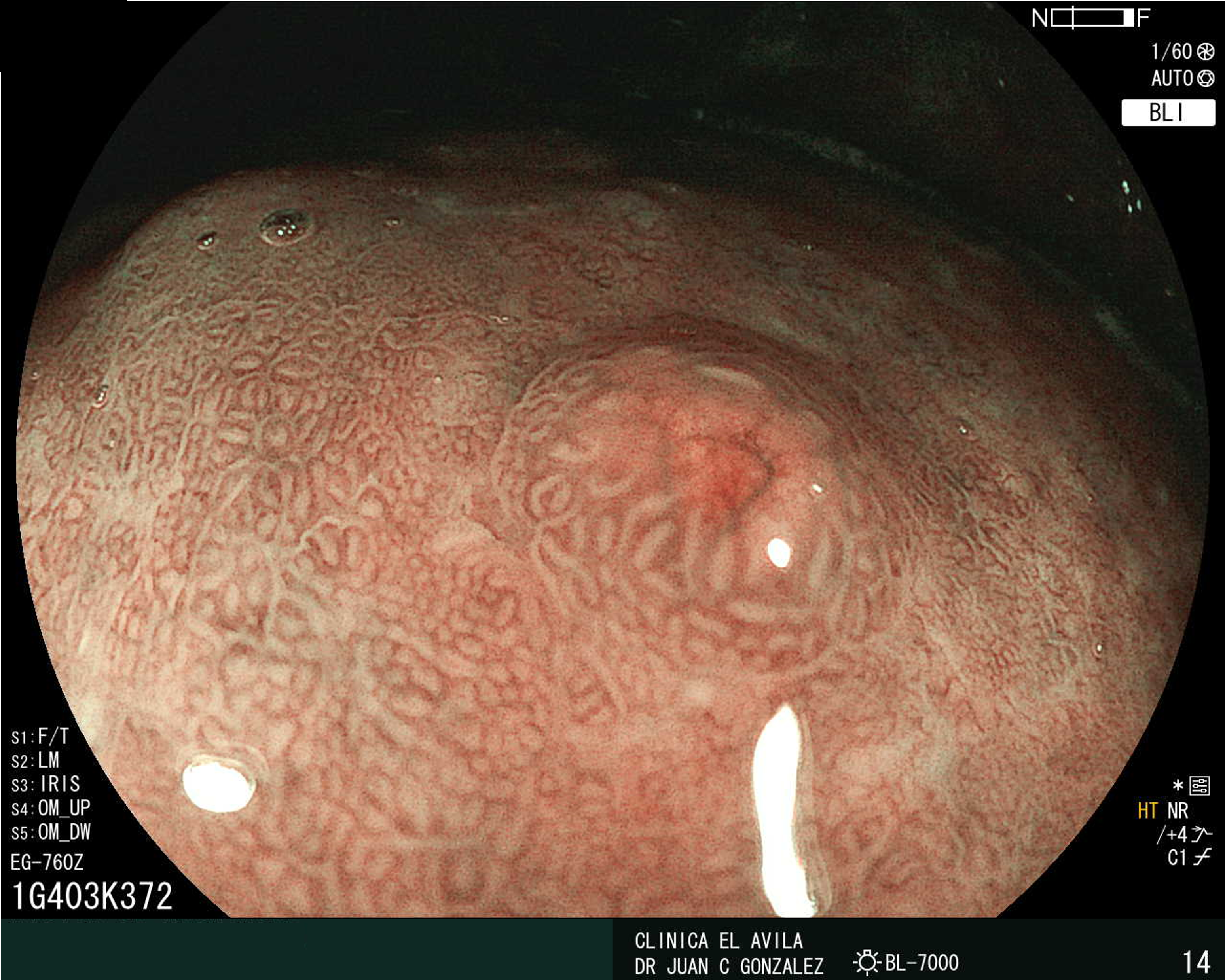
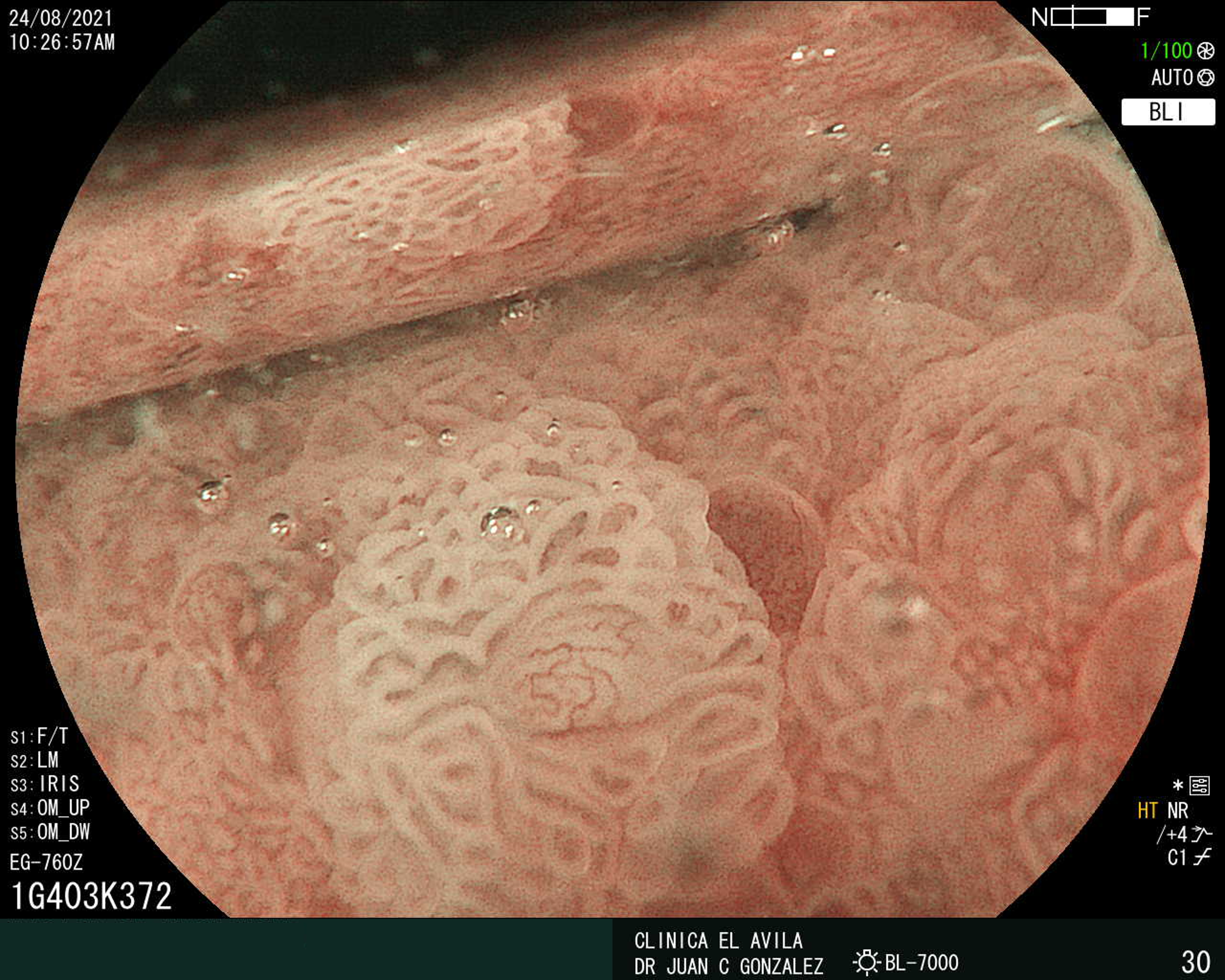
| Figura 1. Tumor Neuroendocrino Gástrico | Figura 2. Hiperplasia de Células Neuroendocrinas en estómago |
 |  |
 |  |  |
ISSN: 0016-3503 e-ISSN: 2477-975X